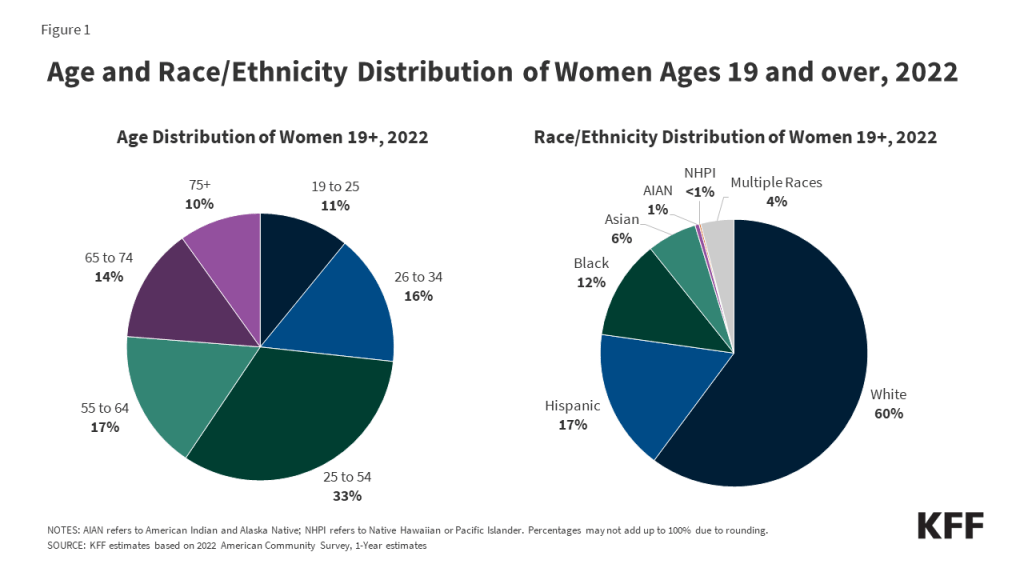
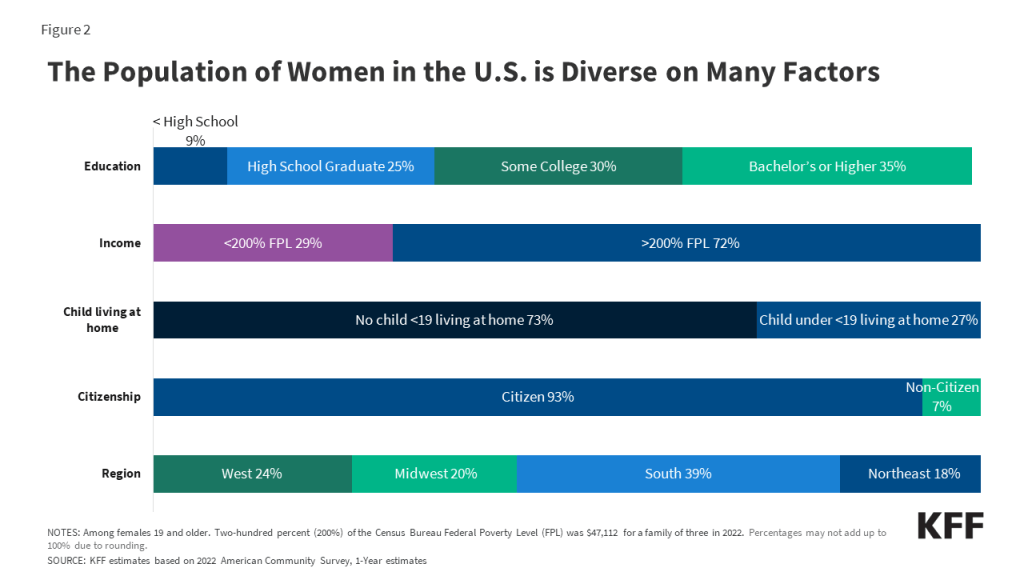
Reproductive Health
Maternity Care
In 2022, there were approximately 3.6 million births in the U.S. Childbirth is the leading reason for hospitalization, and most private insurance plans and the Medicaid program are required to cover care associated with childbirth. Medicaid covers about 4 in 10 births nationally and, in some states, more than half. The Medicaid program prohibits plans from charging out-of-pocket charges for pregnancy-related care, and coverage lasts through one year postpartum in most, but not all, states. For people with private insurance, which finances just over half of births (51%), the federal Pregnancy Discrimination Act requires employer plans to cover maternity care benefits. However, even for those with private insurance, a pregnancy often comes with significant out-of-pocket health expenses that can reach thousands of dollars. A KFF analysis estimated that women enrolled in large group plans pay around $3,000 out-of-pocket for costs associated with pregnancy, childbirth, and post-partum care. On average, Caesarean section births, which account for approximately one-third of births in the U.S., are significantly more expensive than vaginal deliveries. The ACA also requires individual plans to cover maternity care and bans plans from implementing restrictions on coverage of pre-existing health conditions, including pregnancy.
