2016 Employer Health Benefits Survey
Abstract

This annual survey of employers provides a detailed look at trends in employer-sponsored health coverage including premiums, employee contributions, cost-sharing provisions, and employer opinions. The 2016 survey included more than 1,900 interviews with non-federal public and private firms. Annual premiums for employer-sponsored family health coverage reached $18,142 this year, up 3 percent from last year, with workers on average paying $5,277 towards the cost of their coverage, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation/Health Research & Education Trust 2016 Employer Health Benefits Survey. The 2016 survey includes information on the use of incentives for employer wellness programs, plan cost-sharing as well as firm offer rate. Survey results are released here in a variety of ways, including a full report with downloadable tables on a variety of topics, summary of findings, and an article published in the journal Health Affairs.
NEWS RELEASE
- A news release announcing the publication of the 2016 Employer Health Benefits Survey is available here.
SUMMARY OF FINDINGS
- The Summary of Findings provides an overview of the 2016 survey results and is available under the Summary of Findings section.
FULL REPORT
- The complete Employer Health Benefits Survey Report includes over 200 exhibits and is available under the Report section. The Report section contains 14 separate sections. Users can view each section separately or download the section exhibits from the bottom of the respective section page.
HEALTH AFFAIRS
- The peer-reviewed journal Health Affairs has published an article with key findings from the 2016 survey: Health Benefits In 2016: Family Premiums Rose Modestly, And Offer Rates Remained Stable.
WEB BRIEFING
- On Wednesday, September 14, 2016, the Kaiser Family Foundation and the Health Research & Educational Trust (HRET) held a reporters-only web briefing to release the 2016 Employer Health Benefits Survey.
INTERACTIVE GRAPHIC
- This graphing tool allows users to look at changes in premiums and worker contributions for covered workers at different types of firms over time: Premiums and Worker Contributions Among Workers Covered by Employer-Sponsored Coverage, 1999-2016.
KEY EXHIBITS – CHARTPACK
- Over twenty overview slides from the 2016 Employer Health Benefits Survey are available as a slideshow or PDF.
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
- Standard errors for selected estimates are available in the Technical Supplement here.
- Employer Health Benefits Surveys from 1998-2015 are available here. Please note that historic survey reports have not been revised with methodological changes.
- Researchers may request for a public use dataset by going to Contact Us and choosing “TOPIC: Health Costs.”
Researchers at the Kaiser Family Foundation, NORC at the University of Chicago, and Health Research & Educational Trust designed and analyzed the survey.
Summary Of Findings
Employer-sponsored insurance covers over half of the non-elderly population; approximately 150 million nonelderly people in total.1 To provide current information about employer-sponsored health benefits, the Kaiser Family Foundation (Kaiser) and the Health Research & Educational Trust (HRET) conduct an annual survey of private and nonfederal public employers with three or more workers. This is the eighteenth Kaiser/HRET survey and reflects employer-sponsored health benefits in 2016.
HEALTH INSURANCE PREMIUMS AND WORKER CONTRIBUTIONS
In 2016, the average annual premiums for employer-sponsored health insurance are $6,435 for single coverage and $18,142 for family coverage. The average family premium rose 3% over the 2015 average premium while the increase in the premium for single coverage was not statistically significant. The average premium for family coverage is lower for covered workers in small firms (3-199 workers) than for workers in large firms (200 or more workers) ($17,546 vs. $18,395). Workers’ wages increased 2.5% and inflation increased 1.1% over the period.2 Premiums for family coverage have increased 20% since 2011 and 58% since 2006. Average premiums for high-deductible health plans with a savings option (HDHP/SOs) are considerably lower than the overall average for all plan types for both single and family coverage, at $5,762 and $16,737 respectively (Exhibit A). These premiums do not include any employer contributions to workers’ health savings accounts or health reimbursement arrangements. As discussed below, the share of covered workers with HDHP/SOs has grown eight percentage points over the last two years; this change in enrollment has reduced the growth in single and family premiums by roughly a half percentage point each of the last two years.3
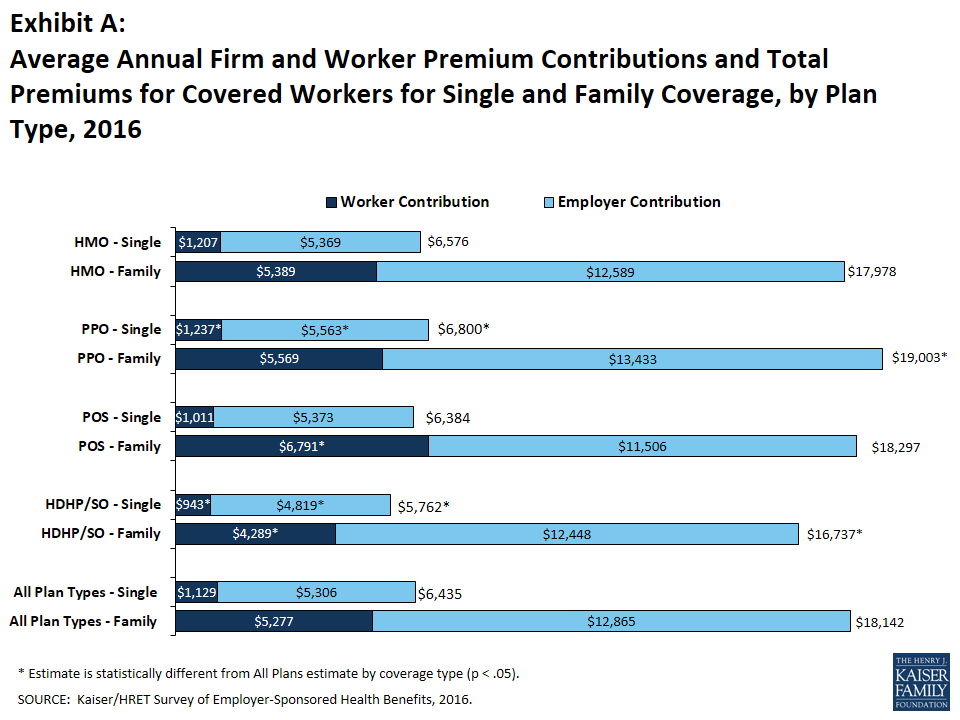
Premiums vary significantly around the averages for both single and family coverage, reflecting differences in health care costs and compensation decisions across regions and industries. Seventeen percent of covered workers are in plans with an annual total premium for family coverage of at least $21,771 (120% or more of the average family premium), and 19% of covered workers are in plans where the family premium is less than $14,514 (less than 80% of the average family premium) (Exhibit B).
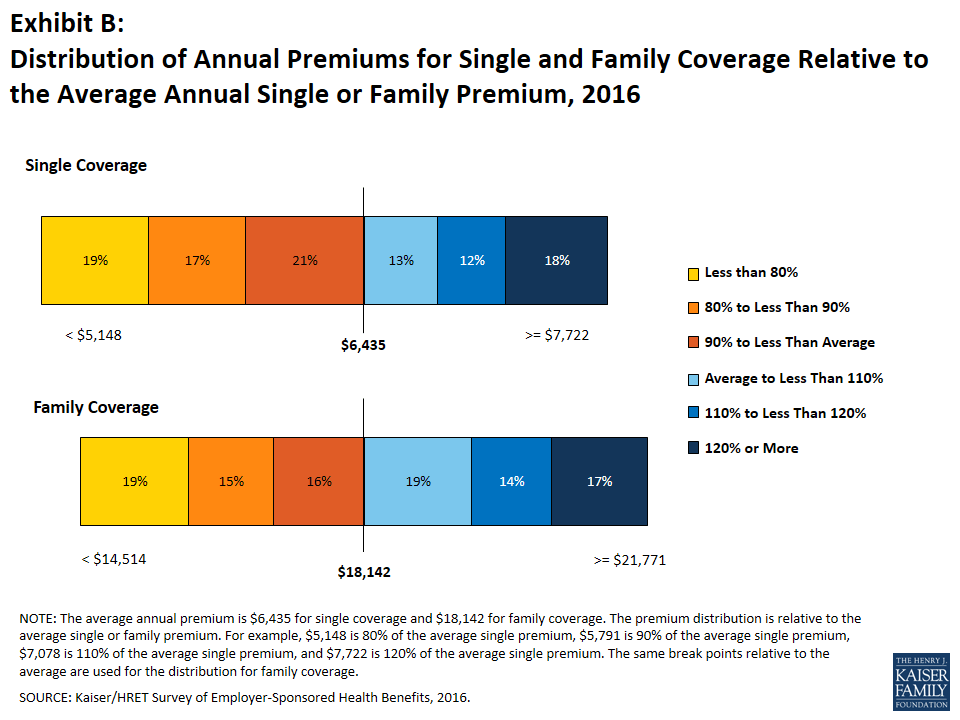
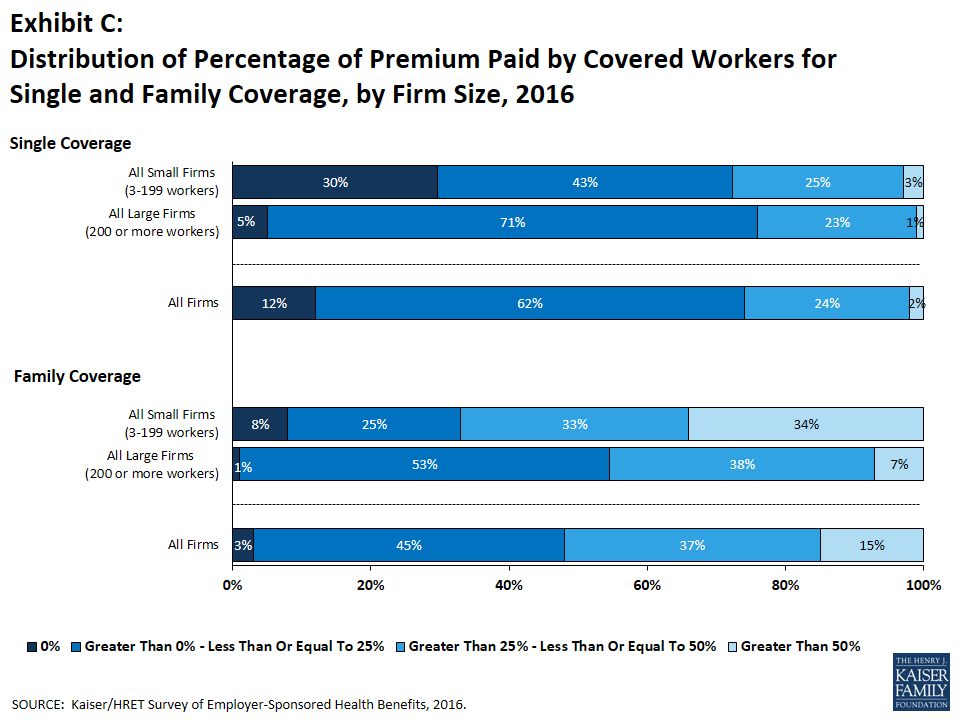
Most covered workers make a contribution towards the cost of the premium for their coverage. On average, covered workers contribute 18% of the premium for single coverage and 30% of the premium for family coverage, similar percentages to the recent past. Workers in small firms contribute a higher average percentage of the premium for family coverage (39% vs. 26%) than workers in large firms. Covered workers in firms with a relatively high percentage of lower-wage workers (at least 35% of workers earn $23,000 a year or less) contribute higher percentages of the premium for single (23% vs. 18%) and family (35% vs. 30%) coverage than workers in firms with a smaller share of lower-wage workers. As with total premiums, the share of the premium contributed by workers varies considerably. For single coverage, 12% of covered workers are in plans that do not require them to make a contribution, 62% are in plans which require a contribution of 25% or less of the total premium, and 2% are in plans that require a contribution of more than half of the premium. For family coverage, 3% of covered workers are in plans that do not require them to make a contribution, 45% are in a plan that requires a contribution of 25% or less of the total premium, and 15% are in plans that require more than half of the premium (Exhibit C). Covered workers in small firms are much more likely to be in a plan that requires the worker to contribute more than 50% of the total family premium than covered workers in larger firms (34% vs. 7%).
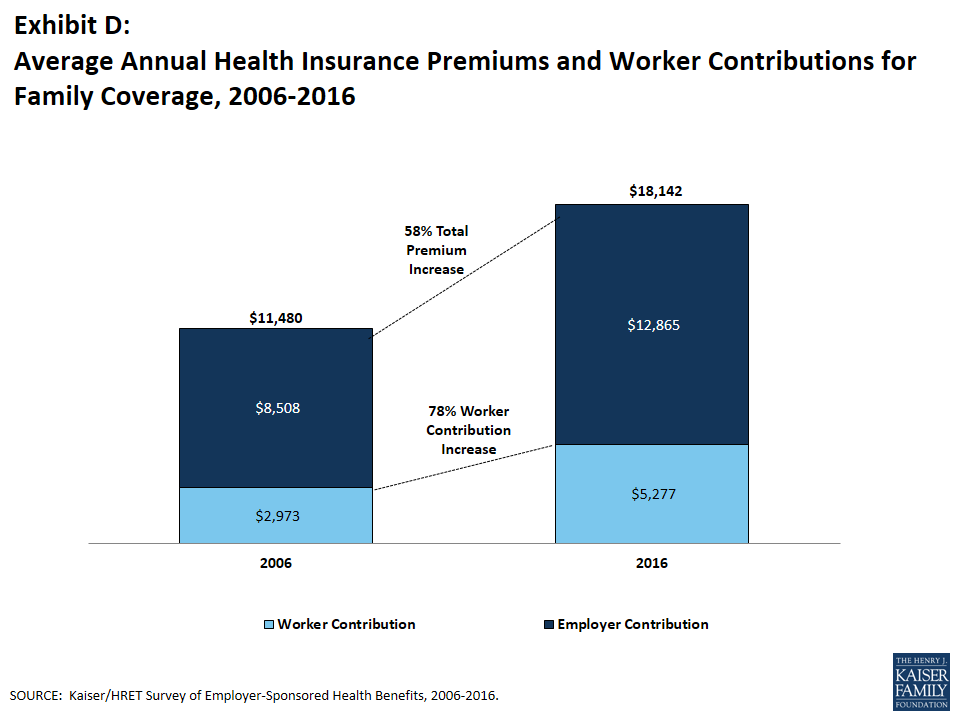
One reason for this variation is the different approaches that employers use to structure employee contributions, particularly for family coverage. Of firms that offer family coverage: 45% of small firms and 18% of large firms provide the same dollar contribution for single and family coverage, which means that employees must pay the full additional premium cost to enroll family members in their plan; 45% of small firms and 67% of large firms make a higher dollar contribution for family coverage than for single coverage, 3% of small firms and 6% of large firms vary their approach with the class of the employee; and the remaining 7% of small firms and 9% of large firms take some other approach. Fifteen percent of firms that offer health benefits require workers who use tobacco to contribute more towards the premium than those who do not use tobacco. Looking at the dollar amounts that workers contribute, the average annual premium contributions for 2016 are $1,129 for single coverage and $5,277 for family coverage. Covered workers’ average dollar contribution to family coverage has increased 78% since 2006 (Exhibit D) and 28% since 2011 (data not shown). Covered workers in small firms have lower average contributions for single coverage than workers in large firms ($1,021 vs. $1,176), but higher average contributions for family coverage ($6,597 vs. $4,719). Average contribution amounts for covered workers in HDHP/SOs are lower for single and family coverage than for covered workers in other plan types (Exhibit A).
PLAN ENROLLMENT
PPOs continue to be the most common plan type in 2016, enrolling 48% of covered workers. Twenty-nine percent of covered workers are enrolled in a high-deductible plan with a savings option (HDHP/SO), 15% in an HMO, 9% in a POS plan, and less than 1% in a conventional (also known as an indemnity) plan. Over the last two years, enrollment in PPOs has fallen 10 percentage points while enrollment in HDHP/SOs has increased 8 percentage points (Exhibit E).4
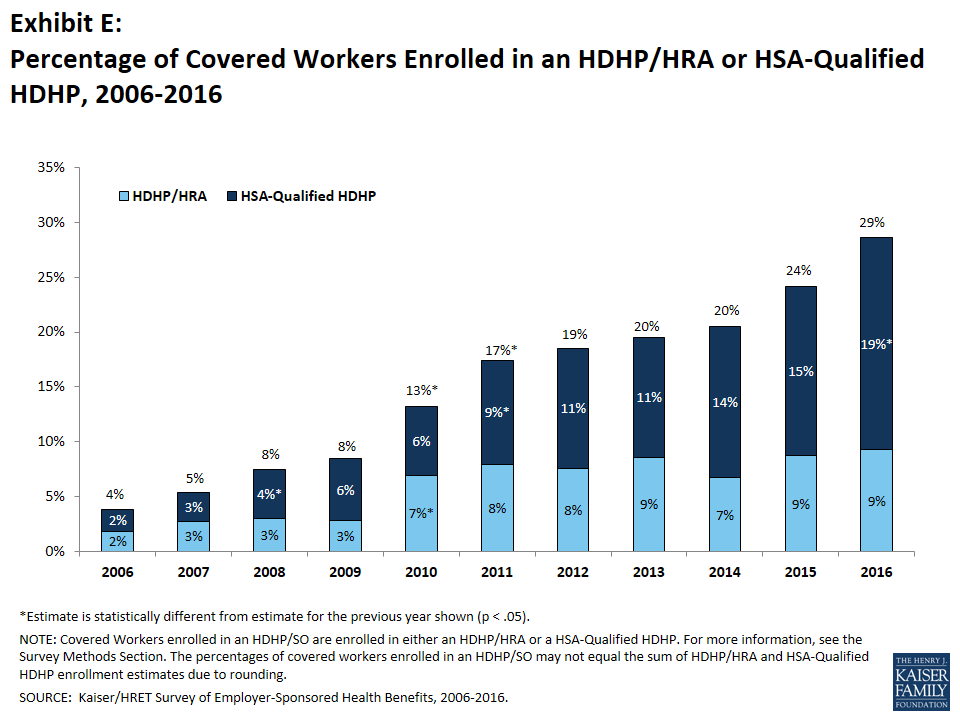
Plan enrollment differs with firm size: 52% of covered workers in large firms are enrolled in PPOs, compared to 39% percent in small firms; 18% percent of covered workers in small firms are enrolled in POS plans, compared to 4% in large firms.
