How Will the Uninsured in Wisconsin Fare Under the Affordable Care Act?
The 2010 Affordable Care Act (ACA) has the potential to extend coverage to many of the 47 million nonelderly uninsured people nationwide, including the 566,000 uninsured Wisconsinites. The ACA establishes coverage provisions across the income spectrum, with the expansion of Medicaid eligibility for adults serving as the vehicle for covering low-income individuals and premium tax credits to help people purchase insurance directly through new Health Insurance Marketplaces serving as the vehicle for covering people with moderate incomes. With the June 2012 Supreme Court ruling, the Medicaid expansion became optional for states, and as of December 2013, Wisconsin was not planning to implement the full expansion. Instead, the state amended its Medicaid state plan and existing Section 1115 waiver to cover adults up to 100% FPL in Medicaid, but did not adopt the expansion. As the ACA coverage expansions are implemented and coverage changes are assessed, it is important to understand the potential scope of the law in the state.
How Does the ACA Expand Health Insurance Coverage in Wisconsin?
Historically, Medicaid had gaps in coverage for adults because eligibility was restricted to specific categories of low-income individuals, such as children, their parents, pregnant women, the elderly, or individuals with disabilities. In most states, adults without dependent children were ineligible for Medicaid, regardless of their income, and income limits for parents were very low—often below half the poverty level.1 However, some states, including Wisconsin, had expanded coverage to parents at higher income levels or provided coverage to adults without children. The ACA aimed to extend Medicaid to nearly all nonelderly adults with incomes at or below 138% of poverty (about $32,500 for a family of four in 2013).
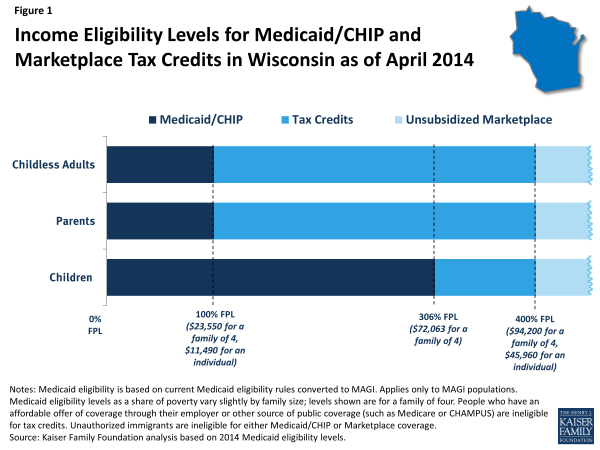
In states that do not implement the expansion (such as Wisconsin), Medicaid eligibility for adults will remain below 138% of poverty, as shown by the dark blue shading in Figure 1. As of April 2014, in Wisconsin, Medicaid eligibility for non-disabled adults will be limited to parents and adults without dependent children with incomes below 100% of poverty, or about $23,600 a year for a family of four and $11,500 for an individual. All states previously expanded eligibility for children to higher levels than adults through Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), and in Wisconsin, children with family incomes up to 306% of poverty (about $72,100 for a family of four) are eligible for Medicaid or CHIP. As was the case before the ACA, undocumented immigrants remain ineligible to enroll in Medicaid, and recent lawfully residing immigrants are subject to certain Medicaid eligibility restrictions.2
Under the ACA, people with incomes between 100% and 400% of poverty may be eligible for premium tax credits when they purchase coverage in a Marketplace, as indicated by the bright blue shading in Figure 1. The amount of the tax credit is based on income and the cost of insurance, and tax credits are only available to people who are not eligible for other coverage, such as Medicaid/CHIP, Medicare, or employer coverage, and who are citizens or lawfully-present immigrants. Thus, the effective lower income limit for tax credits in Wisconsin is 306% of poverty for children and 100% of poverty for adults, as indicated by the bright blue shading in Figure 1. Citizens and lawfully-present immigrants with incomes above 400% of poverty can purchase unsubsidized coverage through the Marketplace. Because the ACA envisioned low-income people receiving coverage through Medicaid, people below poverty are not eligible for Marketplace subsidies.
How Many Uninsured Wisconsinites Are Eligible for Assistance Under the ACA?
Under the ACA, in Wisconsin, seven in ten (70%) uninsured nonelderly people are eligible for financial assistance to gain coverage through either Medicaid or the Marketplaces (Figure 2). With the state’s expansion of Medicaid to 100% of poverty, over one-third (36%) of uninsured Wisconsinites are eligible for either Medicaid or CHIP as of 2014. An additional third (34%) of those currently uninsured in the state are eligible for premium tax credits to help them purchase coverage in the Marketplace.
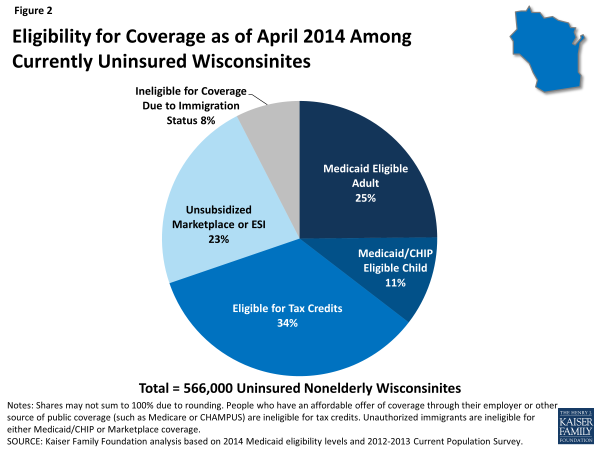
Other uninsured Wisonsinites may gain coverage under the ACA but will not receive direct financial assistance. These people include the 23 percent with incomes too high to be eligible for premium tax subsidies or who have an affordable offer of coverage through their employer. Some of these people are still able to purchase unsubsidized coverage in the Marketplace, which may be more affordable or more comprehensive than coverage they could obtain on their own through the individual market. Lastly, the approximately 8 percent of uninsured people in Wisconsin who are undocumented immigrants are ineligible for financial assistance under the ACA and barred from purchasing coverage through the Marketplaces. This group is likely to remain uninsured, though they will still have a need for health care services.
***
The ACA will help millions of currently uninsured Wisconsinites gain health coverage, and the state’s expansion to adults with income up to 100 percent of poverty will extend coverage to many uninsured poor adults. The impact of the ACA will depend on take-up of coverage among the eligible uninsured, and outreach and enrollment efforts will be an important factor in determining how the law affects the uninsured rate in the state. The ACA includes a requirement that most individuals obtain health coverage, but some people (such as the lowest income or those without an affordable option) are exempt and others may still remain uninsured. Notably, there is no deadline for state decisions about implementing the Medicaid expansion, and open enrollment in the Marketplaces continues through March 2014. Continued attention to who gains coverage as the ACA is fully implemented and who is excluded from its reach—as well as whether and how their health needs are being met—can help inform decisions about the future of health coverage in Wisconsin.
- Some states had expanded coverage to parents at higher income levels or provided coverage to adults without children. See http://modern.kff.org/medicaid/fact-sheet/medicaid-eligibility-for-adults-as-of-january-1-2014/ for more detail on pre- and post-ACA Medicaid eligibility for adults. ↩︎
- For more detail on Medicaid coverage for immigrants, see: http://modern.kff.org/disparities-policy/fact-sheet/key-facts-on-health-coverage-for-low/. ↩︎