In recent years, there has been growing attention to pregnancy-related quality of care and maternal health. Maternal and infant mortality rates in the U.S. are far higher than those in similarly large and developed countries, and people of color are at a considerably higher risk for poor maternal and infant health outcomes compared to their White peers. Despite continued advancements in medical care, rates of maternal mortality and morbidity and preterm birth have been rising in the U.S., characterized by stark racial disparities. Notably, rates of pregnancy-related death (deaths within one year of pregnancy) among Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander (NHPI), Black, and American Indian and Alaska Native (AIAN) women are over four to two times higher, respectively, compared to the rate for White women (14.1 and 62.8 vs. 39.9 vs. 32 per 100,000 births) (Figure 9). The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has determined that many of these pregnancy-related deaths were preventable, caused by cardiac-related conditions, infection, hemorrhage, and mental health conditions, including substance use. Maternal death rates increased during the COVID-19 pandemic and racial disparities widened for Black women. Black, AIAN, and Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander (NHPI) women also have higher shares of preterm births, low birthweight births, or births for which they received late or no prenatal care compared to White women. Infants born to Black, AIAN, and NHOPI people have markedly higher mortality rates than those born to White women.
The disparities in maternal and infant health are symptoms of broader underlying social and economic inequities that are rooted in racism and discrimination. Differences in health insurance coverage and access to care play a role, but notably, disparities in maternal and infant health persist even when controlling for certain underlying social and economic factors, such as education and income, pointing to the roles racism and discrimination play in driving disparities. Moreover, with the overturning of Roe v. Wade and the numerous states that have enacted abortion bans across the nation, increased barriers to abortion for people of color may widen the already existing large disparities in maternal and infant health.
There have been efforts at the policy level and in clinical circles to improve maternal health and address disparities. The Biden Administration issued the White House Blueprint for Addressing the Maternal Health Crisis, outlining policy priorities and strategies. These include funding to expand and diversify the perinatal workforce, enhancing training for clinicians to better listen to patient concerns, investing in maternal mental health care, and strengthening perinatal care in rural communities. At the state and local levels, multidisciplinary maternal mortality review committees and perinatal quality collaboratives have focused on data collection and reviewing the causes behind pregnancy-related deaths in their communities to try to prevent deaths in the future.
Fertility Assistance
Many people require fertility assistance to have children. These services include diagnostic services, treatment services, and fertility preservation. People seek fertility assistance for several reasons, such as if they or their partner has infertility, or because they are in a same-sex relationship or are single and desire children. Both female and male factors contribute to infertility, including problems with ovulation (when the ovary releases an egg), structural problems with the uterus or fallopian tubes, problems with sperm quality or motility, and hormonal factors. About 25% of the time, infertility is caused by more than one factor, and in about 10% of cases, infertility is unexplained. Infertility estimates, however, do not account for LGBTQ+ or single individuals who may also need fertility assistance for family building. Thus, there are varied reasons that may prompt individuals to seek fertility care.
Despite a need for fertility services, fertility care in the U.S. is inaccessible to many due to the cost. Fertility treatments are expensive and often are not covered by insurance. While some private insurance plans cover diagnostic services, there is very little coverage for costly treatment services such as intrauterine insemination, in vitro fertilization, and cryopreservation.