EMPLOYEE COST SHARING
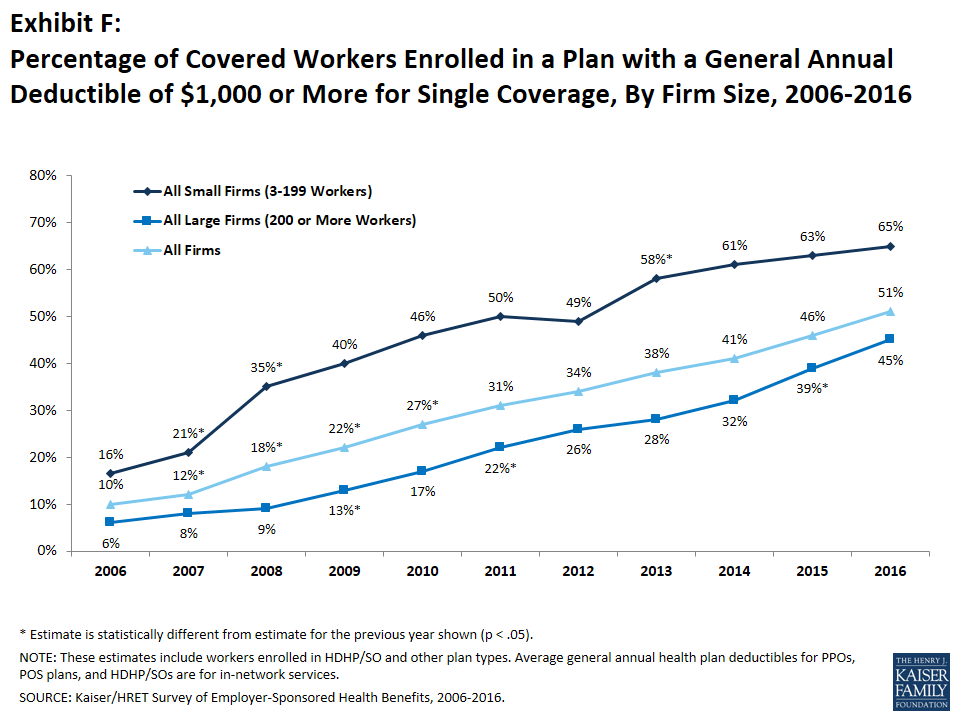
Most covered workers must pay a share of the cost when they use health care services. Eighty-three percent of covered workers have a general annual deductible for single coverage that must be met before most services are paid for by the plan. Even workers without a general annual deductible often face other types of cost sharing when they use services, such as copayments or coinsurance for office visits and hospitalizations. Among covered workers with a general annual deductible, the average deductible amount for single coverage is $1,478, higher than the average deductible last year ($1,318). Among all covered workers, those enrolled at firms with a deductible and those without, the average deductible is $1,221, significantly more than $1,077 in 2015. The average deductible for covered workers is higher in small firms than in large firms ($2,069 vs. $1,238). Sixty-five percent of covered workers in small firms and 45% of covered workers in large firms are in a plan with a deductible of at least $1,000 for single coverage, similar to the percentages last year (Exhibit F); a similar pattern exists for those in plans with a deductible of at least $2,000 (41% for small firms vs. 16% for large firms).
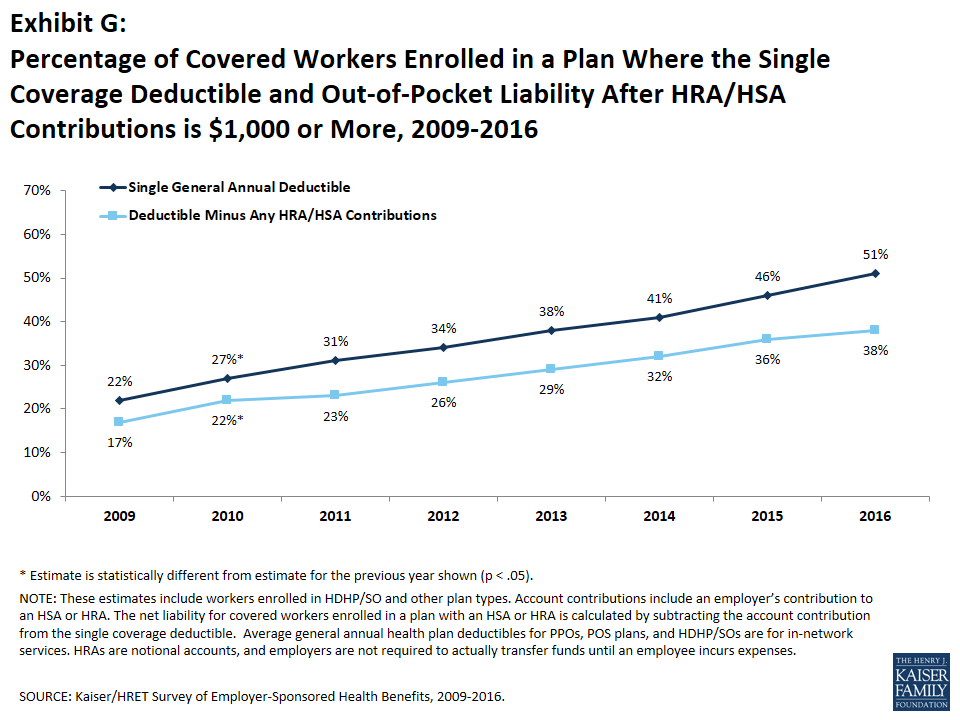
Deductibles have increased in recent years due to higher deductible amounts within plan types (particularly PPO plans) and to higher enrollment in HDHP/SOs. While growing deductibles in PPOs and other plan types generally increases enrollee out-of-pocket liability, the shift in enrollment to HDHP/SOs does not necessarily do so because most HDHP/SO enrollees receive an account contribution from their employers, which in essence reduces the high cost sharing in these plans. Fourteen percent of covered workers in an HDHP with a Health Reimbursement Arrangement (HRA) and 7% of covered workers in a Health Savings Account (HSA)-qualified HDHP receive an account contribution for single coverage at least equal to their deductible, while another 47% of covered workers in an HDHP with an HRA and 28% of covered workers in an HSA-qualified HDHP receive account contributions that, if applied to their deductible, would reduce their deductible to less than $1,000. If we reduce the deductibles that workers face by employer account contributions, the percentage of covered workers with a deductible liability of $1,000 or more would be reduced from 51% to 38% (Exhibit G).
Whether they face a general annual deductible or not, a large share of covered workers also pay a portion of the cost when they visit a physician. For primary care, 67% of covered workers face a copayment (a fixed dollar amount) when they visit a doctor and 25% face coinsurance (a percentage of the covered amount). For specialty care, 66% face a copayment and 26% face coinsurance. The average in-network copayments are $24 for primary care and $38 for specialty care. The average in-network coinsurance is 18% for primary and 19% for specialty care. These amounts are similar to those in 2015. Most workers also face additional cost sharing for a hospital admission or an outpatient surgery episode. After any general annual deductible is met, 64% of covered workers have a coinsurance and 14% have a copayment for hospital admissions. Lower percentages have per day (per diem) payments (6%), a separate hospital deductible (1%), or both copayments and coinsurance (10%). The average coinsurance rate for hospital admissions is 19%. The average copayment is $282 per hospital admission, the average per diem charge is $281, and the average separate annual hospital deductible is $898. The cost sharing provisions for outpatient surgery follow a similar pattern to those for hospital admissions; most covered workers have either coinsurance (66%) or copayments (17%). For covered workers with cost sharing for outpatient surgery, the average coinsurance rate is 19% and the average copayment is $170. While almost all (98%) covered workers are in plans with a limit on in-network cost sharing (called an “out-of-pocket maximum”) for single coverage, there is considerable variation in the actual dollar limits. Fourteen percent of these workers are in a plan with an annual out-of-pocket maximum for single coverage of less than $2,000 while 18% are in a plan with an out-of-pocket maximum of $6,000 or more.
AVAILABILITY OF EMPLOYER-SPONSORED COVERAGE
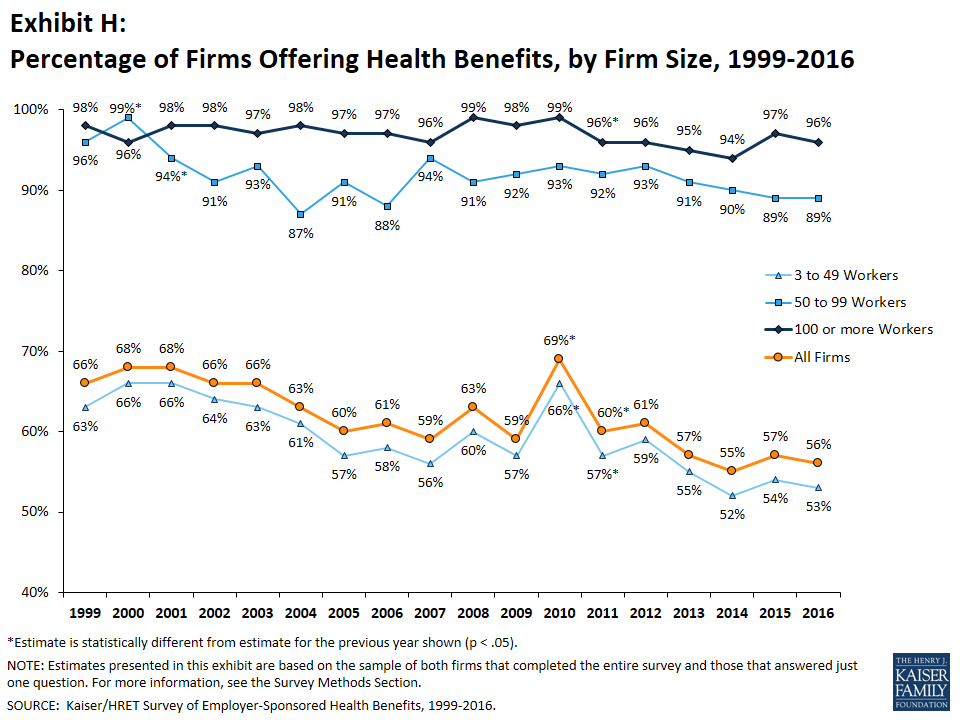
Fifty-six percent of firms offer health benefits to at least some of their workers, similar overall to percentages in recent years (Exhibit H). The percentages of smaller firms (10 to 49 workers) offering coverage, however, has fallen since 2011 and years before. This trend precedes the ACA coverage expansions and is consistent with longer-term trends reported elsewhere.
The likelihood of offering health benefits differs significantly by firm size, with only 46% of employers with 3 to 9 workers offering coverage while virtually all employers with 1,000 or more workers offer coverage. Eighty-nine percent of workers are in a firm that offers health benefits to at least some of its employees, similar to recent years. Even when firms do offer health benefits, not all of their workers are covered there. Some workers are not eligible to enroll (e.g., waiting periods or part-time or temporary work status) and others who are eligible choose not to enroll (e.g., they feel the coverage is too expensive or they are covered through another source). In firms that offer coverage, an average of 79% of workers are eligible for the health benefits offered by the firm, and of those eligible, 79% take up the firm’s offer, resulting in 62% of workers in offering firms having coverage through their employer. If we look across workers both in firms that offer and those that do not offer health benefits, 55% of workers are covered by health plans offered by their employer. All of these percentages are similar to 2015. Over the longer term, however, the percentage of workers in all firms covered by a health plan from their employer has fallen from 59% in 2006 and 58% in 2011 to 55% in 2016 (Exhibit I).
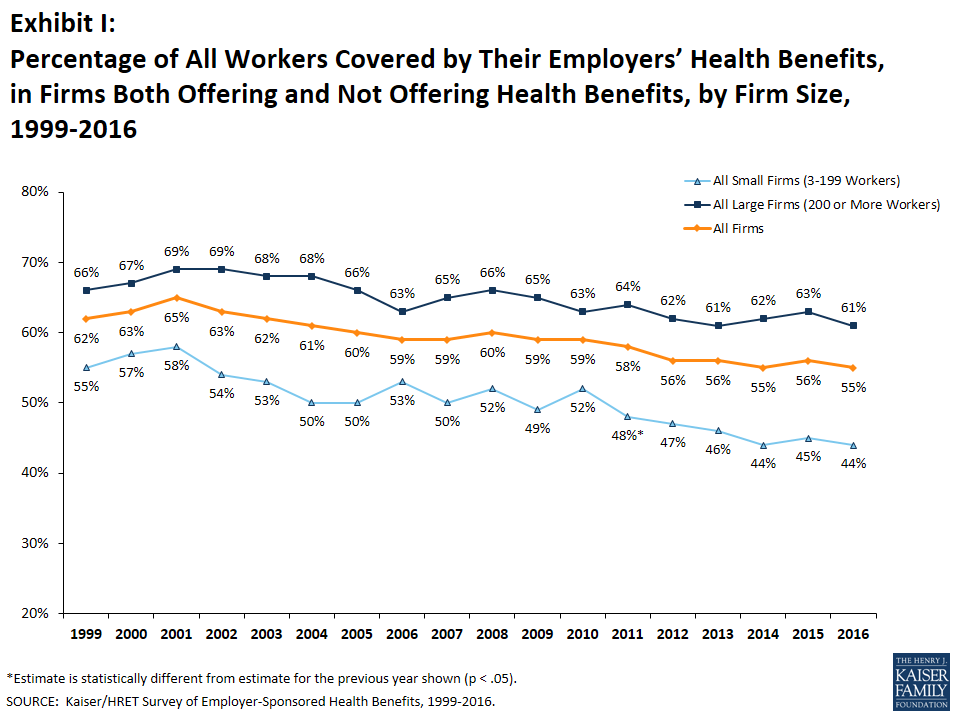
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) provision requiring employers with at least 50 full-time equivalent employees (FTEs) to offer health benefits that meet minimum standards for value and affordability to their full-time workers or pay a penalty took full effect in 2016. Ninety-seven percent of firms with at least 50 FTEs reported that they offer coverage to at least 95% of their employees who work on average 30 hours per week or more, and 96% responded that they offer at least one plan that met the ACA standards for affordability and minimum value. These firms were also asked about changes they planned to make or had made in the past year in response to the employer responsibility requirement. Two percent said they changed or planned to change the job classifications of some employees from full-time to part-time so that they would not be eligible for health benefits, while 7% said they changed or planned to change job classifications of some employees from part-time to full-time so that they would become eligible for health benefits. Other actions included 4% reducing or planning to reduce the number of full-time employees that they intended to hire because of the cost of providing health benefits to them, 2% increasing or planning to increase the waiting period before new employees become eligible for benefits, 12% extending or planning to extend eligibility for health benefits to workers who were not previously eligible, and 2% extending or planning to extend eligibility for more comprehensive benefits to employees previously eligible only for limited benefit plans. Coverage for Spouses and Unmarried Partners. Virtually all firms offering health benefits offer coverage for spouses, although 13% of small firms and 5% of large firms say that spouses are ineligible to enroll if a spouse is offered coverage from another source, and an additional 5% of small firms and 8% of large firms say that spouses offered coverage from other sources can enroll only under certain conditions. Twelve percent of firms offering coverage to spouses have a higher contribution or cost sharing for spouses who are eligible for coverage from another source, while 10% of firms offering coverage give additional compensation to employees who choose to enroll in their spouse’s plan. Two percent of firms offering coverage to spouses report that they made a significant reduction in the amount that they contributed for covering employees’ spouses during the last year. All of these percentages are similar for small and large firms. Among firms offering family coverage, 32% offer coverage to same-sex unmarried partners, with an additional 33% saying they do not know or have not encountered the situation. Large firms are more likely to offer coverage to same-sex unmarried partners than small firms (49% vs. 32%); small firms are much more likely to say they do not know or have not encountered the situation (34% vs. 5%). Twenty-seven percent of firms offering family coverage offer to unmarried opposite-sex partners, with an additional 28% saying that do know or have not encountered the situation. Large firms are more likely to offer coverage to unmarried opposite-sex partners than smaller firms (42% vs. 26%); small firms are more likely to report they do not know or have not encountered the situation (28% vs. 2%).
RETIREE COVERAGE
Of the large firms offering health benefits in 2016, 24% also offer health benefits to retirees, similar to the percentage in 2015 (23%). Among large firms that offer retiree health benefits, 92% offer health benefits to early retirees (workers retiring before age 65) and 72% offer health benefits to Medicare-age retirees. Six percent of large firms offering retiree benefits offer some retiree benefits through a corporate or private exchange, and 17% (down from 26% in 2015) report they are considering changing the way they offer retiree coverage because of the new health insurance exchanges established by the ACA.
WELLNESS, HEALTH RISK ASSESSMENTS AND BIOMETRIC SCREENINGS
Employers continue to show interest in programs that encourage employees to identify health issues and to take steps to improve their health (Exhibit J). A large share now offer health screening programs including health risk assessments, which are questionnaires asking employees about lifestyle, stress or physical health, and in-person examinations such as biometric screenings. Many employers have incentive programs that reward or penalize employees for completing assessments, participating in wellness programs, or meeting biometric outcomes. These survey questions on these topics were revised for 2016 and are asked only of firms offering health benefits. Because there was considerable uncertainty among small firms on some questions, particularly those related to incentives, findings are reported only for large firms in some instances.
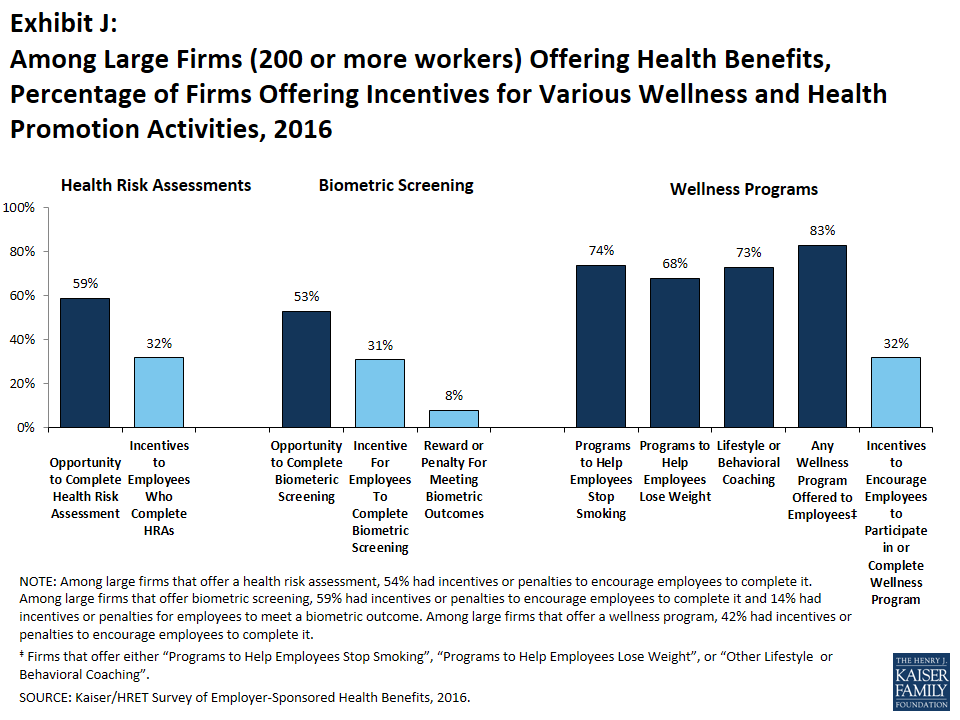
Health Risk Assessments. Among firms offering health benefits, 32% of small firms and 59% of large firms provide employees with an opportunity to complete a health risk assessment. A health risk assessment includes questions about a person’s medical history, health status, and lifestyle. Fifty-four percent of large firms with a health risk assessment program offer a financial incentive to encourage employees to complete the assessment. Among large firms with an incentive, the incentives include: lower premium contributions or cost sharing (51% of firms); requiring a completed health risk assessment to be eligible for other wellness incentives (44% of firms); and cash, contributions to health-related savings accounts, or merchandise (60% of firms). Biometric Screening. Twenty percent of small firms and 53% of large firms offering health benefits offer employees the opportunity to complete biometric screening. Biometric screening is a health examination that measures an employee’s risk factors such as body weight, cholesterol, blood pressure, stress, and nutrition. Fifty-nine percent of large firms with biometric screening programs offer employees an incentive to complete the screening. Among large firms with an incentive, the incentives include: lower premium contributions or cost sharing (52% of firms); requiring a completed biometric screening to be eligible for other wellness incentives (32% of firms); and cash, contributions to health-related savings accounts, or merchandise (56% of firms). In addition, 14% of large employers with biometric screening programs have financial incentives tied to whether or not employees met or were able to meet specified biometric outcomes, such as a targeted body mass index (BMI) or cholesterol level. Health and Wellness Promotion Programs. Many employers offer wellness or health promotion programs to help employees improve their health and avoid unhealthy behaviors. Forty-six percent of small firms and 83% of large firms offer a program in at least one of these areas: smoking cessation; weight management; behavioral or lifestyle coaching. Three percent of small firms and 16% of large firms report collecting health information from employees through wearable devices such as a Fitbit or Apple Watch. Forty-two percent of large firms with one of these health and wellness programs offer employees a financial incentive to participate in or complete the program. Among large firms with an incentive for completing wellness programs, incentives include: lower premium contributions or cost sharing (34% of firms); cash, contributions to health-related savings accounts, or merchandise (76% of firms); some other type of incentive (14% of firms). Some firms separate financial incentives for different programs and some others have incentives that require participation in more than one type of program (e.g., completing an assessment and participating in a health promotion activity). We asked firms that had any incentives for health risk assessments, biometric screening or the specified health and wellness promotion programs what the maximum financial incentive was for a worker for all of their programs combined. Among large firms with any type of incentive, 26% have a maximum financial incentive of less than $150, 35% have a maximum incentive between $150 and $500, 23% have a maximum incentive between $500 and $1,000, 9% have a maximum incentive between $1,000 and $2,000, and 7% have a maximum incentive of $2000 or more.