Most people who use fertility services must pay out of pocket, with costs often reaching thousands of dollars depending on the services received. This means that in the absence of insurance coverage, fertility care is out of reach for many people. Few states require private insurance plans to cover fertility assistance services, but these only apply to a subset of insurance plans and beneficiaries. Additionally, even fewer states have any fertility coverage requirement under Medicaid, the health coverage program for people with low incomes.
Abortion
Nearly 1 in 4 women in the U.S. have an abortion in their lifetime. Starting with the 1973 landmark Supreme Court ruling in Roe v. Wade, women in the U.S. had the right to abortion up until the point of viability, regardless of where they lived. On June 24, 2022, the Supreme Court issued a ruling in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization that overturned the constitutional right to abortion as well as the federal standards of abortion access, established by prior decisions in the cases Roe v. Wade and Planned Parenthood v. Casey. The Dobbs decision allows states to set policies regarding the legality of abortions and establish gestational limits. Access to and availability of abortions vary widely between states, with large swaths of the country banning or restricting almost all abortions, with few exceptions, and some states enshrining and protecting abortion rights (Figure 10).
Decades of research have shown that abortion is a very safe medical service. Still, despite its strong safety profile, abortion is the most highly regulated medical service in the country and is now banned or restricted to early gestational stages in many states. In addition to bans on abortion altogether, many states impose other limitations on abortion that are not medically indicated, including waiting periods, ultrasound requirements, and parental notification and consent requirements. These restrictions typically delay receipt of services and can increase costs associated with abortion care.
Paradoxically, the total number of abortions in the U.S. appears to have increased slightly following the Dobbs decision. This rise could be due to increased interstate travel for abortion access, expanded in-person and virtual/telehealth capacity to see patients, increased measures to protect and cover abortion care for residents and out-of-state patients, and the broader availability of low-cost abortion medication. However, these aggregated trends mask the sharp decline in abortions provided in states with total bans or severe restrictions as well as the hardships that many pregnant people experience in accessing abortion care.
Obtaining an abortion can be costly, with median costs exceeding $500 in out-of-pocket expenses for patients who self-pay. On average, the costs are higher for abortions in the second trimester than in the first trimester. People may have to travel if abortions are prohibited or not available in their area, adding costs related to travel and lodging. Given abortion bans and Hyde Amendment restrictions on payment for abortions under Medicaid and state restrictions on insurance coverage of abortion services, many people pay for abortion services out of pocket. Some people are able to receive assistance from local abortion funds if they need financial support to obtain abortion services, particularly if they have to travel out of state or have low incomes and cannot afford the costs of the abortion. For some, however, the costs of abortion services and travel will put the service out of reach and force them to have a birth that is not desired or is a risk to their health or life.
Insurance coverage for abortion services is heavily restricted in some state-regulated private insurance plans and public programs, like Medicaid and Medicare. Private insurance covers most women of reproductive age, and states can choose whether abortion coverage is included or excluded in private plans that are not self-insured. Prior to the Dobbs ruling, about half of the states had enacted private plan restrictions and banned abortion coverage from ACA Marketplace plans. Since the Dobbs ruling, some of these states have also banned the provision of abortion services altogether. However, 10 states have enacted laws that require private plans to cover abortion, typically without cost-sharing.
The Hyde Amendment has banned the use of federal funds for abortion unless the pregnancy is a result of rape, incest, or it endangers the woman’s life. States may use non-federal state-only funds to pay for abortions under other circumstances for women covered by Medicaid, which 17 states currently do. However, more than half (56%) of women covered by Medicaid live in states where they have no coverage for abortion, unless they qualify for an exception.
The impact of the Dobbs decision goes far beyond abortion care. It has also affected the provision of related health care services, including management of miscarriages and pregnancy-related emergencies, treatments for cancer and other chronic illnesses, contraceptive options, and much more. Women with low incomes, women of color, sexual/gender minorities, and other pregnant people have been disproportionately affected by the sweeping impacts of this ruling, as they are less likely to have the resources to travel potentially long distances to seek care.