Sites of Care
Telemedicine. Thirty-nine percent of large firms that offer health benefits cover the provision of some health care services through telecommunication in their largest health plan. We revised our questions for 2016 to clarify that we were asking about payment for services and not just the electronic exchange of information. Among these firms, 33% reported that workers have a financial incentive to receive services through telemedicine as instead of visiting a physician’s office. Retail Health Clinics. Sixty percent of small firms and 73% of large firms cover services offering health benefits provided in retail health clinics, such as those found in pharmacies and supermarkets, in their largest health plan. Among large firms covering services in retail clinics, 10% reported that workers had a financial incentive to receive services in a retail clinic instead of visiting a traditional physician’s office. On-Site Health Clinics. Among firms with at least 50 employees offering health benefits, five percent provide health services to employees through an on-site health clinic in at least one of their major locations. Eighty-six percent of these firms provided some services for non-work-related illnesses through the on-site clinic. Firms with at least 1,000 workers were more likely to have an on-site health clinic than smaller firms (25% vs. 4%).
PROVIDER NETWORKS
High Performance or Tiered Networks. Fourteen percent of large firms offering health benefits have high performance or tiered networks in their largest health plan, down from 24% last year. These programs identify providers that are more efficient or have higher quality care, and may provide financial or other incentives for enrollees to use the selected providers. Narrow Networks. Seven percent of firms offering health benefits offer a health plan that they consider to have a narrow network (i.e., a network they would consider more restrictive than a standard HMO network), similar to the percentage reported last year. There is no difference between small and large firms on this measure. Six percent of firms reported that they or their insurer had eliminated a hospital or health system from any of their plans’ networks in order or reduce costs. There is no difference between small and large firms on this measure.
OTHER TOPICS
Self-Funding. Thirteen percent of covered workers in small firms and 82% in large firms are enrolled in plans that are either partially or completely self-funded, similar to last year. Overall, 61% of covered workers are enrolled in a plan that is either partially or completely self-funded. Private Exchanges. Four percent of firms offering health benefits with at least 50 employees offer health benefits through a private exchange. Private exchanges are arrangements, usually created by consultants, brokers or insurers, which allow employers to offer their employees a choice of different benefit options, often from different insurers. Among firms offering health benefits that do not currently offer through a private exchange, 18% with at least 50 workers, including 28% with at least 5,000 workers, say they have considered offering coverage through a private exchange. Professional Employment Organization. Some firms provide for health and other benefits by entering into a co-employment relationship with a Professional Employer Organization (PEO). Under this arrangement, the firm manages the day-to-day responsibilities of employees, but the PEO hires the employees and acts as the employer for insurance, benefits, and other administrative purposes. Four percent of small firms offering health benefits offer coverage through a PEO, similar to last year. Grandfathered Health Plans. The ACA exempts “grandfathered” health plans from a number of its provisions, such as the requirement to cover preventive benefits without cost sharing or the new rules for small employers’ premiums ratings and benefits. An employer-sponsored health plan can be grandfathered if it covered a worker when the ACA became law (March 23, 2010) and if the plan has not made significant changes that reduce benefits or increase employee costs.5 Twenty-three percent of firms offering health benefits offer at least one grandfathered health plan in 2016, down from 35% last year. Twenty-three percent of covered workers are enrolled in a grandfathered health plan, similar to the percentage in 2015.
EXCISE TAX ON HIGH-COST HEALTH PLANS
Under the ACA, employer health plans in 2020 will be subject to an excise tax of 40% on the amount by which their cost exceeds specified thresholds.6 The tax was scheduled to take effect in 2018, but its effective date was delayed two years. The tax is calculated with respect to each employee based on the combination of health benefits received by that employee, including the employer and employee share of health plan premiums and account contributions. Of firms offering health benefits, 15% of small firms and 64% of large firms say they have conducted an analysis to determine if they will exceed the thresholds, with 29% of the small firms and 27% of the large firms saying that their largest health plan would exceed the threshold in 2020. Some plans report planning or taking action in the last year in anticipation of the assessment: four percent of small firms and 15% of large firms increased cost sharing; three percent of small firms and nine percent of large firms switched to a lower cost plan or eliminated a plan option; three percent of small firms and eight percent of large firms moved benefit options to an account-based plan; and four percent of small firms and two percent of large firms selected a plan with a smaller network of providers.
CONCLUSION
This is the fifth straight year of relatively low premium growth (family coverage growing between 3 and 4 percentage points each year), but the stability for premiums belies some other changes that have occurred during the period. Deductibles continued to grow in 2016; over the last five years, the percentage of covered workers facing a general annual deductible has grown from 74% to 83%, while the average single deductible amount (among those facing a deductible) increased from $991 to $1,478. These higher deductibles likely contributed to the moderating premium increases over this period. The higher deductibles have resulted, in part, by growing enrollment in HDHP/SOs, where enrollment has gone from 17% of covered workers in 2011 to 29% in 2016. Just in the last two years, enrollment in HDHP/SOs has grown by eight percentage points while PPO enrollment has declined by ten. More enrollment in HDHP/SOs has several implications for costs: they have higher deductibles than other plan types, but many enrollees also receive contributions to their HSA or HRAs that offset some or all of the cost sharing; they have lower total premiums and worker contribution amounts, although contributions by employers toward enrollee HRAs and HSAs offset some of the impact of the lower premiums for employers. There has been a reduction in offering for firms with 10 to 49 workers over the period, decreasing from 74% in 2011 (and 76% in 2012) to 66% in 2016. This change precedes the introduction of public marketplaces and premium tax credits, and other sources show a longer term reduction in offer rates among small private firms. Across all workers (both in firms that offer and do not offer coverage) during the period, the percentage of workers with coverage from their own employer has fallen from 58% in 2011 to 55% in 2016. Employers, particularly larger ones who employ most workers, continue to show interest in programs to improve health and in new delivery options. Significant shares of small and large employers offer employees the opportunity to complete health risk assessments or biometric screening or to participate in lifestyle coaching or other health promotion programs; many large employers provide employees with financial incentives to complete assessments or participate in programs. Employers also are covering services through new venues, such as retail health clinics and telemedicine, sometimes providing financial incentives for employees to use these new options. Finally, the continuing implementation of the ACA does not appear to be causing major disruptions in employer market. The employer responsibility provision was fully implemented in 2016, with virtually all employers with 50 or more FTEs saying that they offer coverage to full-time employees that meets affordability and minimum value standards. Relatively few employers made changes to working hours or hiring as a result of the provision, with more taking actions that increased coverage offers than reducing them, similar to the results last year. Most large employers, but few small employers, have analyzed how the high cost plan tax will affect them when it takes effect in 2020, with about 12% of offering firms saying they have taken some action in response to the tax. Looking forward, there are several emerging issues to watch. One is growth of HDHO/SOs, which after a lull, have seen significant enrollment growth in the last two years. These plans have relatively high cost sharing, but as discussed above, some workers receive significant account contributions to offset some of these costs. Another issue is whether the share of smaller firms offering coverage continues to fall. These firms are not required to offer coverage under the ACA, and in some cases, their workers might have more affordable options in public marketplaces than through work, which could encourage employers to stop offering. And, while the high-cost plan excise tax has been delayed until 2020, a meaningful share of employers estimates that they will be subject to the assessment. Only small shares of firms have reacted so far, but this may accelerate over the next couple of years if the 2020 date remains in place.
METHODOLOGY
The Kaiser Family Foundation/Health Research & Educational Trust 2016 Annual Employer Health Benefits Survey (Kaiser/HRET) reports findings from a telephone survey of 1,933 randomly selected public and private employers with three or more workers. Researchers at the Health Research & Educational Trust, NORC at the University of Chicago, and the Kaiser Family Foundation designed and analyzed the survey. National Research, LLC conducted the fieldwork between January and June 2016. In 2016, the overall response rate is 40%, which includes firms that offer and do not offer health benefits. Among firms that offer health benefits, the survey’s response rate is also 40%. We asked all firms with which we made phone contact, even if the firm declined to participate in the survey: “Does your company offer a health insurance program as a benefit to any of your employees?” A total of 3,110 firms responded to this question (including the 1,933 who responded to the full survey and 1,177 who responded to this one question). Their responses are included in our estimates of the percentage of firms offering health benefits. The response rate for this question is 65%. Since firms are selected randomly, it is possible to extrapolate from the sample to national, regional, industry, and firm size estimates using statistical weights. In calculating weights, we first determine the basic weight, then apply a nonresponse adjustment, and finally apply a post-stratification adjustment. We use the U.S. Census Bureau’s Statistics of U.S. Businesses as the basis for the stratification and the post-stratification adjustment for firms in the private sector, and we use the Census of Governments as the basis for post-stratification for firms in the public sector. Some numbers in the report’s exhibits do not sum up to totals because of rounding effects, and, in a few cases, numbers from distribution exhibits referenced in the text may not add due to rounding effects. Unless otherwise noted, differences referred to in the text and exhibits use the 0.05 confidence level as the threshold for significance. For more information on the survey methodology, please visit the Methodology section at http://ehbs.kff.org/. The Kaiser Family Foundation, a leader in health policy analysis, health journalism and communication, is dedicated to filling the need for trusted, independent information on the major health issues facing our nation and its people. The Foundation is a non-profit private operating foundation based in Menlo Park, California. The Health Research & Educational Trust (HRET) Founded in 1944, the Health Research & Educational Trust (HRET) is the not-for-profit research and education affiliate of the American Hospital Association (AHA). HRET’s mission is to transform health care through research and education. HRET’s applied research seeks to create new knowledge, tools and assistance in improving the delivery of health care by providers and practitioners within the communities they serve.
Section One: Cost Of Health Insurance
The average annual premiums in 2016 are $6,435 for single coverage and $18,142 for family coverage. The average family premiums increased approximately 3% since 2015. The average family premium has increased 58% since 2006 and 20% since 2011. The average family premium for covered workers in small firms (3-199 workers) ($17,546) is significantly lower than average family premiums for workers in large firms (200 or more workers) ($18,395).
Premium Costs for Single and Family Coverage
- The average premium for single coverage in 2016 is $536 per month, or $6,435 per year. The average premium for family coverage is $1,512 per month or $18,142 per year 1.
- The average annual premiums for covered workers in HDHP/SOs are lower for single ($5,762) and family coverage ($16,737) than the overall average premiums for covered workers. The average premiums for covered workers enrolled in PPO plans are higher for single ($6,800) and family coverage ($19,003) than the overall plan average 1.
- The average annual premium for family coverage for covered workers in small firms ($17,546) is lower than the average premium for covered workers in large firms ($18,395) 2.
- The average family premium for covered workers is lower in the South ($17,429) than the average premium for covered workers in all other regions 3.
- The average single premium for covered workers employed in the retail industry ($5,807) is lower than the average premium for covered workers in all other industries. The average single premium for covered workers employed in the state/local government industry ($7,218) is higher than the average premium for covered workers in all other industries 4.
- The average family premium for covered workers employed in the retail industry ($16,321) is lower than the average premium for covered workers in all other industries 4.
- The average single premium for covered workers in firms with a larger share of younger workers (where 35% or more of the workers are age 26 or younger) is lower than the average premium for covered workers in firms with a lower share of younger workers ($6,047 vs. $6,472) 5.
- The average family premium for covered workers in firms with some union workers ($18,906) is higher than the average premium for covered workers in firms without union workers ($17,748) 6.
The Distribution of Premiums
- There is considerable variation in premiums for both single and family coverage.
- Eighteen percent of covered workers are employed in a firms with a single premium at least 20% higher than the average single premium, while 19% of covered workers are in firms with a single premium less than 80% of the average single premium 7 and 8.
- For family coverage, 17% of covered workers are employed in a firm with a family premium at least 20% higher than the average family premium, while 19% of covered workers are in firms with a family premium less than 80% of the average family premium7 and 8.
- Seven percent of covered workers are in a firm with a premium of $9,000 a year or more for single coverage 9. Nine percent of covered workers are in a firm with a premium of $24,000 a year or more for family coverage 10.
Premium Changes Over Time
- The 2016 average family coverage premiums are three percent higher than the 2015 average premiums 11.
- The $18,142 average family premium in 2016 is 20% higher than the average family premium in 2011 and 58% higher than the average family premium in 2006 11 and 16. The 20% family premium growth in the last five years is smaller than the 31% growth between 2006 and 2011, or the 63% premium growth between 2001 and 2006 16.
- The average family premiums for both small and large firms have seen a similar increase since 2011 (24% for small and 19% for large). For small firms (3 to 199 workers), the average family premium rose from $14,098 in 2011 to $17,546 in 2016. For large firms (200 or more workers), the average family premium rose from $15,520 in 2011 to $18,395 in 2016 13.
- The rates of growth for the average family premiums in small firms and large firms since 2006 also have been similar. Since 2006, the average family premium for small firms increased 55% ($17,546 in 2016 vs. $11,306 in 2006), and the average family premium for large firms increased 59% ($18,395 in 2016 vs. $11,575 in 2006) 13.
- For covered workers in large firms, the average family premium in firms that are fully insured has grown between 2011 to 2016 at a similar rate to premiums for workers in fully or partially self-funded firms (21% for fully insured plans and 18% for self-funded firms) 17.
Section Two: Health Benefits Offer Rates
While nearly all large firms (200 or more workers) offer health benefits to at least some employees, small firms (3-199 workers) are significantly less likely to do so. The percentage of all firms offering health benefits in 2016 (56%) is similar to the percentages of firms offering health benefits in 2006 (61%) and 2011 (60%). The percentages of smaller firms (10 to 49 workers) offering coverage, however, has fallen since 2011 and years before. This trend precedes the ACA coverage expansions and is consistent with longer-term trends reported elsewhere.
Firms not offering health benefits continue to cite cost as the most important reason they do not do so. Almost all firms that offer coverage offer to dependents such as children and the spouses of eligible employees.
- In 2016, 56% of firms offer health benefits, similar to the 57% who reported doing so in 2015 1.
- Ninety-eight percent of large firms offer health benefits to at least some of their workers 3. In contrast, only 55% of small firms offer health benefits in 2016. The percentage of both small and large firms offering health benefits to at least some of their workers is similar to last year 2.
- Since most firms in the country are small, variation in the overall offer rate is driven largely by changes in the percentages of the smallest firms (3-9 workers) offering health benefits. For more information on the distribution of firms in the country, see the Survey Design and Methods Section and Exhibit M1.7
- Ninety-six percent of firms with 100 or more workers offer health benefits to at least some of their employees in 2016. Eighty-nine percent of firms with 50 to 99 workers offer benefits to at least some workers 4.
- The percentages of smaller firms (10 to 49 workers) offering coverage has fallen since 2011 and years before.
- The overall percentage of firms offering coverage in 2016 is similar to the percentage offering coverage in 2011 (60%) and 2006 (61%).
- Offer rates vary across different types of firms.
- Small firms are less likely to offer health insurance: 46% of firms with 3 to 9 workers offer coverage, compared 80% of firms with 25 to 49 workers, and 91% of firms with 50 to 199 employees 3.
- Offer rates throughout different firm size categories in 2016 remain similar to those reported in 2015 2.
Part-Time and Temporary Workers
- Among firms offering health benefits, relatively few offer benefits to their part-time and temporary workers.
- The Affordable Care Act (ACA) defines part-time workers as those who on average work fewer than 30 hours per week. The employer shared responsibility provision of the ACA requires that large firms offer full-time employees a minimum standard of coverage or be assessed a penalty.8 Beginning in 2015, we modified the survey to explicitly ask employers whether they offered benefits to employees working fewer than 30 hours. Our previous question did not include a definition of “part-time”. For this reason, historical data on part-time offer rates are shown, but we did not test whether the differences between 2014 and 2015 were significant. Many employers may work with multiple definitions of part-time; one for their compliance with legal requirements and another for internal policies and programs.
- In 2016, 16% of all firms that offer health benefits offer them to part-time workers 7. Large firms are more likely to offer health benefits to part-time employees than small firms (33% vs. 15%) 9.
- A small percentage (4%) of firms offering health benefits offer them to temporary workers 8. More large firms offering health benefits elect to offer temporary workers coverage than small firms (17% vs. 3%) 10. The percentage of large firms offering health benefits to temporary workers is higher than the 11% reported in 2015.
Spouses, Dependents and Domestic Partner Benefits
- The majority of firms offering health benefits offer to spouses and dependents, such as children. In 2016, 89% of small firms and 99% of large firms offering health benefits offer coverage to spouses 11. Fewer small firms offer coverage to spouses in 2016 than did in 2015 (98%). Eighty-eight percent of small firms and 100% of large firms offering health benefits cover other dependents, such as children, similar to last year. Eleven percent of small firms offering health benefits offer only single coverage to employees, higher than the 2% of small firms last year.
- Employers were also asked whether same-sex or opposite-sex domestic partners were allowed to enroll in the firm’s coverage. While definitions may vary, employers often define domestic partners as an unmarried couple who has lived together for a specified period of time. Firms may define domestic partners separately from any legal requirements a state may have, and also, employers may have a different policy in different parts of the country.
- In 2016, 27% of firms offering health benefits offer coverage to opposite-sex domestic partners, similar to the 28% who did so in 2015. Thirty-two percent of firms offering health benefits offer coverage to same-sex domestic partners, similar to the 42% who did so last year 13.
- When we ask employers if they offer health benefits to opposite or same-sex domestic partners, many firms report that they have not encountered this issue. At many small firms, the firm may not have formal human resource policies on domestic partners simply because none of the firm’s employees have asked to cover a domestic partner. Regarding health benefits for opposite-sex domestic partners, 28% of firms report in 2016 that they have not encountered this request or that the question was not applicable 12. The vast majority of firms in the United States are small businesses; 61% of firms have between 3 and 9 employees and 98% have between 3 and 199 employees (Exhibit M.1). Therefore, statistics about the percentage of firms that offer domestic partner benefits are largely determined by small businesses. More small firms (28%) compared to large firms (2%) indicate that they have not encountered this request or that the question was not applicable 12. Regarding health benefits for same-sex domestic partners, 33% of firms report that they have not encountered the request or that the question was not applicable. More small firms (34%) than large firms (5%) report that they have not encountered the issue of offering benefits to same-sex domestic partners 12.
- Virtually all firms offering family coverage offer coverage to spouses. Among firms offering health benefits to spouses, 13% do not allow an employee’s spouse to enroll in the firm’s plan if that spouse is offered coverage from another source, and an additional 5% allow the spouse to enroll subject to conditions 14. Among firms offering health benefits to spouses, 12% require an employee’s spouse to contribute more to the coverage if that spouse is offered coverage from another source. Very large firms (5,000 or more workers) are more likely than smaller firms to require higher spousal contributions when the spouse is offered coverage elsewhere (26% vs. 12%).
- Among firms offering health benefits to spouses, 2% have made a significant reduction in the amount they contribute to cover an employee’s spouse in the last year, with no difference between small and large firms 15.
- Among all firms that offer health benefits, 10% report providing additional compensation or benefits to employees if they enroll in a spouse’s plan, and 9% provide additional compensation or benefits to employees if they do not participate in the firm’s health benefits 16.
Firms Not Offering Health Benefits
- The survey asks firms that do not offer health benefits if they have offered insurance or shopped for insurance in the recent past, and about their most important reasons for not offering coverage. Because such a small percentage of large firms report not offering health benefits, we present responses for small non-offering firms only.
- The cost of health insurance remains the primary reason cited by firms for not offering health benefits. Among small firms not offering health benefits, 34% cite high cost as “the most important reason” for not doing so, followed by “employees are generally covered under another plan” (24%) 17. Relatively few small employers indicate that they do not offer because they believe that employees will get a better deal on the health insurance exchanges (1%).
- Many non-offering small firms have either offered health insurance in the past five years, or shopped for health insurance in the past year. Nineteen percent of non-offering small firms have offered health benefits in the past five years, while 23% have shopped for coverage in the past year 18. The 19% of non-offering small firms that have offered coverage in the past five years is similar to the 25% reported last year.
- Thirty percent of non-offering small firms report that they stopped offering coverage within the last year, similar to the percentage (38%) last year.
- Among non-offering small firms, 11% report that they provide funds to their employees to purchase health insurance on their own in the individual market or through a health insurance exchange 19. The IRS has issued guidance limiting the circumstances in which employers can contribute to an employee’s non-group plan going forward.9
SHOP Exchanges
The Small Business Health Options Program (SHOP) is federal or state sponsored exchanges in which employers may offer and contribute to health insurance provided to their employees. Firms with 50 or fewer full-time equivalent workers (FTEs) are eligible to participate in a SHOP exchange. Beginning in 2016, states have the option to expand SHOP to include firms with up to 100 FTEs. Some employers are eligible for tax credits when purchasing coverage on the exchanges.
- Eighteen percent of firms with 3 to 50 FTEs who do not offer health benefits said they looked at coverage on a SHOP exchange 20.
- Thirteen percent of firms with 3 to 50 FTEs who offer health benefits said they looked at coverage on a SHOP exchange 20.
- Among non-offering firms with 50 or fewer FTEs that looked at coverage but chose not to purchase on a SHOP exchange, 70% reported they did not do so because the plans were too expensive 21.
- Among offering firms with 50 or fewer FTEs that looked at coverage but chose not to purchase on a SHOP exchange, their reasons included that they like their current insurer or broker (67%) and that they got a better deal elsewhere (64%) 22.
Section Three: Employee Coverage, Eligibility, And Participation
Employers are the principal source of health insurance in the United States, providing health benefits for about 150 million non-elderly people in America.10 Most workers are offered health coverage at work, and the majority of workers who are offered coverage take it. Workers may not be covered by their own employer for several reasons: their employer may not offer coverage, they may be ineligible for the benefits offered by their firm, they may elect to receive coverage through their spouse’s employer, or they may refuse coverage from their firm. Before eligible employees may enroll, almost three-quarters (72%) of covered workers face a waiting period, although the average length waiting periods for covered workers with waiting periods has decreased since 2014 when an ACA provision prescribing a maximum waiting period of 90 days was implemented.
- Among workers at firms offering health benefits, 62% percent of workers are covered by health benefits through their own employer 2.
- Among workers in all firms, including those that offer and those that do not offer health benefits, 55% of workers are covered by health benefits offered by their employer, similar to the percentage (56%) last year. The coverage rate in 2016 is lower than the coverage rate in 2006 (59%) and in 2011 (58%) 1.
Eligibility
- Not all employees are eligible for the health benefits offered by their firm, and not all eligible employees “take up” (i.e., elect to participate in) the offer of coverage. The share of workers covered in a firm is a product of both the percentage of workers who are eligible for the firm’s health insurance and the percentage that choose to take up the benefit. The percentage of workers eligible for health benefits at offering firms in 2016 is similar to last year for both small firms and large firms 6.
- Seventy-nine percent of workers in firms offering health benefits are eligible for the coverage offered by their employer. The percentage of eligible workers is higher is small firms than in large firms (82% vs. 78%) 2.
- Eligibility varies considerably by wage level. Employees in firms with a larger share of higher-wage workers (35% or more earn $59,000 or more annually) are more likely to be eligible for health benefits than employees in firms with a smaller share of higher-wage workers (86% vs. 73%) 3.
- Eligibility also varies by the age of the workforce. Those in firms with a smaller share of younger workers (less than 35% of workers are age 26 or younger) are more likely to be eligible for health benefits than those in firms with a larger share of younger workers (81% vs. 64%) 3.
- The average eligibility rate is particularly low (55%) in retail firms 2.
Take-up Rate
- Employees who are offered health benefits generally elect to take up the coverage. In 2016, 79% of eligible workers take up coverage when it is offered to them, unchanged from last year 6.11
- The likelihood of a worker accepting a firm’s offer of coverage also varies with the workforce’s wage level. Eligible employees in firms with a smaller share of lower-wage workers are more likely to take up coverage than eligible employees in firms with a larger share of lower-wage workers (35% or more of workers earn $23,000 or less annually) (80% vs. 61%). A similar pattern exists in firms with a larger share of higher-wage workers, with workers in these firms being more likely to take up coverage than those in firms with a smaller share of higher-wage workers (84% vs. 73%) 4.
- The percentage of eligible workers taking up benefits in offering firms varies considerably by industry 2.
Coverage
- The percentage of workers at firms offering health benefits that are covered by their firm’s health plan in 2016 is 62%. The coverage rate at firms offering health benefits is similar to last year for both small firms and large firms 6.
- There is significant variation by industry in the coverage rate among workers in firms offering health benefits. For example, only 37% of workers in retail firms offering health benefits are covered by the health benefits offered by their firm, compared to 77% of workers in manufacturing, and 77% of workers in the state/local government industry category 2.
- Among workers in firms offering health benefits, those in firms with a smaller share of lower-wage workers (less than 35% of workers earn $23,000 or less annually) are more likely to be covered by their own firm than workers in firms with a larger share of lower-wage workers (64% vs. 45%). A comparable pattern exists in firms with a larger share of higher-wage workers (35% or more earn $59,000 or more annually), with workers in these firms more likely to be covered by their employer’s health benefits than those in firms with a smaller share of higher-wage workers (72% vs. 54%) 5.
- Among workers in firms offering health benefits, those in firms with a smaller share of younger workers (less than 35% of workers are age 26 or younger) are more likely to be covered by their own firm than those in firms with a larger share of younger workers (65% vs. 43%) 5.
- Among workers in all firms, including those that offer and those that do not offer health benefits, 55% of workers are covered by health benefits offered by their employer, similar to the percentage (56%) last year. The coverage rate in 2016 is lower than the coverage rate in 2006 (59%) and in 2011 (58%),
Waiting Periods
- Waiting periods are a specified length of time after beginning employment before employees are eligible to enroll in health benefits. With some exceptions, the Affordable Care Act requires that waiting periods cannot exceed 90 days.12 For example, employers are permitted to have orientation periods before the waiting period begins which, in effect, means an employee is not eligible for coverage 3 months after hire. If an employee is eligible to enroll on the 1st of the month after three months of employment, this survey rounds up and considers the firm’s waiting period four months. For these reasons, some employers still have waiting periods exceeding the 90-day maximum.
- Seventy-two percent of covered workers face a waiting period before coverage is available, similar to last year 9. Covered workers in small firms (3-199 workers) are more likely than those in large firms to have a waiting period (78% vs. 70%) 7.
- The average waiting period among covered workers who face a waiting period is 1.9 months 7. A small percentage (3%) of covered workers with a waiting period have a waiting period of more than 3 months.
- Among firms with a waiting period of greater than 4 months, a majority of firms indicated that they have an employee measurement period. 13
Section Four: Types Of Plans Offered
Most firms that offer health benefits offer only one type of health plan (83%) (see text box). Large firms (200 or more workers) are more likely to offer more than one type of health plan than small firms (3-199 workers). Employers are most likely to offer their workers a PPO plan and are least likely to offer a conventional plan (sometimes known as indemnity insurance).
- Eighty-three percent of firms offering health benefits in 2016 offer only one type of health plan. Large firms are more likely to offer more than one plan type than small firms (53% vs. 16%) 1.
- In addition to looking at the percentage of firms that offer multiple plan types, the percentage of covered workers at firms that offer multiple plan types can also be analyzed. Fifty-nine percent of covered workers are employed in a firm that offers more than one health plan type. Sixty-nine percent of covered workers in large firms are employed by a firm that offers more than one plan type, compared to 35% in small firms 2.
- Nearly three quarters (74%) of covered workers in firms offering health benefits work in firms that offer one or more PPO plans; 56% work in firms that offer one or more HDHP/SO plans; 33% work in firms that offer one or more HMO plans; 13% work in firms that offer one or more POS plans; and 2% work in firms that offer one or more conventional plans 4.14
- Among firms offering only one type of health plan, covered workers in large firms are more likely to be offered PPO plans than covered workers in small firms (62% vs. 39%), while covered workers in small firms are more likely to be offered HMO (12%) and POS (22%) plans than covered workers in large firms (3% and 4%, respectively) 5.
- Among firms offering only one type of health plan, 29% of covered workers are in firms that only offer an HDHP/SO and 51% of covered workers are in firms that only offer a PPO 5.
The survey collects information on a firm’s plan with the largest enrollment in each of the plan types. While we know the number of plan types a firm has, we do not know the total number of plans a firm offers workers. In addition, firms may offer different types of plans to different workers. For example, some workers might be offered one type of plan at one location, while workers at another location are offered a different type of plan.
HMO is health maintenance organization.
PPO is preferred provider organization.
POS is point-of-service plan.
HDHP/SO is high-deductible health plan with a savings option such as an HRA or HSA.
Section Five: Market Shares Of Health Plans
Enrollment remains highest in PPO plans, covering just under half of covered workers, followed by HDHP/SOs, HMO plans, POS plans, and conventional plans. Enrollment distribution varies by firm size: for example, PPOs are relatively more popular for covered workers at large firms (200 or more workers) than small firms (3-199 workers) (52% vs. 39%) and POS plans are relatively more popular among small firms than large firms (18% vs. 4%). Enrollment in HDHP/SOs has increased significantly over the past two years while enrollment in PPOs has fallen.
- Forty-eight percent of covered workers are enrolled in PPOs, followed by HDHP/SOs (29%), HMOs (15%), POS plans (9%), and conventional plans (< 1%) 1. More covered workers are enrolled in HDHP/SO plans than in HMOs in both small firms and large firms 2.
- The percentage of covered workers enrolled in HDHP/SOs in is similar to last year but has grown significantly since 2014 (29% vs. 20%).15 Since 2014, enrollment in PPOs has fallen significantly (48% vs. 58%) 1.
- Plan enrollment patterns vary by firm size.
- Covered workers in large firms are more likely than covered workers in small firms to enroll in PPOs (52% vs. 39%). Covered workers in small firms are more likely than covered workers in large firms to enroll in POS plans (18% vs. 4%) 2.
- The share of covered workers in HDHP/SOs is similar for large firms and small firms 2.
- Plan enrollment patterns also differ across regions.
- HMO enrollment is significantly higher in the West (30%) and significantly lower in the South (10%) and Midwest (6%) 3.
- Covered workers in the South (57%) are more likely to be enrolled in PPOs than workers in other regions; covered workers in the West (35%) and the Northeast (39%) are less likely to be enrolled in a PPO 3.
- Enrollment in HDHP/SOs is similar across regions 3.
- Plan enrollment patterns differ by industry as well.
- Covered workers in the agriculture/mining/construction, (5%), manufacturing (8%) and finance (8%) are less likely to be enrolled in an HMO plan than covered workers in other industries. Covered workers in the service industry (20%) are more likely to be enrolled in an HMO than covered workers in other industries 3.
- Covered workers in the state/local government (64%) are more likely to be enrolled in a PPO plan than covered workers in other industries. Covered workers in the finance industry (32%) are less likely to be enrolled in a PPO than covered workers in other industries 3.
- Covered workers in the state/local government (19%) and agriculture/mining/construction industries (15%) are less likely to be enrolled in an HDHP/SO plan than covered workers in other industries. Covered workers in the finance industry (49%) are more likely to be enrolled in an HDHP/SO than covered workers in other industries
Section Six: Worker And Employer Contributions For Premiums
In 2016, premium contributions by covered workers average 18% for single coverage and 30% for family coverage.16 The average monthly worker contributions are $94 for single coverage ($1,129 annually) and $440 for family coverage ($5,277 annually).17 Covered workers in small firms (3-199 workers) have a lower average contribution amount for single coverage ($1,021 vs. $1,176), but a higher average contribution amount for family coverage ($6,597 vs. $4,719) than covered workers in large firms (200 or more employees).
- In 2016, covered workers on average contribute 18% of the premium for single coverage and 30% of the premium for family coverage 1. These contribution percentages have remained stable in recent years for both single and family coverage.
- Covered workers in small firms contribute a higher percentage of the premium for family coverage (39% vs. 26%) than covered workers in large firms 23.
- On average, workers with single coverage contribute $94 per month ($1,129 annually), and workers with family coverage contribute $440 per month ($5,277 annually) towards their health insurance premiums 2, 3, and 4.
- The average worker contribution in HDHP/SOs is lower than the overall average worker contribution for single coverage ($943 vs. $1,129) and family coverage ($4,289 vs. $5,277) 5.
- Worker contributions also differ by firm size. As in previous years, workers in small firms contribute a lower amount annually for single coverage than workers in large firms ($1,021 vs. $1,176). In contrast, workers in small firms with family coverage contribute significantly more annually than workers in large firms ($6,597 vs. $4,719) 6.
- The average worker contributions for single coverage and family coverage are similar to last year for both small firms and large firms 8 and 9.
Variation in Worker Contributions to the Premium
- The majority of covered workers are employed by a firm that contributes at least half of the premium for single and family coverage.
- Twelve percent of covered workers are in plans where the employer pays the entire premium for single coverage; three percent of covered workers are in plans where the employer pays the entire premium for family coverage 17.
- Covered workers in small firms are much more likely to work for a firm that pays 100% of the premium than workers in large firms. Thirty percent of covered workers in small firms have an employer that pays the full premium for single coverage, compared to five percent of covered workers in large firms 18. For family coverage, eight percent of covered workers in small firms have an employer that pays the full premium, compared to one percent of covered workers in large firms 19.
- Fifteen percent of covered workers have a plan where they are required to contribute more than 50% of the cost of family coverage.
- Three percent of covered workers in small firms and 1% of covered workers in large firms contribute more than 50% of the premium for single coverage 18. For family coverage, 34% of covered workers in small firms work in a firm where they must contribute more than 50% of the premium, compared to seven percent of covered workers in large firms 19.
- There is considerable variation around the distribution of the average dollar contribution amounts. Note that we changed our methods beginning in 2016: previously, the percentages were calculated excluding workers who do not make a premium contribution; now all covered workers are included (with a zero dollar contribution value for those workers where the employer pays 100% of the premium).
- For single coverage, 34% of covered workers contribute $1,355 or more annually (120% or more of the average worker contribution), while 41% of covered workers have an annual worker contribution of less than $903 (less than 80% of the average worker contribution) 16.
- For family coverage, 27% of covered workers contribute $6,332 or more annually (120% or more of the average worker contribution), while 41% of covered workers have an annual worker contribution of less than $4,222 (less than 80% of the average worker contribution) 16.
Differences by Firm Characteristics
- The percentage of the premium paid by covered workers varies by several firm characteristics.
- Covered workers in firms with a larger share of lower-wage workers (35% or more earn $23,000 or less annually) contribute a greater percentage of the premium for single coverage (23% v. 18%) and family coverage (35% vs. 30%) than those in firms with a smaller share of lower-wage workers 21 and 22. Covered workers in firms with a larger share of higher-wage workers (35% or more earn $59,000 or more a year) contribute less on average for family coverage (27% vs. 33%) than those in firms with a smaller share of higher-wage workers.
- Looking at dollar amounts, covered workers in firms with a larger share of lower-wage workers (35% or more earn $23,000 or less annually) on average contribute $1,322 for single coverage compared with $1,115 for covered workers in firms with a smaller share of lower-wage workers 15.
- Covered workers in large firms that have at least some union workers have lower average contribution percentages for family coverage than those in firms without any unionized workers (22% vs. 29%). Covered workers at firms with some union workers have a lower average contribution amount for family coverage ($4,264 vs. $5,800) 15 and 22.
- Covered workers in large firms that are partially or completely self-funded have a lower average percentage contribution for family coverage than workers in large firms that are fully insured (25% vs. 30%) 22.18
- Covered workers in public organizations have lower average premium contributions for single and family coverage than workers in private for-profit firms 21 and 22.
Contribution approaches
- Firms take different approaches for contributing towards family coverage. Among firms offering health benefits, 45% of small firms and 18% of large firms contribute the same dollar amount for single coverage as for family coverage, which means that the worker must pay the entire difference between the cost of single and family coverage if they wish to enroll their family members. Forty-five percent of small firms and 67% of large firms make a larger dollar contribution for family coverage than for single coverage 26.
- Among firms offering health benefits, 15% require workers who use tobacco to contribute more towards the premium or cost-sharing than those who do not use tobacco 28.
Changes over Time
- The average worker contributions for single and family coverage have increased 80% and 78%, respectively, over the last 10 years, and 23% and 28%, respectively, over the last five years.
- The average premium contributions for covered workers with single and family coverage have grown at similar rates in small firms and large firms 8 and 9.
Section Seven: Employee Cost Sharing
In addition to any required premium contributions, most covered workers face cost sharing for the medical services they use. Cost sharing for medical services can take a variety of forms, including deductibles (an amount that must be paid before most services are covered by the plan), copayments (fixed dollar amounts), and/or coinsurance (a percentage of the charge for services). The type and level of cost sharing often vary by the type of plan in which the worker is enrolled. Cost sharing may also vary by the type of service, such as office visits, hospitalizations, or prescription drugs.
The cost-sharing amounts reported here are for covered workers using services provided in-network by participating providers. Plan enrollees receiving services from providers that do not participate in plan networks often face higher cost sharing and may be responsible for charges that exceed plan allowable amounts. The framework of this survey does not allow us to capture all of the complex cost-sharing requirements in modern plans, particularly for ancillary services (such as durable medical equipment or physical therapy) or cost-sharing arrangements that vary across different settings (such as tiered networks). Therefore, we do not collect information on all plan provisions and limits that affect enrollee out-of-pocket liability.
General Annual Deductibles For Workers in Plans with Deductibles
- A general annual deductible is an amount that must be paid by enrollees before most services are covered by their health plan. Non-grandfathered health plans are required to cover some services such as preventive care without cost sharing. Some plans require enrollees to meet a service-specific deductible such as on prescription drugs or hospital admissions in lieu of or in addition to a general deductible.