Since the Dobbs ruling, there has been a constant stream of legal challenges, with a plethora of cases that seek to challenge abortion bans as well as block access to abortion medication or services. While most of the litigation is in state courts, in 2024 the Supreme Court considered a case involving the FDA’s approved conditions for using mifepristone, one of the drugs used for medication abortion, as well as a case about potential conflict between state-level abortion bans and Emergency Medical Treatment and Labor Act (EMTALA), the federal law that requires hospitals to provide care to stabilize patients experiencing medical emergencies. However, in June 2024 the Supreme Court did not rule on the merits of either of these cases, maintaining the status quo for now and allowing for litigation in the future.
Contraception
Contraceptive care is an important component of overall health care for many women and people capable of becoming pregnant. Federal and state policies shape access to and the availability of contraceptive care, but factors such as provider characteristics, as well as individual preferences and experiences also impact contraceptive choices and use. For most people, private insurance coverage and Medicaid greatly reduce or eliminate financial barriers to contraceptive care. However, access is still limited in many parts of the U.S. with more than 19 million women living in contraceptive deserts where they may not have access to a health center offering the full range of contraceptive methods. There have been more efforts to broaden contraceptive availability outside of traditional clinical settings, including through commercial apps that use telehealth platforms, state efforts to allow pharmacists to prescribe birth control, and, most recently, over-the-counter (OTC) access to contraceptives without a traditional prescription.
The importance and impact of contraceptives in women’s lives are unquestionable. The 2022 KFF Women’s Health Survey highlighted that the majority of females 18 to 64 (90%) have used contraception at some point in their reproductive years, with most reporting they have used oral contraceptives and male condoms at some point in their lives (Figure 11). Many women have used more than one contraceptive method throughout their lifetime (76%), a reflection of changing needs and preferences across the lifespan.
The ACA requires that most private plans cover contraceptive services for females without cost-sharing – this includes patient education and counseling and FDA-approved methods of contraception with a prescription. This provision has dramatically reduced cost-sharing for contraception among females with private insurance plans, though some privately insured females who are eligible for no-cost coverage are still paying some of the cost of their contraceptives (Figure 12). Reasons include someone using a brand-name contraceptive that is not in the plan’s formulary or consumers unaware of or not offered a generic alternative.
Despite its far-reaching impact, the ACA’s requirement for contraceptive coverage has been challenged in the courts on multiple occasions, with three cases reaching the Supreme Court. The earlier cases, Burwell v. Hobby Lobby (2014) and Zubik v. Burwell (2016), challenged the Obama Administration’s regulations implementing the contraceptive coverage requirement, contending that the requirement violated some employers’ religious rights. The most recent cases, Little Sisters of the Poor v. Pennsylvania (2020) and Trump v. Pennsylvania (2020), involved regulations issued by the Trump Administration, which currently exempt employers with religious objections from providing contraceptive coverage to their employees.
For people with lower incomes, the Medicaid program is the primary funding source for contraceptives. The federal Medicaid statute establishes minimum standards, and, for decades, has classified family planning as a mandatory benefit category that all state programs must cover. States may not charge any out-of-pocket costs for family planning services and must allow beneficiaries to see any Medicaid provider within their state for family planning care. Many states also have programs that provide Medicaid coverage just for family planning services to people who have lower incomes but do not qualify for full Medicaid benefits.
Additionally, the federal Title X family planning program, administered by the HHS Office of Population Affairs (OPA), is the only federal program specifically dedicated to supporting the delivery of family planning care for individuals who are uninsured and have lower incomes. The program provides funding to more than 4,000 health clinics, public health departments, and nonprofit agencies across the country to deliver contraceptives and other family planning services to individuals with low incomes. Title X-funded providers must follow the program’s requirements, which include offering a broad range of family planning methods for low or no cost and ensuring confidentiality for adolescents. Federal rules also require that participating clinics offer their patients non-directive pregnancy option counseling that includes abortion, adoption, and prenatal referral for those who seek those services.