- Eighty-three percent of covered workers are enrolled in a plan with a general annual deductible for single coverage, similar to 81% in 2015. Since 2011, the percentage of covered workers with a general annual deductible for single coverage has increased from 74% to 83% 2.
- The percentage of covered workers enrolled in a plan with a general annual deductible for single coverage is similar for small firms (3-199 workers) and large firms (200 0r more workers) (82% and 83%) 1.
- The likelihood of having a deductible varies by plan type. Covered workers in HMOs are less likely to have a general annual deductible for single coverage than workers in other plan types. Fifty-four percent of workers in HMOs do not have a general annual deductible for single coverage, compared to 24% of workers in POS plans and 16% of workers in PPOs 1. The percentage of covered workers in HMO plans with a general annual deductible for single coverage has increased from 29% in 2011 to 46% in 2016 2.
- Covered workers in plans without a general annual deductible often have other forms of cost sharing when they are hospitalized or use other medical services. For covered workers in plans without a general annual deductible with single coverage, 82% in HMOs, 64% in PPOs, and 78% in POS plans are in plans that require some cost sharing for hospital admissions. The percentages are similar for family coverage 4.
- For covered workers in a plan with a general annual deductible, the average annual deductible for single coverage is $1,478, an increase over the average deductible ($1,318) last year 7.
- Average deductibles vary considerably by plan type. For covered workers in plans with a general annual deductible, the average deductibles for single coverage are $917 in HMOs, $1,028 in PPOs, $1,737 in POS plans, and $2,199 for HDHP/SOs 5.
- Deductibles for single coverage are generally higher for covered workers in small firms than for covered workers in large firms across plan types. For example, for covered workers in PPOs with a general annual deductible, the average deductible amount for single coverage in small firms is more than twice as large as the average deductible amount in large firms ($1,662 vs. $814). Overall, for covered workers in plans with a general annual deductible, the average deductible amount for single coverage in small firms is higher than the average deductible amount in large firms ($2,069 vs. $1,238) 5.
- The average general annual deductible for single coverage for covered workers in plans with a deductible has increased 49% over the last five years, from $991 in 2011 to $1,478 in 2016 7.
- There is considerable variation in the dollar values of general annual deductibles for covered workers at different firms. For example, 25% of covered workers enrolled in a PPO plan with a general annual deductible for single coverage have a deductible of less than $500 while 14% have a deductible of $2,000 or more 16.
- For family coverage, the majority of covered workers with general annual deductibles have an aggregate deductible, meaning all family members’ out-of-pocket expenses count toward meeting the deductible amount. Among those with a general annual deductible for family coverage, the percentages of covered workers with an average aggregate general annual deductible are 61% for workers in HMOs, 64% for workers in PPOs, and 77% for workers in POS plans 18.
- The average deductible amounts for covered workers with an aggregate deductible for family coverage are $2,245 for HMOs, $2,147 for PPOs, $3,769 for POS plans, and $4,343 for HDHP/SOs 19. Deductible amounts for aggregate family deductibles are similar to last year for plan types other than POS plans 20.
- The other type of family deductible, a separate per-person deductible, requires each family member to meet a separate per-person deductible amount before the plan covers expenses for that member. Many plans with separate per-person family deductibles (71%) consider the deductible met for all family members if a prescribed number of family members each reaches his or her separate deductible amounts 23. Plans may also require each family member to meet a separate per-person deductible until the family’s combined spending reaches a specified dollar amount.
- For covered workers in health plans that have separate per-person general annual deductible amounts for family coverage, the average deductibles are $632 for HMOs, $1,052 for PPOs, $1,180 for POS plans, and $2,411 for HDHP/SOs 19.
- Most covered workers in plans with a separate per-person general annual deductible for family coverage have a limit to the number of family members required to meet the separate deductible amounts 23.19 Among those covered workers in plans with a limit on the number of family members, the most frequent number of family members required to meet the separate deductible amounts is two (45%) 24.
- The majority of covered workers with a general annual deductible are in plans where the deductible does not have to be met before certain services, such as physician office visits or prescription drugs, are covered.
- Large majorities of covered workers (87% in HMOs, 72% in PPOs, and 60% in POS plans) with general annual deductibles are enrolled in plans where the deductible does not have to be met before physician office visits for primary care are covered 26.
- Similarly, among workers with a general annual deductible, large shares of covered workers in HMOs (93%), PPOs (91%), and POS plans (89%) are enrolled in plans where the general annual deductible does not have to be met before prescription drugs are covered 26.
General Annual Deductibles Among All Covered Workers
- As discussed above, the share of covered workers in plans with a general annual deductible has increased significantly over time: from 55% in 2006, to 74% in 2011, to 83% in 2016, as have the average deductible amounts for covered workers in plans with deductibles: from $584 in 2006, to $991 in 2011, to $1,478 in 2016. Neither trend by itself captures the full impact of changes in deductibles on covered workers. We can look at the average impact of both trends together on covered workers by assigning a zero deductible value to covered workers in plans with no deductible and looking at how the resulting averages change over time. These average deductible amounts are lower in any given year but the changes over time reflect both the higher deductibles in plans with deductibles and the fact that more workers face them.
- Using this approach, the average general annual deductible for single coverage for all covered workers in 2016 is $1,221 9.
- The 2016 value is 63% higher than the average general annual deductible of $747 in 2011 and 300% higher than the average general annual deductible of $303 in 2006 9.
- Another way to look at deductibles is the percentage of all covered workers who are in a plan with a deductible that exceeds certain thresholds. Fifty-one percent of covered workers are in plans with a general annual deductible of $1,000 or more for single coverage, similar to the percentage in 2015 (46%) 10.
- Over the last five years, the percentage of covered workers with a general annual deductible of $1,000 or more for single coverage has grown substantially, increasing from 31% to 51% 10.
- Workers in small firms are more likely to have a general annual deductible of $1,000 or more for single coverage than workers in large firms (65%vs. 45%) 8.
- Twenty-three percent of covered workers are enrolled in a plan with a deductible of $2,000 or more, similar to the percentage last year (19%) 12. Forty-one percent of covered workers at small firms have a general annual deductible of $2,000 or more, in contrast to 16% in large firms 8.
- One of the reasons for the growth in deductible amounts has been the growth in enrollment in HDHP/SOs, which have higher deductibles than other plans. While growing deductibles in PPOs and other plan types generally increases enrollee out-of-pocket liability, the shift in enrollment to HDHP/SOs does not necessarily do so because most HDHP/SO enrollees receive an account contribution from their employers, which in essence reduces the high cost sharing in these plans.
- Fourteen percent of covered workers in an HDHP with an HRA and 7% of covered workers in an HSA-qualified HDHP receive an account contribution for single coverage at least equal to their deductible, while another 47% of covered workers in an HDHP with an HRA and 28% of covered workers in an HSA-qualified HDHP receive account contributions that, if applied to their deductible, would reduce the deductible to $1,000 or less 14.
- If we reduce the deductibles that workers face by employer account contributions, the percentage of covered workers with a deductible liability of $1,000 or more would be reduced from 51% to 38% 11.
Hospital and Outpatient Surgery Cost Sharing
- Whether or not a worker has a general annual deductible, most workers face additional types of cost sharing (such as a copayment, coinsurance, or a per diem charge) when admitted to a hospital or having outpatient surgery. The distribution of workers with cost sharing for hospital and outpatient surgery does not equal 100% as workers may face a combination of types of cost sharing. In addition, the average copayment and coinsurance rates for hospital admissions include workers who may have a combination of these types of cost sharing.
- For hospital admissions, 64% of covered workers have coinsurance and 14% have copayments. Lower percentages of workers have per day (per diem) payments (6%), a separate hospital deductible (1%), or both copayments and coinsurance (10%), while 16% have no additional cost sharing for hospital admissions after any general annual deductible has been met. For covered workers in HMO plans, copayments are more common (46%) and coinsurance (24%) is less common than in other plan types. Only 2% of covered workers in HDHP/SOs have a copayment for hospital admissions, lower than other plan types 27.
- The percentage of covered workers in a plan that requires coinsurance for hospital admissions has increased from 55% in 2011 to 64% in 2015.
- The average coinsurance rate for hospital admission is 19%; the average copayment is $282 per hospital admission; the average per diem charge is $281; and the average separate annual hospital deductible is $898 29.
- The cost-sharing provisions for outpatient surgery are similar to those for hospital admissions, as most workers have coinsurance or copayments. Sixty-six percent of covered workers have coinsurance and 17% have copayments for an outpatient surgery episode. In addition, 1% has a separate annual deductible for outpatient surgery, and 4% have both copayments and coinsurance, while 17% have no additional cost sharing after any general annual deductible has been met 28.
- For covered workers with cost sharing for outpatient surgery, the average coinsurance rate is 19% and the average copayment is $170 29.
Cost Sharing for Physician Office Visits
- The majority of covered workers are enrolled in health plans that require cost sharing for an in-network physician office visit, in addition to any general annual deductible20 .
- The most common form of physician office visit cost sharing for in-network services is copayments. Sixty-seven percent of covered workers have a copayment for a primary care physician office visit and 25% have coinsurance. For office visits with a specialty physician, 66% of covered workers have copayments and 26% have coinsurance. Workers in HMOs, PPOs, and POS plans are much more likely to have copayments than workers in HDHP/SOs for both primary care and specialty care physician office visits. For primary care physician office visits, 64% of covered workers in HDHP/SOs have coinsurance, 18% have no cost sharing after the general annual plan deductible is met, and 16% have copayments 30.
- Among covered workers with a copayment for in-network physician office visits, the average copayment is $24 for primary care and $38 for specialty physician office visits 31, similar to the amounts last year 31.
- Among workers with coinsurance for in-network physician office visits, the average coinsurance rates are 18% for a visit with a primary care physician and 19% for a visit with a specialist 31, the same rates as last year.
Out-Of-Pocket Maximum Amounts
- Most covered workers are in a plan that partially or totally limits the cost sharing that a plan enrollee must pay in a year. These limits are generally referred to as out-of-pocket maximum amounts. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires that non-grandfathered health plans have an out-of-pocket maximum of $6,850 or less for single coverage and $13,700 for family coverage.21 Many plans have complex out-of-pocket structures, which makes it difficult to accurately collect information on this element of plan design.
- In 2016, 98% percent of covered workers are in a plan with an out-of-pocket maximum for single coverage. This is a significant increase from 83% in 2011.
- For covered workers in plans with out-of-pocket maximums for single coverage, there is wide variation in spending limits.
- Fourteen percent of covered workers in plans with an out-of-pocket maximum for single coverage have an out-of-pocket maximum of less than $2,000, while 18% have an out-of-pocket maximum of $6,000 or more 36.
Section Eight: High-deductible Health Plans With Savings Option
To help cover out-of-pocket expenses not covered by a health plan, some employers offer high deductible plans that are paired with an account that allows enrollees to use tax-preferred savings to pay plan cost sharing and other out-of-pocket medical expenses. The two most common are health reimbursement arrangements (HRAs) and health savings accounts (HSAs). HRAs and HSAs are financial accounts that workers or their family members can use to pay for health care services. These savings arrangements are often (or, in the case of HSAs, always) paired with health plans with high deductibles. The survey treats high-deductible plans paired with a savings option as a distinct plan type – High-Deductible Health Plan with Savings Option (HDHP/SO) – even if the plan would otherwise be considered a PPO, HMO, POS plan, or conventional health plan. Specifically for the survey, HDHP/SOs are defined as (1) health plans with a deductible of at least $1,000 for single coverage and $2,000 for family coverage22 offered with an HRA (referred to as HDHP/HRAs); or (2) high-deductible health plans that meet the federal legal requirements to permit an enrollee to establish and contribute to an HSA (referred to as HSA-qualified HDHPs).23
Percentage of Firms Offering HDHP/HRAs and HSA-Qualified HDHPs, and Enrollment
- Twenty-eight percent of firms offering health benefits offer an HDHP/HRA, an HSA-qualified HDHP, or both. Among firms offering health benefits, 5% offer an HDHP/HRA and 24% offer an HSA-qualified HDHP 1. The percentage of firms offering an HDHP/SO is similar to last year but has increased since 2006 (7%).
- Large firms (200 or more workers) are more likely than small firms (3-199 workers) to offer an HDHP/SO (51% vs. 27%). 2.
Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) are medical care reimbursement plans established by employers that can be used by employees to pay for health care. HRAs are funded solely by employers. Employers may commit to make a specified amount of money available in the HRA for premiums and medical expenses incurred by employees or their dependents. HRAs are accounting devices, and employers are not required to expend funds until an employee incurs expenses that would be covered by the HRA. Unspent funds in the HRA usually can be carried over to the next year (sometimes with a limit). Employees cannot take their HRA balances with them if they leave their job, although an employer can choose to make the remaining balance available to former employees to pay for health care.
HRAs often are offered along with a high-deductible health plan (HDHP). In such cases, the employee pays for health care first from his or her HRA and then out-of-pocket until the health plan deductible is met. Sometimes certain preventive services or other services such as prescription drugs are paid for by the plan before the employee meets the deductible.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) are savings accounts created by individuals to pay for health care. An individual may establish an HSA if he or she is covered by a “qualified health plan” –a plan with a high deductible (i.e., a deductible of at least $1,300 for single coverage and $2,600 for family coverage in 2016) that also meets other requirements.[1] Employers can encourage their employees to create HSAs by offering an HDHP that meets the federal requirements. Employers in some cases also may assist their employees by identifying HSA options, facilitating applications, or negotiating favorable fees from HSA vendors.
Both employers and employees can contribute to an HSA, up to the statutory cap of $3,350 for single coverage and $6,750 for family coverage in 2016. Employee contributions to the HSA are made on a pre-income tax basis, and some employers arrange for their employees to fund their HSAs through payroll deductions. Employers are not required to contribute to HSAs established by their employees but if they elect to do so, their contributions are not taxable to the employee. Interest and other earnings on amounts in an HSA are not taxable. Withdrawals from the HSA by the account owner to pay for qualified health care expenses are not taxed. The savings account is owned by the individual who creates the account, so employees retain their HSA balances if they leave their job.
1 See U.S. Department of the Treasury, Health Savings Accounts, available at http://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-drop/rp-14-30.pdf
- Enrollment in HDHP/SO plans has increased over time from 17% of covered workers in 2011 to 29% in 2016.
- Nine percent of covered workers are enrolled in HDHP/HRAs in 2016, similar to last year (9%). The percentage of covered workers enrolled in HSA-qualified HDHPs increased from 15% in 2015 to 19% in 2016 5.
- A similar percentage of covered workers at small firms (3-199 workers) and large firms are enrolled in HDHP/SOs 5
Plan Deductibles
- As expected, workers enrolled in HDHP/SOs have higher deductibles than workers enrolled in HMOs, PPOs, or POS plans.
- The average general annual deductible for single coverage is $2,031 for HDHP/HRAs and $2,295 for HSA-qualified HDHPs 7. These averages are similar to the amounts reported in recent years. There is wide variation around these averages: 17% of covered workers enrolled in an HDHP/SO are in a plan with a deductible of $1,000 to $1,499 while 21% are in a plan with a deductible of $3,000 or more 9.
- The survey asks employers whether the family deductible amount is (1) an aggregate amount (i.e., the out-of-pocket expenses of all family members are counted until the deductible is satisfied), or (2) a per-person amount that applies to each family member (typically with a limit on the number of family members that would be required to meet the deductible amount) (for more information see Section 7).
- The average aggregate deductibles for workers with family coverage are $4,321 for HDHP/HRAs and $4,364 for HSA-qualified HDHPs 7. As with single coverage, there is wide variation around these averages for family coverage: 15% of covered workers enrolled in HDHP/SOs with an aggregate family deductible have a deductible of $2,000 to $2,999 while 19% have a deductible of $6,000 dollars or more 11.
Out-of-Pocket Maximum Amounts
- HSA-qualified HDHPs are legally required to have a maximum annual out-of-pocket liability of no more than $6,550 for single coverage and $13,100 for family coverage in 2016. Non-grandfathered HDHP/HRA plans starting in 2016 are required to have out-of-pocket maximums of no more than $6,850 for single coverage and $13,700 for family coverage. Virtually all HDHP/HRA plans have an out of pocket maximum for single coverage in 2016.
- The average annual out-of-pocket maximum for single coverage is $4,264 for HDHP/HRAs and $4,083 for HSA-qualified HDHPs 7.
Premiums
- The average annual premiums in 2016 for covered workers in HDHP/HRAs are $5,860 for single coverage and $17,734 for family coverage. The average single premium for covered workers in HDHP/HRAs is lower than the average single premium for covered workers in non-HDHP/SO plans 8.
- The average annual premium for workers in HSA-qualified HDHPs is $5,719 for single coverage and $16,246 for family coverage. These amounts are significantly less than the average single and family premium for covered workers in plans that are not HDHP/SOs 8.
- The average single and family coverage premiums for HSA-qualified HDHPs are similar to the premiums for covered workers enrolled in HDHP/HRAs.
Worker Contributions to Premiums
- The average annual worker contributions to premiums for workers enrolled in HDHP/HRAs are $1,143 for single coverage and $5,105 for family coverage 8.
- The average annual worker contributions to premiums for workers in HSA-qualified HDHPs are $849 for single coverage and $3,930 for family coverage. The average contributions for single and family coverage for covered workers in HSA-qualified HDHPs are significantly less than the average premium contribution made by covered workers in plans that are not HDHP/SOs 8.
Employer Contributions to Premiums and Savings Options
- Employers contribute to HDHP/SOs in two ways: through their contributions toward the premium for the health plan and through their contributions (if any, in the case of HSAs) to the savings account option (i.e., the HRAs or HSAs themselves).
- Looking at only the annual employer contributions to premiums, covered workers in HDHP/HRAs on average receive employer contributions of $4,717 for single coverage and $12,628 for family coverage. The average employer contribution for covered workers in HDHP/HRAs for single coverage is lower than the average contribution for covered workers in plans that are not HDHP/SOs 8.
- The average annual employer contributions to premiums for workers in HSA-qualified HDHPs are $4,870 for single coverage and $12,316 for family coverage. The average employer contribution for covered workers in HSA qualified HDHPs for single coverage is lower than the average contribution for covered workers in plans that are not HDHP/SOs 8.
- When looking at employer contributions to the savings option, covered workers enrolled in HDHP/HRAs on average receive an annual employer contribution to their HRA of $1,059 for single coverage and $1,867 for family coverage 8.
- HRAs are generally structured in such a way that employers may not actually spend the whole amount that they make available to their employees’ HRAs.24 Amounts committed to an employee’s HRA that are not used by the employee generally roll over and can be used in future years, but any balance may revert back to the employer if the employee leaves his or her job. Thus, the employer contribution amounts to HRAs that we capture in the survey may exceed the amount that employers will actually spend.
- Covered workers enrolled in HSA-qualified HDHPs on average receive an annual employer contribution to their HSA of $686 for single coverage and $1,208 for family coverage 8. These amounts do not include the 1% of covered workers in HSA-qualified HDHPs whose employers say they vary account contributions based on certain factors, such as participation in a wellness program or job classification.
- In many cases, employers that sponsor HSA-qualified HDHP/SOs do not make contributions to HSAs established by their employees. Fifty-two percent of employers offering single coverage and 55% offering family coverage through HSA-qualified HDHPs do not make contributions towards the HSAs that their workers establish. Twenty-five percent of workers with single coverage and 25% percent of workers with family coverage in an HSA-qualified HDHP do not receive an account contribution from their employer (see notes in 14 and 15.
- The average HSA contributions reported above include the portion of covered workers whose employer contribution to the HSA is zero. When those firms that do not contribute to the HSA are excluded from the calculation, the average employer contribution for covered workers is $916 for single coverage and $1,617 for family coverage.
- The percentage of covered workers enrolled in a plan where the employer makes no HSA contribution for single coverage (25%) is similar to the percentage in recent years.
- Employer contributions to savings account options (i.e., the HRAs and HSAs themselves) for their employees can be added to their health plan premium contributions to calculate total employer contributions toward HDHP/SOs.–We note that HRAs are a promise by an employer to pay up to a specified amount and that many employees will not receive the full amount of their HRA in a year, so adding the employer premium contribution amount and the HRA contribution represents an upper bound for employer liability that overstates the amount that is actually expended. Since employer contributions to employee HSA accounts immediately transfer the full amount to the employee, adding employer premium and HSA contributions is a good way to look at their total liability under these plans.
- For HDHP/HRAs, the average annual total employer contribution for covered workers is $5,776 for single coverage and $14,495 for family coverage. The average total employer contribution amounts for covered workers for family coverage in HDHP/HRAs are higher than the average amount that employers contribute towards family coverage in health plans that are not HDHP/SOs 8.
- For HSA-qualified HDHPs, the average total annual firm contribution for covered workers is $5,561 for single coverage and $13,528 for workers with family coverage. The average total firm contribution amounts for single and family coverage in HSA-qualified HDHPs are similar to the average firm contributions towards single and family coverage in health plans that are not HDHP/SOs 8.
Variation in Employer Contributions to Savings Options
- There is considerable variation in the amount that employers contribute to savings accounts.
- Looking at how contributions vary around the average, 30% of covered workers in HDHP/HRAs have an HRA contribution for single coverage of less than $635 (60% of the average), while 21% have an account contribution of $1,482 (140% of the average) or more 16.
- Thirty-eight percent of covered workers in HSA-qualified HDHPs have an annual HSA contribution for single coverage of less than $411 (60% of the average) while 29% have an account contribution of $960 (140% of the average) or more 17.
Cost Sharing for Office Visits, Outpatient Surgery and Hospital Surgery
- The cost-sharing pattern for primary care office visits differs for workers enrolled in HDHP/SOs. Thirty-three percent of covered workers in HDHP/HRAs have a copayment for primary care physician office visits compared to 8% enrolled in an HSA-qualified HDHP 19. Workers in other plan types are much more likely to face copayments than coinsurance for physician office visits (see Section 7 for more information).
Section Nine: Prescription Drug Benefits
Almost all covered workers have coverage for prescription drugs. For 2016, to reduce burden on respondents, we revised the survey to ask respondents about the attributes of prescription drug coverage only in their largest health plan; previously, we asked about prescription coverage in their largest plan for each of the plan types that they offered. In addition, we began asking employers about their cost sharing for tiers that cover specialty drugs exclusively. In cases in which a tier covers only specialty drugs, we report the plan attributes under the specialty banner, rather than as one of the four standard tiers. Therefore, the number of tiers a firm reports may not correspond with the number of tiers for which we have cost-sharing information. For more information, see the survey design and methods section. While this new approach produces estimates that are quite similar to those obtained by the prior method, we do not do statistical comparisons with 2016 estimates and those from prior years.25
- Nearly all (more than 99%) covered workers work at a firm that provides prescription drug coverage in their largest health plan.
- A large share of covered workers (89%) work at a firm whose largest health plan has a tiered cost-sharing formula for prescription drugs 1. Cost-sharing tiers generally refer to a health plan placing a drug on a formulary or preferred drug list that classifies drugs into categories that are subject to different cost sharing or management. It is common for there to be different tiers for generic, preferred and non-preferred drugs. In recent years, plans have created additional tiers which, for example, may be used for lifestyle drugs or expensive biologics. Some plans may have multiple tiers for different categories; for example, a plan may have preferred and non-preferred specialty tiers. The survey obtains information about the cost-sharing structure for up to five tiers.
- Eighty-four percent of covered workers work at a firm that has three, four, or more tiers of cost sharing for prescription drugs in their largest health plan 1.
- Covered workers at large firms (200 or more workers) whose largest health plan is an HDHP/SO have a different cost-sharing pattern for prescription drugs than covered workers with other plan types: they are more likely to be in a plan with the same cost sharing regardless of drug type (17% vs. 3%) or in a plan that has no cost sharing for prescriptions once the plan deductible is met (8% vs. <1%) 2.
Three or More Tiers
- Thirty-two percent of covered workers work at a firm whose largest health plan has four or more tiers of cost sharing for prescription drugs 1.
- For covered workers at firms whose largest plan has three or more tiers of cost sharing for prescription drugs, copayments are the most common form of cost sharing in the first three tiers and coinsurance is the next most common. Among those with a fourth tier, 46% have a coinsurance requirement and 41% have a copayment (difference not significant) 3.
- Among covered workers at firms whose largest health plan has three or more tiers of cost sharing for prescription drugs, the average copayments are $11 for first-tier drugs, $33 second-tier drugs, $57 third-tier drugs, and $102 for fourth-tier drugs 4.
- Among covered workers at firms whose largest health plan has three or more tiers of cost sharing for prescription drugs, the average coinsurance rates are 17% for first-tier drugs, 25% second-tier drugs, 37% third-tier drugs, and 29% for fourth-tier drugs 4.
Single and Two Tiers
- Five percent of covered workers work at firms whose largest health plan has two tiers for prescription drug cost sharing 1. For these workers, copayments are more common than coinsurance for both first-tier and second-tier drugs. The average copayment for the first tier is $12 and the average copayment for the second tier is $29 7.
- Seven percent of covered workers at firms whose largest health plan covers prescription drugs have the same cost sharing regardless of the type of drug 1.
- Among these workers, 19% have copayments and 81% have coinsurance 8. The average coinsurance rate is 22% and the average copayment is $12 9.
- Thirteen percent of these workers are at firms whose largest health plan limits coverage for prescriptions to generic drugs 10.
Limits on Coinsurance
- Coinsurance rates for prescription drugs often have maximum and/or minimum dollar amounts associated with the coinsurance rate. Depending on the plan design, coinsurance maximums may significantly limit an enrollee’s out-of-pocket spending on higher cost drugs.
- These coinsurance minimum and maximum amounts vary across the tiers. Among covered workers at firms whose largest health plan has coinsurance for the first cost-sharing tier, 20% have only a maximum dollar amount attached to the coinsurance rate, 4% have only a minimum dollar amount, 26% have both, and 50% have neither. For those with coinsurance for the fourth cost-sharing tier, 76% have a maximum dollar amount, 3% have a minimum dollar amount, and 21% have neither 12.
Specialty drugs
- Specialty drugs such as biologics may be used to treat chronic conditions and often require special handling and administration. We revised the questions in the 2016 survey regarding specialty drugs, and are reporting results only among large firms because a large share of small firms were unsure whether their largest plan covered these drugs.
- Ninety-eight percent of covered workers at large firms work for employers whose largest health plan provides coverage for specialty drugs 13. Among these workers, 43% work at firms whose largest plan has a cost-sharing tier just for specialty drugs 14.
- Among covered workers at large firms whose largest plan has a separate tier for specialty drugs, 43% have a copayment for specialty drugs and 46% have a coinsurance requirement 15. The average copayment is $89 and the average coinsurance rate is 26% 16. Seventy-eight percent of those with a coinsurance requirement have a maximum dollar limit on the amount of coinsurance they must pay.
- Specialty drugs are typically high cost; firms use a variety of strategies to contain these costs. Among covered workers at large firms whose largest health plan provides coverage for specialty drugs, 38% use a different pharmacy benefit manager for specialty drugs; 28% have a dispensing program with incentives to encourage enrollees to receive specialty drugs in an alternative setting; 68% use a step therapy approach where enrollees must try alternatives before specialty drugs are covered; 61% use tight limits on the number of units administered at a single time; 70% use utilization management programs to review discharges, care settings and effectiveness; 82% require prior authorization; and 89% have a mail order option for specialty drugs 17.26
Generic drugs: Drugs product that are no longer covered by patent protection and thus may be produced and/or distributed by multiple drug companies.
Preferred drugs: Drugs included on a formulary or preferred drug list; for example, a brand-name drug without a generic substitute.
Non-preferred drugs: Drugs not included on a formulary or preferred drug list; for example, a brand-name drug with a generic substitute.
Fourth-tier drugs: New types of cost-sharing arrangements that typically build additional layers of higher copayments or coinsurance for specifically identified types of drugs, such as lifestyle drugs or biologics.
Brand-name drugs: Generally, a drug product that is covered by a patent and is thus manufactured and sold exclusively by one firm. Cross-licensing occasionally occurs, allowing an additional firm to market the drug. After the patent expires, multiple firms can produce the drug product, but the brand name or trademark remains with the original manufacturer’s product.
Section Ten: Plan Funding
Federal law (the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, or ERISA) exempts self-funded plans from most state insurance laws, including reserve requirements, mandated benefits, premium taxes, and consumer protection regulations. Sixty-one percent of covered workers are in a self-funded health plan. Self-funding is common among larger firms because they can spread the risk of costly claims over a large number of employees and dependents. Many self-funded plans use insurance, often called stoploss coverage, to limit the plan sponsor’s liability for very large claims or an unexpected level of expenses. Nearly three in five covered workers in fully or partially self-funded plans are in plans with stoploss protection.
Self-Funded Plan: An insurance arrangement in which the employer assumes direct financial responsibility for the costs of enrollees’ medical claims. Employers sponsoring self-funded plans typically contract with a third-party administrator or insurer to provide administrative services for the self-funded plan. In some cases, the employer may buy stoploss coverage from an insurer to protect the employer against very large claims.
Fully Insured Plan: An insurance arrangement in which the employer contracts with a health plan that assumes financial responsibility for the costs of enrollees’ medical claims.
- Sixty-one percent of covered workers are in a plan that is completely or partially self-funded, similar to last year. The percentage of covered workers who are in a self-funded plan has increased over time from 49% in 2000 and 54% in 2005. In recent years, the percentage of covered workers enrolled in a self-funded plan has remained steady: 60% of covered workers were in such an arrangement in 2011; similar to 61% in 2016 1.
- The percentage of covered workers enrolled in self-funded plans has been stable in recent years in both small firms (3-199 workers) and large firms (200 or more workers) 2.
- The percentage of covered workers in self-funded plans differs by plan type: 69% of covered workers in PPOs, 67% in HDHP/SOs, 37% in HMOs, and 24% in POS plans are in a self-funded plan 3.
- As expected, covered workers in large firms are significantly more likely to be in a self-funded plan than covered workers in small firms (82% vs. 13%). The percentage of covered workers in self-funded plans increases as the number of employees in a firm increases. Eighty-three percent of covered workers in firms with 1,000 to 4,999 workers and 94% of covered workers in firms with 5,000 or more workers are in self-funded plans in 2016 4.
Stoploss Coverage and Attachment Points
- Fifty-seven percent of workers in self-funded health plans are in plans that have stoploss insurance 10. Stoploss coverage may limit the amount of claims that must be paid for each employee or may limit the total amount the plan sponsor must pay for all claims over the plan year.
- The percentage of workers in self-funded health plans with stoploss insurance is unchanged from 2011, when the survey first asked about stoploss insurance (58% in 2011 and 57% in 2016).
- Ninety-one percent of covered workers in self-funded plans that have stoploss protection are in plans where the stoploss insurance limits the amount that the plan must spend on each employee 11. This includes stoploss insurance plans that limit a firm’s per-employee spending and plans that limit both a firm’s overall spending and per-employee spending.
- Firms with per-enrollee stoploss coverage were asked for the dollar amount where the stoploss coverage would start to pay for most or all of the claim (called an attachment point). The average attachment point in small firms is $160,000. For large firms with a per-person limit, the average attachment point is $330,000 11.
- Among firms that purchase insurance underwritten by an insurer, 1% plan to self-insure because of ACA provisions 14.
Section Eleven: Retiree Health Benefits
Retiree health benefits are an important consideration for older workers making decisions about their retirement. Health benefits for retirees provide an important supplement to Medicare for retirees age 65 or older. Over time, the percentage of firms offering retiree coverage has decreased.
- Twenty-four percent of large firms (200 or more workers) that offer health benefits to their employees offer retiree coverage in 2016, similar to recent years. There has been a downward trend in the percentage of firms offering retirees coverage, from 34% in 2006 and 40% in 1999 1.
- The offering of retiree health benefits varies considerably by firm characteristics.
- Among large firms offering health benefits, the likelihood that a firm will offer retiree health benefits increases with size: from 21% of firms with 200-999 workers, to 36% of firms with 1,000-4,999 workers, to 46% of firms with 5,000 or more workers 2.
- The share of large firms offering retiree health benefits varies considerably by industry. State and local governments (72%), firms in transportation/utilities/communication (55%) and firms in finance (46%) have particularly high rates of offer while retail firms (2%) have a particularly low rate 2.
- Among large firms offering health benefits, those with a larger share of older workers (35% or more of workers are age 50 or older) are more likely to offer retiree health benefits than large firms with a smaller share of older workers (32% vs. 18%) 3.
- Among large firms offering health benefits, those with a larger share of higher-wage workers (35% or more earn at least $59,000 per year) are more likely to offer retiree health benefits than those with a smaller share of higher-wage workers (30% vs. 20%) 3.
- Among large firms offering health benefits, the share of public firms offering retiree benefits (58%) is higher than the shares of private for-profit firms (14%) or private not-for-profit firms (21%) offering retiree benefits 3.
- Large firms with at least some union workers are more likely to offer retiree health benefits than large firms without any union workers (43% vs. 17%) 3.
- Among all large firms offering retiree health benefits, most firms offer to early retirees under the age of 65 (92%). A lower percentage (72%) of large firms offering retiree health benefits offer to Medicare-age retirees. These percentages are similar to those in recent years 4.
- Among all large firms offering retiree health benefits, 64% offer health benefits to both early and Medicare-age retirees.
Private Exchanges and Public Exchanges
- Private exchanges have received considerable attention over the last several years. They are typically created by a consulting company, broker, or insurer, and are different than the public exchanges created under the Affordable Care Act (ACA). Private exchanges allow employees or retirees to choose from several health benefit options offered on the exchange. Six percent of large firms (200 or more workers) offering retiree health benefits report they offer benefits through a private exchange, similar to the percentage last year (7%) 7. For more information on the use of private exchanges for active employees, please see section 14.
- Since 2014, households with an income between 100% and 400% of the federal poverty level and without an offer of employer coverage may be eligible for subsidized health insurance on federal and state exchanges. Some current retirees may be eligible for premium tax credits for coverage provided through these marketplaces.
- Seventeen percent of large firms offering retiree health coverage report they are considering changes in the way they offer retiree health benefits because of the new marketplaces, lower than the percentage last year (26%) 9.
Section Twelve: Health Risk Assessment, Biometrics Screening And Wellness Programs
Employers continue to show considerable interest in programs that help employees identify health issues and manage chronic conditions. Many employers believe that improving the health of their workers and their family members can improve morale, productivity and reduce health care costs.
In addition to offering wellness programs, a majority of large employers now offer health screening programs including health risk assessments, which are questionnaires asking employees about lifestyle, stress or physical health, and biometric screening, which we define as in-person health examinations conducted by a medical professional. Employers and insurers may use the health information collected during screenings to target wellness offerings or other health services to employees with risk conditions or behaviors that pose a risk for their health. Some employers have incentive programs that reward or penalize employees for different activities, including participating in wellness programs or completing health screenings.
In 2015 we revised the survey to better capture employers’ evolving approaches to wellness programs and health screening, including collecting information on employers’ use of incentive programs, so in most cases, statistics reported in 2015 and 2016 are not comparable to previous years’ findings because of these changes. Only firms offering health benefits were asked about their wellness and health promotion programs. Information about incentives is reported only for large firms (200 or more employees) because large shares of small firms (3-199 workers) did not know this information about their programs.
In 2016, of large firms offering health benefits, 59% offer employees the opportunity to complete health risk assessments, 53% offer employees the opportunity to complete biometric screening, and 83% offer employees wellness programs such as programs to help employees stop smoking, programs to help employees lose weight, or other lifestyle and behavioral coaching. Substantial shares of these large firms provide financial incentives for employees to participate in or complete the programs.
Health Risk Assessments
Some firms provide their employees the opportunity to complete a health risk assessment to identify potential health issues. Health risk assessments generally include questions about medical history, health status, and lifestyle.
- Among firms offering health benefits, 32% of small firms and 59% of large firms provide employees the opportunity to complete a health risk assessment 1. Each of these is higher than the corresponding percentage for 2015 (18% for small firms and 50% for large firms) 2.
- Seventy-four percent of firms offering health benefits with 5,000 or more employees provide employees the opportunity to complete a health risk assessment, similar to the percentage last year (72%) 1.
- Some firms offer financial incentives to encourage employees to complete health risk assessments.
- Among large firms that have a health risk assessment, 54% offer an incentive to employees to complete the assessment 4. Some firms offer more than one type of incentive to employees.
- Among large firms offering incentives for employees to complete a health risk assessment, 51% lower premium contributions or reduce cost sharing; 60% offer cash, gift cards, merchandise or contributions to HSAs or HRAs; 44% require completion of a health risk assessment to be eligible for incentives under wellness or health promotion programs; and 5% offer additional paid time off 5.
- Forty-one percent of covered workers in large firms providing the opportunity to complete a health risk assessment complete the assessment, similar to the percentage in 2015 (45%).
- There is considerable variation in the percentage of workers who complete the assessment. Nineteen percent of large firms providing employees the opportunity to complete a health risk assessment report that more than 75% of their employees complete the assessment, while 41% report no more than 25% of employees complete the assessment 3.
Biometric Screening
Biometric screening is a health examination that measures an employee’s risk factors for certain medical issues such as cholesterol, blood pressure, stress, and nutrition. Biometric outcomes may include meeting a target body mass index (BMI) or cholesterol level. As defined by this survey, goals related to smoking are not included.
- Among firms offering health benefits, 20% of small firms and 53% of large firms provide employees the opportunity to complete biometric screenings 7. These percentages are similar to last year (13% and 50%) 8.
- Sixty-two percent of firms offering health benefits with 5,000 or more workers have biometric screening programs 7.
- Firms that provide employees the opportunity to complete biometric screenings may include additional incentives for those employees who do so.
- Among large firms with biometric screening programs, 59% offer an incentive for employees to complete the screening 10. Firms with 5,000 or more employees with biometric screening programs are more likely to have an incentive to complete the screening (70%) than firms in other size categories. Some firms report having more than one type of incentive.
- Among large firms with an incentive for employees to complete biometric screening, 52% lower premium contributions or reduce cost sharing; 56% offer cash, gift cards, merchandise or contributions to HSAs or HRAs; 32% require completion of the screening to be eligible for incentives under wellness or health promotion programs; and 7% offer additional paid time off 11.
- Among large firms with biometric screening programs, 14% have rewards or penalties for workers based on achieving specified biometric outcomes (e.g., meeting target BMI) 10.
- There is considerable variation in the size of the incentives that employers offer for meeting biometric outcomes. Among large firms offering a reward or penalty for meeting biometric outcomes, the maximum reward is valued at a $150 dollars or less for 10% percent of firms and $1,000 or more for 21% of firms 13. Twenty-two percent of these firms combine the reward with incentives for other programs.
Wellness and Health Promotion Programs
Many employers and health plans offer programs to help employees engage in healthy lifestyles and reduce health risks. Wellness and health promotion programs may include exercise programs, health education classes, and stress-management counseling. These programs may be offered directly by the firm, an insurer, or a third-party contractor.