While there have been numerous over-the-counter contraceptive methods available (e.g. condoms, spermicides), in July 2023, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first over-the-counter daily oral contraceptive pill, known as Opill. FDA’s approval of Opill makes it the most effective form of contraception available OTC intended for regular use. Private insurers and Medicaid generally require a prescription to cover OTC products, so even though Opill and other OTC products are available without needing a prescription from a clinician, coverage without a prescription will be limited without federal or state action.
Mental Health
Mental health has emerged as a rapidly growing concern in recent years, with 90% of Americans saying there is a mental health crisis in a recent KFF-CNN poll. Women experience several mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and eating disorders more frequently than men, and some also experience mental health disorders that are unique to women, such as perinatal depression (including prenatal and postpartum depression) and premenstrual dysphoric disorders that may occur when hormone levels change.
A KFF survey found that in 2022, a significantly higher share of women (50%) than men (35%) thought they needed mental health services in the past two years. The rates were particularly higher among younger women (64% of women ages 18-25). However, barriers to accessing timely and affordable mental health services persist for many. Almost half of women who said they needed mental health services and tried to get care were able to get an appointment within a month, but more than one-third of women had to wait longer. Among those who could not get an appointment, women cite limited provider availability and cost as the main reasons they were unable to access mental health care. Significantly larger shares of women who are uninsured (60%) say they could not get an appointment due to affordability reasons, compared to those who have health insurance either through private plans (33%) or Medicaid (30%) (Figure 13).
Prior KFF research has documented the challenges some consumers with health insurance face when finding in-network mental health care. In fact, 2 in 10 privately insured women with a mental health care appointment in the past two years say their provider did not accept their insurance. The option is effectively not available to women who have low incomes or are on Medicaid and lack the financial resources to pay for out-of-network care.
Among the COVID-19 pandemic and the rise of racist attacks, the ongoing opioid epidemic is a commonly cited stressor that has exacerbated long-standing mental health issues and prompted growing demand for mental health services in the past several years. Women face unique gender and sex-related differences when it comes to substance use, including greater physical, psychological, and social harms associated with drug use. Use of certain substances in women has been linked to increased rates of depression and anxiety disorders. Studies have also shown that women who use substances are at risk for issues related to pregnancy, fertility, breastfeeding, menstrual cycle, and more. All of these factors also shape the availability of treatment and services accessible to women.
Intimate Partner Violence Against Women
Intimate partner violence (IPV), defined as sexual violence, stalking, physical violence, and psychological aggression perpetrated by a current or former intimate partner, affects nearly a third of all Americans at some point in their lives. Although IPV affects men and women of all ages, women experience IPV at higher rates. Rates are higher among some groups of women, particularly those who are young, Black, American Indian or Alaska Native, and LGBTQ. It is difficult to quantify the number of people who experience IPV, as many cases are not reported. Some studies have estimated 9 million women in the U.S. experience sexual violence, physical violence, or stalking by an intimate partner in a single year. People who experience IPV are more likely to experience a range of health problems such as chronic pain, cardiovascular problems, and neurological problems. Both the CDC and U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) have identified IPV as a significant public health issue in the US.
Several federal programs and laws fund health care services and supports to survivors of IPV. The Violence Against Women Act (VAWA) has a broad scope, covering domestic violence, sexual harassment, stalking, and sexual assault. VAWA provides grants to states, local governments, and other organizations to establish their own violence-related programs and protocols. While some of the focus of VAWA and other public policies is prosecution of those who commit violence, provisions in VAWA also address health care coverage and costs for people who have experienced IPV.
It is well recognized that the health care system can serve as a site of IPV screening and support, and some professional medical organizations recommend that clinicians screen women for IPV. Under the ACA, IPV screening is considered a preventive service as screening is recommended by the USPSTF and Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) preventive services for women. When health care providers routinely screen patients for IPV, it helps identify cases and connect survivors to resources and supports. However, this can be challenging as a KFF survey of OBGYNs found that many clinicians say they do not have sufficient resources within their practices to provide follow-up services when cases of IPV are identified. Connections to community-based services are particularly important for clinicians to be able to care for patients who disclose IPV.