- Among firms offering health benefits, 37% of small firms and 74% of large firms offer programs to help employees stop smoking, 33% of small firms and 68% of large firms offer programs to help employees lose weight, and 36% of small firms and 73% of large firms offer some other lifestyle or behavioral coaching program. Forty-six percent of small firms and 83% of large firms offering health benefits offer at least one of these three programs 15.
- To encourage participation in wellness programs, firms may offer financial incentives to employees who participate in or complete wellness programs.
- Forty-two percent of large firms offering one of these wellness or health promotion programs offer an incentive to encourage employees to participate in or complete the programs 16. Fifty-two percent of firms with more than 5,000 employees offering one of these wellness or health promotion programs offer an incentive to participate in or complete the programs.
- Among large firms offering incentives to employees to participate in or complete wellness or health promotion programs, 34% lower premium contributions or reduce cost sharing; 76% offer cash, gift cards, merchandise or contributions to HSAs or HRAs; and 14% have some other type of incentive 17.
- Firms with incentives for health risk assessment, biometric screening, or wellness or health promotion programs were asked to report the maximum reward or penalty an employee could earn for all of the firm’s health promotion activities combined. Some employers do not offer incentives for individual activities, but offer rewards to employees who complete a variety of activities. Among large firms offering incentives for any of these programs, the maximum value for all wellness-related incentives is $150 or less in 26% of firms and more than $1,000 in 16% of firms 18.
- Firms with incentives for health risk assessment, biometric screening, or wellness or health promotion programs were also asked how effective they believed incentives were for encouraging participation. Thirty-one percent of large firms offering incentives for any one of these programs say the incentives are “very effective” at encouraging employees to participate, 56% say that the incentives are somewhat effect, while 10% say the incentives are not effective 19.
- Among firms offering health benefits, 3% of small firms and 16% of large firms collect information from employees’ wearable devices, such as a Fitbit or Apple Watch, as part of their wellness or health promotion program 21.
Section Thirteen: Grandfathered Health Plans
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) exempts certain health plans that were in effect when the law was passed, referred to as grandfathered plans, from some standards in the law, including the requirement to cover preventive benefits without cost sharing, have an external appeals process, or comply with the new benefit and rating provisions in the small group market. In 2016, 23% of firms offering health benefits offer at least one grandfathered health plan, and 23% of covered workers are enrolled in a grandfathered plan.
Grandfathered Plans: In the employer-sponsored market, health plans that were in place when the ACA was enacted (March 2010) can be grandfathered health plans. Department of Health and Human Services (HSS) rules stipulate that firms cannot significantly change cost sharing, benefits, employer contributions, or access to coverage in grandfathered plans. New employees can enroll in a grandfathered plan as long as the firm has maintained consecutive enrollment in the plan. Grandfathered plans are exempted from many, but not all, of the ACA’s consumer protection provisions.
In responding to the 2016 survey, some employers found it difficult to distinguish between the grandfathering provisions in the ACA and the guidance (sometimes called “grandmothering”) issued by HHS. We would note that smaller firms in particular appear to have some confusion about whether or not they are grandfathered. Many smaller firms, even those offering a health plan in effect in March 2010 (when the ACA was enacted), were unsure about whether their plan was grandfathered.
- Twenty-three percent of offering firms report having at least one grandfathered plan in 2016, down from 35% in 2015 1.
- Twenty-three percent of covered workers are enrolled in a grandfathered health plan in 2016 2.
- The percentage of covered workers enrolled in a grandfathered plan is similar to 2015 (25%), but down from 36% in 2013, 48% in 2012, and 56% in 2011 4.
- Covered workers in the south are more likely to be enrolled in a grandfathered plan and covered workers in the Midwest are less likely to be enrolled in a grandfathered plan than covered workers in other regions 2.
Section Fourteen: Employer Opinions And Health Plan Practices
Employers play a significant role in health insurance coverage – so their opinions and experiences are important factors in health policy discussions. Employer practices continue to evolve, partially in response to Affordable Care Act provisions, including the employer shared responsibility provisions, which require large employers offer coverage or pay a fee, and the impending excise tax on high-cost plans.
Employers continue to innovate as to how they offer, structure, and deliver their benefits. A considerable number of employers have developed strategies to reduce costs or improve quality through changes to their plan’s provider networks.
Shopping for Health Coverage
Fifty-one percent of firms offering health benefits reported shopping for a new health plan or a new insurance carrier in the past year, similar to the percentages in recent years
- Among firms that offer health benefits and who shopped for a new plan or carrier, 21% changed insurance carriers 2.
COBRA Premiums
- Sixteen percent of small firms (3-199 workers) and 1% of large firms (200 or more workers) say they adjust the COBRA premium for former employees based on their age 24.
Networks and Delivery of Care
Many employers and health plans are delivering services through alternative sites of care.
- Sixty-one percent of firms that offer health benefits cover services provided in retail health clinics, such as those found in pharmacies, supermarkets and retail stores 9. These percentages are similar to those reported in 2014 when this question was last asked.
- Large firms are more likely to cover services provided through retail health clinics than small firms (73% vs. 60%) 9.
- Six percent of firms that cover services provided in retail clinics have a financial incentive for enrollee to receive services in a clinic as compared to visiting a physician’s office 9. Large firms are more likely to have such a financial incentive than small firms (10% vs. 6%).
- Thirty-nine percent of large firms offering health benefits cover the provision of some health care services through telecommunication in their largest health plan 7. The question in the survey were revised for 2016 to clarify that we were asking about payment for services and not just the electronic exchange of information.
- Among these firms, 33% report that workers have a financial incentive to receive services through telemedicine rather than visiting a physician’s office 7.
- Among firms with at least 50 employees offering health benefits, 5% provide health services to employees through an on-site health clinic at one of their major locations 11.
- Eighty-six percent of these firms allow employees to receive treatment for non-work-related services through the on-site clinic 11.
- Firms with at least 1,000 workers were more likely to have an on-site health clinic than smaller firms (25% vs. 4%).
A tiered or high-performance network groups providers in the network together based on quality, cost, and/or the efficiency of the care they deliver. These networks encourage patients to visit preferred doctors by either restricting networks to efficient providers, or by having different cost sharing requirements based on the provider’s tier.
- Fourteen percent of large firms that offer health benefits include a high-performance or tiered provider network in their health plan with the largest enrollment, down from 24% in 2015. The largest firms (those with 1,000 or more employees) are more likely to incorporate a high-performance or tiered network into their largest plan 6.
Firms offering health benefits were asked whether they offered a plan that they considered to be a narrow network. Narrow networks are plans that limit the number of providers who can participate in order to reduce costs. Narrow network plans are generally more restrictive than standard HMO networks.
- Six percent of offering firms with 50 or more employees indicated that they offer a plan they considered to be a narrow network plan, similar to the percentages reported in the last few years 4.
Six percent of firms offering health benefits said that either they or their insurer eliminated a hospital or health system from a provider network in order to reduce the plan’s cost
.
Private exchanges
There has been considerable interest in private exchanges recently. An exchange is a marketplace for health insurance. Private exchanges allow employees to choose from several health benefit options offered on the exchange. Private exchanges generally are created by consulting firms, insurers, or brokers, and are different than the public exchanges that have been created by states or the federal government. There is considerable variation in the types of exchanges currently offered; some exchanges allow workers to choose between multiple plans offered by the same carrier while in other cases multiple carriers participate. The exchange operator may establish strict standards for the plans offered or allow the insurers more flexibility in determining their plan offerings.
- Four percent of firms offering health benefits with 50 or more employees offer coverage through a private exchange. Looking at worker enrollment, private exchanges cover 2% of covered workers at firms with 50 or more employees 15. These percentages are similar to those in 2015.
- Firms offering health benefits with 50 or more employees and who do not already offer health benefits through a private exchange were asked whether they were considering private exchanges in the future. Eighteen percent of these firms are considering offering benefits through a private exchange, similar to the percentage last year 14.
Private exchanges may or may not include a defined contribution for premiums. A defined contribution is a set dollar amount offered to the employee by the employer. Employees may then select one of several plans, paying the difference between the defined contribution and the cost of their chosen health insurance plan. This permits an employer to offer a larger variety of health plans to employees and to structure contributions or other rules to encourage employees to choose more efficient plans.
- Firms offering health benefits with 50 or more employees and who do not already offer health benefits through a private exchange were asked whether they were considering a defined contribution approach. Twenty-one percent of these firms were considering such an approach 14.
Employer shared responsibility
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) provision requiring employers with at least 50 full-time equivalent employees (FTEs) to offer health benefits that meet minimum standards for value and affordability to their full-time workers or pay a penalty took full effect in 2016.
- Among firms offering health benefits with at least 50 FTEs, 97% report that they offer a health plan to at least 95% of their employees who worked on average 30 hours per week or more, and 96% report that they offer at least one health plan that meets the ACA standards for affordability and minimum value 22.
- Firms made changes to their employment practices in response to the employer shared responsibility requirement:
- Two percent of firms offering health benefits say they changed or planned to change the job classifications of some employees from full-time to part-time so that they would not be eligible for health benefits, while 7% said they changed or planned to change job classifications of some employees from part-time to full-time so that they would become eligible for health benefits 23.
- Two percent of firms offering health benefit say they increased or were planning to increase the waiting period before new employees become eligible for benefits 23.
- Twelve percent of firms offering health benefits say they extended or were planning to extend eligibility for health benefits to workers who were not previously eligible, and 2% reported extending or planning to extend eligibility for more comprehensive benefits to employees previously eligible only for limited benefits 23. Four percent of these firms reported that they reduced the number of employees they intended to hire because of the cost of providing health benefits 23.
Excise tax on high cost health plans
Under the ACA, employer health plans in 2020 will be subject to an excise tax of 40% on the amount by which their cost exceeds specified thresholds.27 The tax was scheduled to take effect in 2018, but its effective date was delayed two years. The tax is calculated with respect to each employee based on the combinations of health benefits received by that employee, including the employer and employee share of health plan premiums (or premium equivalents for self-funded plans), Flexible Spending Account (FSA) contributions, and employer contributions to health savings accounts and health reimbursement arrangement contributions. In anticipation of the high-cost plan tax (sometimes referred to as the “Cadillac plan tax”), some employers have begun making changes to their health benefits.
- Among firms offering health benefits, 15% of small firms and 64% of large firms say that they have conducted an analysis to determine if one of their plans will be subject to the tax when it takes effect 19.
- Among firms who have conducted an analysis, 29% report their plan with the largest enrollment will exceed the thresholds in 2020 20.
- Some employers have already taken action to mitigate the anticipated impacts of the high-cost plan excise tax.
- Three percent of small firms and 9% of large firms say they have switched to a lower cost plan or eliminated a plan option 19.
- Four percent of small firms and 15% of large firms say they have increased cost sharing 19.
- Four percent of small firms and 2% of large firms say they selected a plan with a smaller network of providers 19.
- Three percent of small firms and 8% of large firms say they moved benefit options to an account-based plan such as an HRA or HSA 19.
- Thirty-one percent of employers who conducted an analysis of the anticipated impact of the high-cost plan excise tax say that the delay in the implantation date from 2018 to 2020 caused them to reconsider or postpone changes that they had planned to make 21.
Survey Design And Methods
The Kaiser Family Foundation and the Health Research & Educational Trust (Kaiser/HRET) conduct this annual survey of employer-sponsored health benefits. HRET, a nonprofit research organization, is an affiliate of the American Hospital Association. The Kaiser Family Foundation designs, analyzes, and conducts this survey in partnership with HRET, and also funds the study. Kaiser contracts with researchers at NORC at the University of Chicago (NORC) to work with the Kaiser and HRET researchers in conducting the study. Kaiser/HRET retained National Research, LLC (NR), a Washington, D.C.-based survey research firm, to conduct telephone interviews with human resource and benefits managers using the Kaiser/HRET survey instrument. From January to June 2016, NR completed full interviews with 1,933 firms.
Survey Topics
Kaiser/HRET asks each participating firm as many as 400 questions about its largest health maintenance organization (HMO), preferred provider organization (PPO), point-of-service (POS) plan, and high-deductible health plan with a savings option (HDHP/SO).28 We treat exclusive provider organizations (EPOs) and HMOs as one plan type and report the information under the banner of “HMO”; if an employer sponsors both an HMO and an EPO, they are asked about the attributes of the plan with the larger enrollment. Similarly, starting in 2013, plan information for conventional (or indemnity) plans was collected within the PPO battery. Less than 1% of firms that completed the PPO section had more enrollment in a conventional plan than in a PPO plan.
The survey includes questions on the cost of health insurance, health benefit offer rates, coverage, eligibility, enrollment patterns, premium contributions,29 employee cost sharing, prescription drug benefits, retiree health benefits, and wellness benefits.
Firms are asked about the attributes of their current plans during the interview. While the survey’s fielding period begins in January, many respondents may have a plan whose 2016 plan year has not yet begun (Exhibit M.4). In some cases, plans may report the attributes of their 2015 plans and some plan attributes (such as HSA deductible limits) may not meet the calendar year regulatory requirements.
Response Rate
After determining the required sample from U.S. Census Bureau data, Kaiser/HRET drew its sample from a Survey Sampling Incorporated list (based on an original Dun and Bradstreet list) of the nation’s private employers and from the Census Bureau’s Census of Governments list of public employers with three or more workers. To increase precision, Kaiser/HRET stratified the sample by ten industry categories and six size categories. Kaiser/HRET attempted to repeat interviews with prior years’ survey respondents (with at least ten employees) who participated in either the 2014 or the 2015 survey, or both. Firms with 3-9 employees are not included in the panel to minimize the impact of panel effects on the offer rate statistic. As a result, 1,457 of the 1,933 firms that completed the full survey also participated in either the 2014 or 2015 surveys, or both.30 The overall response rate is 40%.31 To increase response rates, firms with 3–9 employees were offered an incentive of $75 in cash or as a donation to a charity of their choice to complete the full survey.
The vast majority of questions are asked only of firms that offer health benefits. A total of 1,687 of the 1,933 responding firms indicated they offered health benefits. The response rate for firms that offer health benefits is also 40%.
We asked one question of all firms in the study with which we made phone contact but where the firm declined to participate. The question was, “Does your company offer a health insurance program as a benefit to any of your employees?” A total of 3,110 firms responded to this question (including 1,933 who responded to the full survey and 1,177 who responded to this one question). These responses are included in our estimates of the percentage of firms offering health benefits.32 The response rate for this question is 65%. In 2012, the calculation of the response rates was adjusted to be slightly more conservative than previous years.
Beginning in 2014, we collected whether firms with a non-final disposition code (such as a firm that requested a callback at a later time or date) offered health benefits. By doing so we attempt to mitigate any potential non-response bias of firms either offering or not offering health benefits on the overall offer rate statistic. In 2016, 353 of the 1,173 firm responses that solely answered the offer question were obtained through this pathway.
Firm Size Categories and Key Definitions
Throughout the report, exhibits categorize data by size of firm, region, and industry. Firm size definitions are as follows: small firms: 3 to 199 workers; and large firms: 200 or more workers. (Exhibit M.1) shows selected characteristics of the survey sample. A firm’s primary industry classification is determined from Survey Sampling International’s (SSI) designation on the sampling frame and is based on the U.S. Census Bureau’s North American Industry Classification System (NAICS). A firm’s ownership category and other firm characteristics used in exhibits such as 3.3 and 6.21 are based on respondents’ answers. While there is considerable overlap in firms in the “State/Local Government” industry category and those in the “public” ownership category, they are not identical. For example, public school districts are included in the service industry even though they are publicly owned.
(Exhibit M.3) presents the breakdown of states into regions and is based on the U.S Census Bureau’s categorizations. State-level data are not reported both because the sample size is insufficient in many states and we only collect information on where a firm is headquartered rather than where workers are actually employed. Some mid- and large-size employers have employees in more than one state, so the location of the headquarters may not match the location of the plan for which we collected premium information.
(Exhibit M.2) displays the distribution of the nation’s firms, workers, and covered workers (employees receiving coverage from their employer). Among the over three million firms nationally, approximately 60.8% employ 3 to 9 workers; such firms employ 7.9% of workers, and 3.3% of workers covered by health insurance. In contrast, less than 1% of firms employ 5,000 or more workers; these firms employ 35.4% of workers and 38.9% of covered workers. Therefore, the smallest firms dominate any statistics weighted by the number of employers. For this reason, most statistics about firms are broken out by size categories. In contrast, firms with 1,000 or more workers are the most influential employer group in calculating statistics regarding covered workers, since they employ the largest percentage of the nation’s workforce.
Throughout this report, we use the term “in-network” to refer to services received from a preferred provider. Family coverage is defined as health coverage for a family of four.
The survey asks firms what percentage of their employees earn less than a specified amount in order to identify the portion of a firm’s workforce that has relatively low wages. This year, the income threshold is $23,000 per year for lower-wage workers and $59,000 for higher-wage workers. These thresholds are based on the 25th and 75th percentile of workers’ earnings as reported by the Bureau of Labor Statistics using data from the Occupational Employment Statistics (OES) (2015).33 The cutoffs were inflation-adjusted and rounded to the nearest thousand. Prior to 2013, wage cutoffs were calculated using the now-eliminated National Compensation Survey.
Rounding and Imputation
Some exhibits in the report do not sum to totals due to rounding. In a few cases, numbers from distribution exhibits may not add to the numbers referenced in the text due to rounding. Although overall totals and totals for size and industry are statistically valid, some breakdowns may not be available due to limited sample sizes or a high relative standard error. Where the unweighted sample size is fewer than 30 observations, exhibits include the notation “NSD” (Not Sufficient Data). Many breakouts by subsets may have a large standard error, meaning that even large differences are not statistically different.
To control for item nonresponse bias, Kaiser/HRET imputes values that are missing for most variables in the survey. On average, 6% of observations are imputed. All variables are imputed following a hotdeck approach. The hotdeck approach replaces missing information with observed values from a firm similar in size and industry to the firm for which data are missing. In 2016, there were 12 variables where the imputation rate exceeded 20%; most of these cases were for individual plan level statistics – when aggregate variables were constructed for all of the plans, the imputation rate is usually much lower. There are a few variables that Kaiser/HRET has decided not to impute; these are typically variables where “don’t know” is considered a valid response option (for example, firms’ opinions about the effectiveness of incentives to encourage worker participation in health and wellness programs). In addition, there are several variables in which missing data are calculated based on respondents’ answers to other questions (for example, employer contributions to premiums are calculated from the respondent’s premium and the worker contribution to premiums).
Starting in 2012, the method to calculate missing premiums and contributions was revised; if a firm provides a premium for single coverage or family coverage, or a worker contribution for single coverage or family coverage, that information is used in the imputation. For example, if a firm provided a worker contribution for family coverage but no premium information, a ratio between the family premium and family contribution was imputed and then the family premium was calculated. In addition, in cases where premiums or contributions for both family and single coverage were missing, the hotdeck procedure was revised to draw all four responses from a single firm. The change in the imputation method did not have a significant impact on the premium or contribution estimates.
Starting in 2014, we estimate separate single and family coverage premiums for firms that provide premium amounts as the average cost for all covered workers, instead of differentiating between single and family coverage. This method more accurately accounts for the portion that each type of coverage contributes to the total cost for the 0.4% of covered workers who are enrolled at firms affected by this adjustment.
Sample Design
We determined the sample requirements based on the universe of firms obtained from the U.S. Census Bureau. Prior to the 2010 survey, the sample requirements were based on the total counts provided by Survey Sampling Incorporated (SSI) (which obtains data from Dun and Bradstreet). Over the years, we found the Dun and Bradstreet frequency counts to be volatile due to duplicate listings of firms, or firms that are no longer in business. These inaccuracies vary by firm size and industry. In 2003, we began using the more consistent and accurate counts provided by the Census Bureau’s Statistics of U.S. Businesses and the Census of Governments as the basis for post-stratification, although the sample was still drawn from a Dun and Bradstreet list. In order to further address this concern at the time of sampling, starting in 2009, we use Census Bureau data to determine the number of firms to attempt to interview within each size and industry category.
Starting in 2010, we defined Education as a separate sampling category for the purposes of sampling, rather than as a subgroup of the Service category. In the past, Education firms were a disproportionately large share of Service firms. Education is controlled for during post-stratification, and adjusting the sampling frame to also control for Education allows for a more accurate representation of both the Education and Service industries.
In past years, both private and government firms were sampled from the Dun and Bradstreet database. Beginning in 2009, Government firms were sampled from the 2007 Census of Governments. This change was made to eliminate the overlap of state agencies that were frequently sampled from the Dun and Bradstreet database. The sample of private firms is screened for firms that are related to state/local governments, and if these firms are identified in the Census of Governments, they are reclassified as government firms and a private firm is randomly drawn to replace the reclassified firm. The federal government is not included in the sample frame.
Finally, the data used to determine the 2016 Employer Health Benefits Survey sample frame include the U.S. Census’ 2012 Statistics of U.S. Businesses and the 2012 Census of Governments. At the time of the sample design (December 2015), these data represented the most current information on the number of public and private firms nationwide with three or more workers. As in the past, the post-stratification is based on the most up-to-date Census data available (the 2013 update to the Census of U.S. Businesses was purchased during the survey fielding period).
Weighting and Statistical Significance
Because Kaiser/HRET selects firms randomly, it is possible through the use of statistical weights to extrapolate the results to national (as well as firm size, regional, and industry) averages. These weights allow us to present findings based on the number of workers covered by health plans, the number of total workers, and the number of firms. In general, findings in dollar amounts (such as premiums, worker contributions, and cost sharing) are weighted by covered workers. Other estimates, such as the offer rate, are weighted by firms. Specific weights were created to analyze the HDHP/SO plans that are offered with a Health Reimbursement Arrangement (HRA) or that are Health Savings Account (HSA)-qualified. These weights represent the proportion of employees enrolled in each of these arrangements.
Calculation of the weights follows a common approach. We trimmed the weights in order to reduce the influence of weight outliers. First, we grouped firms into size and offer categories of observations. Within each strata, we identified the median and the interquartile range of the weights and calculated the trimming cut point as the median plus six times the interquartile range (M + [6 * IQR]). Weight values larger than this cut point are trimmed to the cut point. In all instances, very few weight values were trimmed. Finally, we calibrated the weights to U.S. Census Bureau’s 2013 Statistics of U.S. Businesses for firms in the private sector, and the 2012 Census of Governments as the basis for calibration / post-stratification for public sector firms. Historic employer-weighted statistics were updated in 2011.
We conducted a follow-up survey of those firms with 3 to 49 workers that refused to participate in the full survey and conducted a McNemar test to verify that the results of the follow-up survey are comparable to the results from the original survey.
Between 2006 and 2012, only limited information was collected on conventional plans. Starting in 2013, information on conventional plans is collected under the PPO section and therefore, the covered worker weight is representative of all plan types for which the survey collects information.
The survey contains a few questions on employee cost sharing that are asked only of firms that indicate in a previous question that they have a certain cost-sharing provision. For example, copayment amounts for physician office visits are asked only of those that report they have copayments for such visits. Because the composite variables (using data from across all plan types) are reflective of only those plans with the provision, separate weights for the relevant variables were created in order to account for the fact that not all covered workers have such provisions.
To account for design effects, the statistical computing package R and the library package “survey” were used to calculate standard errors.34 ,35 All statistical tests are performed at the .05 confidence level, unless otherwise noted. For figures with multiple years, statistical tests are conducted for each year against the previous year shown, unless otherwise noted. No statistical tests are conducted for years prior to 1999. In 2012, the method to test the difference between distributions across years was changed to use a Wald test, which accounts for the complex survey design. In general, this method is more conservative than the approach used in prior years.
Statistical tests for a given subgroup (firms with 25-49 workers, for instance) are tested against all other firm sizes not included in that subgroup (all firm sizes NOT including firms with 25-49 workers, in this example). Tests are done similarly for region and industry; for example, Northeast is compared to all firms NOT in the Northeast (an aggregate of firms in the Midwest, South, and West). However, statistical tests for estimates compared across plan types (for example, average premiums in PPOs) are tested against the “All Plans” estimate. In some cases, we also test plan-specific estimates against similar estimates for other plan types (for example, single and family premiums for HDHP/SOs against single and family premiums for HMO, PPO, and POS plans); these are noted specifically in the text. The two types of statistical tests performed are the t-test and the Wald test. The small number of observations for some variables resulted in large variability around the point estimates. These observations sometimes carry large weights, primarily for small firms. The reader should be cautioned that these influential weights may result in large movements in point estimates from year to year; however, these movements are often not statistically significant.
2016 Survey
Between 2015 and 2016, we conducted a series of focus groups that led us to the conclusion that human resource and benefit managers at firms with between 20 and 49 employees think about health insurance premiums more similarly to benefit managers at smaller firms than larger firms. Therefore, starting in 2016, we altered the health insurance premium question pathway for firms with between 20-49 employees to match that of firms with 3-19 employees rather than firms with 50 or more employees. This change affected firms representing 8% of the total covered worker weight. We believe that these questions produce comparable responses and that this edit does not create a break in trend.
Firms with 50 or more workers were asked: “Does your firm offer health benefits for current employees through a private or corporate exchange?” Employers were still asked for plan information about their HMO, PPO, POS and HDHP/SO plan regardless of whether they purchased health benefits through a private exchange or not.
Starting in 2015, employers were asked how many full-time equivalent workers (FTEs) they employed. In cases in which the number of full-time equivalents was relevant to the question, interviewer skip patterns may have depended on the number of FTEs. In 2016, questions were added to ask firms to estimate the number of hours that a typical part-time worker averaged over the course of one week in order to more accurately determine which firms might be subject to the Employer Shared Responsibility Provision of the Affordable Care Act. In cases where a firm did not know how many FTEs it employed, we calculated the number based on the number of part-time hours the firm reported. In all cases, we assumed that firms with more than 250 full time employees had more than 50 FTES.
Starting in 2016, we made significant revisions to how the survey asks employers about their prescription drug coverage. In most cases, information reported in Prescription Drug Benefits (Section 9) is not comparable with previous years’ findings. First, in addition to the four standard tiers of drugs (generics, preferred, non-preferred, and lifestyle), we began asking firms about cost sharing for a drug tier that covers only specialty drugs. This new tier pathway in the questionnaire has an effect on the trend of the four standard tiers, since respondents to the 2015 survey might have previously categorized their specialty drug tier as one of the other four standard tiers. We did not modify the question about the number of tiers a firm’s cost-sharing structure has, but in cases in which the highest tier covered exclusively specialty drugs we reported it separately. For example, in Exhibits 9.3 and 9.4, a firm with three tiers may only have copays or coinsurances for two tiers because their third tier copay or coinsurance is being reported as a specialty tier. Furthermore, in order to reduce survey burden, firms were asked about the plan attributes of only their plan type with the most enrollment. Therefore, in most cases, we no longer make comparisons between plan types. Lastly, prior to 2016, we required firms’ cost sharing tiers to be sequential, meaning that the second tier copay was higher than the first tier, the third tier was higher than the second, and the fourth was higher than the third. As drug formularies have become more intricate, many firms have minimum and maximums attached to their copays and coinsurances, leading us to believe it was no longer appropriate to assume that a firm’s cost sharing followed this sequential logic.
In cases where a firm had multiple plans, they were asked about their strategies for containing the cost of specialty drugs for the plan type with the largest enrollment. Between 2015 and 2016, we modified the series of ‘Select All That Apply’ questions regarding cost containment strategies for specialty drugs. In 2016, we elected to impute firms’ responses to these questions. We removed the option “Separate cost sharing tier for specialty drugs” and added specialty drugs as their own drug tier questionnaire pathway. We added question options on mail order drugs and prior authorization.
We discovered that the HRA and HSA distribution cutoff thresholds presented in prior years’ High Deductible Health Plan Section (Section 8) were calculated using each firm’s covered worker weight rather than the HRA- or HSA-specific enrollment weights. Starting in 2016, the means and their subsequent distributions are now calculated using these plan-specific enrollment weights and therefore those thresholds are not directly comparable to prior-year statistics.
In our 2015 calculation of out-of-pocket (OOP) maximums, we mistakenly included plans in our calculations with $0 OOP maximums, representing 2.4% the total of covered worker weight, which pushed the distribution downward in 2015 Exhibit 7.31. In the same 2016 exhibit (7.36), firms with $0 OOP maximums have been excluded.
Twenty-five firms reported allowing flexible spending account (FSA) employee contributions above the legal limit of $2,550 in 2016. Although these firms were asked to confirm that their maximum contributions were above $2,550, we nonetheless recoded their responses to the legal ceiling of $2,550 and intend to provide additional clarification that we are interested in only a firm’s health FSA in the future.
In 2016, we modified our questions about telemedicine to clarify that we were interested in the provision of health care services, and not merely the exchange of information, through telecommunication. We also added dependent and spousal questions to our health risk assessment question pathway.
In 2016, we ceased publication of the slide “Percentage of Firms Offering Health Benefits, by Firm Characteristics” (Exhibit 2.4 in the 2015 EHBS report). Since firm characteristics are not collected from respondents that solely answer the offer question, this exhibit had been calculated using the employer weight derived from only firms that had completed the full survey.
Annual inflation estimates are usually calculated from April to April. The 12 month percentage change for May to May was 1%.36
Historical Data
Data in this report focus primarily on findings from surveys jointly authored by the Kaiser Family Foundation and the Health Research & Educational Trust, which have been conducted since 1999. Prior to 1999, the survey was conducted by the Health Insurance Association of America (HIAA) and KPMG using a similar survey instrument, but data are not available for all the intervening years. Following the survey’s introduction in 1987, the HIAA conducted the survey through 1990, but some data are not available for analysis. KPMG conducted the survey from 1991-1998. However, in 1991, 1992, 1994, and 1997, only larger firms were sampled. In 1993, 1995, 1996, and 1998, KPMG interviewed both large and small firms. In 1998, KPMG divested itself of its Compensation and Benefits Practice, and part of that divestiture included donating the annual survey of health benefits to HRET.
This report uses historical data from the 1993, 1996, and 1998 KPMG Surveys of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits and the 1999-2015 Kaiser/HRET Survey of Employer-Sponsored Health Benefits. For a longer-term perspective, we also use the 1988 survey of the nation’s employers conducted by the HIAA, on which the KPMG and Kaiser/HRET surveys are based. The survey designs for the three surveys are similar.
Endnotes
- Kaiser Commission on Medicaid and the Uninsured. The uninsured: A primer—key facts about health insurance and the uninsured in America [Internet]. Washington (DC): The Commission; 2015 Nov [cited 2016 Aug 1]. https://modern.kff.org/uninsured/report/the-uninsured-a-primer/. See supplemental tables – Table 1: 270.2 million non-elderly people, 55.5% of whom are covered by ESI. ↩︎
- Kaiser/HRET surveys use the April-to-April time period, as do the sources in this and the following note. The inflation numbers are not seasonally adjusted. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Consumer Price Index – All Urban Consumers: Department of Labor; 2015. [cited 2016 July 28] http://data.bls.gov/timeseries/CUUR0000SA0?output_view=pct_1mth. Wage data are from the Bureau of Labor Statistics and based on the change in total average hourly earnings of production and nonsupervisory employees. Employment, hours, and earnings from the Current Employment Statistics survey: Department of Labor; 2016 [cited 2016 July 28]. http://data.bls.gov/timeseries/CES0500000008 ↩︎
- The change in enrollment in HDHP/SO between 2014 (20%) and 2016 (29%) is 8% due to rounding. ↩︎
- The change in enrollment in HDHP/SO between 2014 (20%) and 2016 (29%) is 8% due to rounding. ↩︎
- Federal Register. Vol. 75, No. 221, November 17, 2010. http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2010-11-17/pdf/2010-28861.pdf ↩︎
- Internal Revenue Service. Section 4980I—Excise Tax on High Cost Employer-Sponsored Health Coverage: Notice 2015-16. https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-drop/n-15-16.pdf ↩︎
- Because surveys only collect information from a portion of the total number of firms in the country, there is uncertainty in any estimate. Since there are so many small firms, sometimes even seemingly large differences are not statistically different. For more information on the Employer Health Benefits Survey’s weighting and design please see the Survey Design and Methods section. ↩︎
- Internal Revenue Code. 26 U.S. Code § 4980H – Shared responsibility for employers regarding health coverage. 2011. https://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/USCODE-2011-title26/pdf/USCODE-2011-title26-subtitleD-chap43-sec4980H.pdf ↩︎
- Internal Revenue Service. “Employer Health Care Arrangements”. Last updated March 4, 2016. http://www.irs.gov/Affordable-Care-Act/Employer-Health-Care-Arrangements ↩︎
- Kaiser Commission on Medicaid and the Uninsured. The uninsured: A primer—key facts about health insurance and the uninsured in America [Internet]. Washington (DC): The Commission; 2015 Nov [cited 2016 Aug 1]. https://modern.kff.org/uninsured/report/the-uninsured-a-primer/. See supplemental tables – Table 1: 270.2 million non-elderly people, 55.5% of whom are covered by ESI. ↩︎
- In 2009, Kaiser/HRET began weighting the percentage of workers that take up coverage by the number of workers eligible for coverage. The historical take up estimates have also been updated. See the Survey Design and Methods section for more information. ↩︎
- Variable hour employees may have a measurement period of up to 12 months before it is determined if they are eligible for benefits. Employers may require a cumulative service requirement of up to 1,200 hours before an employee may enroll. Federal Register. Vol. 79, No. 36. Feb 12, 2014. https://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2014-02-24/pdf/2014-03809.pdf ↩︎
- Under the ACA, employers may determine whether or not an employee is a full-time employee by looking back at the number of hours an employee has worked during a defined period. See https://www.irs.gov/affordable-care-act/employers/identifying-full-time-employees ↩︎
- Starting in 2010, we included firms that said they offer a plan type even if there are no covered workers enrolled in that plan type. ↩︎
- The change in enrollment in HDHP/SO between 2014 (20%) and 2016 (29%) is 8% due to rounding. ↩︎
- Estimates for premiums, worker contributions to premiums, and employer contributions to premiums presented in Section 6 do not include contributions made by the employer to Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs). See Section 8 for estimates of employer contributions to HSAs and HRAs. ↩︎
- The average percent contribution is calculated as a weighted average of all a firm’s plan types and may not necessarily equal the average worker contribution divided by the average premium. ↩︎
- For definitions of Self-Funded and Fully-Insured plans, see the introduction to Section 10. ↩︎
- Some workers with separate per-person deductibles or out-of-pocket maximums for family coverage do not have a specific number of family members that are required to meet the deductible amount and instead have another type of limit, such as a per-person amount with a total dollar amount limit. These responses are included in the averages and distributions for separate family deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums. ↩︎
- Starting in 2010, the survey asked about the prevalence and cost of physician office visits separately for primary care and specialty care. Prior to the 2010 survey, if the respondent indicated the plan had a copayment for office visits, we assumed the plan had a copayment for both primary and specialty care visits. The survey did not allow for a respondent to report that a plan had a copayment for primary care visits and coinsurance for visits with a specialist physician. The changes made in 2010 allow for variations in the type of cost sharing for primary care and specialty care visits. The survey includes cost sharing for in-network services only. ↩︎
- For those enrolled in an HDHP/HSA, the out-of-pocket maximum is $6,550 for an individual plan and $13,100 for a family plan. ↩︎
- There is no legal requirement for the minimum deductible in a plan offered with an HRA. The survey defines a high-deductible HRA plan as a plan with a deductible of at least $1,000 for single coverage and $2,000 for family coverage. Federal law requires a deductible of at least $1,300 for single coverage and $2,600 for family coverage for HSA-qualified HDHPs in 2016. See the Text Box for more information on HDHP/HRAs and HSA-qualified HDHPs. ↩︎
- The definitions of HDHP/SOs do not include other consumer-driven plan options, such as arrangements that combine an HRA with a lower-deductible health plan or arrangements in which an insurer (rather than the employer as in the case of HRAs or the enrollee as in the case of HSAs) establishes an account for each enrollee. Other arrangements may be included in future surveys as the market evolves. ↩︎
- The survey asks “Up to what dollar amount does your firm promise to contribute each year to an employee’s HRA or health reimbursement arrangement for single coverage?” We refer to the amount that the employer commits to make available to an HRA as a contribution for ease of discussion. As discussed, HRAs are notional accounts, and employers are not required to actually transfer funds until an employee incurs expenses. Thus, employers may not expend the entire amount that they commit to make available to their employees through an HRA. Some employers may make their HRA contribution contingent on other factors, such as completing wellness programs. ↩︎
- See the Methods Section for more information. In cases in which a firm indicated that one of their tiers was exclusively for specialty drugs, we reported the cost-sharing structure and any copay or coinsurance information under the specialty drug banner. Therefore, a firm that has three tiers of cost sharing may only have plan attributes for the generic and preferred tier. ↩︎
- See the Methods Section for changes in these questions and responses as compared to 2015. ↩︎
- Internal Revenue Service. Section 4980I—Excise Tax on High Cost Employer-Sponsored Health Coverage: Notice 2015-16. https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-drop/n-15-16.pdf ↩︎
- HDHP/SO includes high-deductible health plans with a deductible of at least $1,000 for single coverage and $2,000 for family coverage and that offer either a Health Reimbursement Arrangement (HRA) or a Health Savings Account (HSA). Although HRAs can be offered along with a health plan that is not an HDHP, the survey collected information only on HRAs that are offered along with HDHPs. For specific definitions of HDHPs, HRAs, and HSAs, see the introduction to Section 8. ↩︎
- HDHP/SO premium estimates do not include contributions made by the employer to Health Savings Accounts or Health Reimbursement Arrangements. ↩︎
- In total, 124 firms participated in 2014, 269 firms participated in 2015, and 1,064 firms participated in both 2014 and 2015. ↩︎
- Response rate estimates are calculated by dividing the number of completes over the number of refusals and the fraction of the firms with unknown eligibility to participate estimated to be eligible. Firms determined to be ineligible to complete the survey are not included in the response rate calculation. ↩︎
- Estimates presented in Exhibits 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 and 2.5 are based on the sample of both firms that completed the entire survey and those that answered just one question about whether they offer health benefits. ↩︎
- General information on the OES can be found at http://www.bls.gov/oes/oes_emp.htm#scope. A comparison between the OES and the NCS is available at http://www.bls.gov/oes/oes_ques.htm ↩︎
- Analysis of the 2011 survey data using both R and SUDAAN (the statistical package used prior to 2012) produced the same estimates and standard errors. ↩︎
- A supplement with standard errors for select estimates can be found online at Technical Supplement: Standard Error Tables for Selected Estimates, http://ehbs.kff.org ↩︎
- Bureau of Labor Statistics, Consumer Price Index, U.S. City Average of Annual Inflation (April to April), 2000-2016; http://data.bls.gov/timeseries/CUUR0000SA0?output_view=pct_1mth ↩︎
