
The independent source for health policy research, polling, and news.
New Kaiser/New York Times Survey Finds One in Five Working-Age Americans With Health Insurance Report Problems Paying Medical Bills
Among the Insured with Medical Bill Problems, 63% Report Using Up Most or All Their Savings and 42% Took on an Extra Job or Worked More Hours
Half of People Without Health Insurance Report Problems With Medical Bills, and They Face Similar Financial and Personal Consequences As Those With Insurance
Among people with health insurance, one in five (20%) working-age Americans report having problems paying medical bills in the past year that often cause serious financial challenges and changes in employment and lifestyle, finds a comprehensive new Kaiser Family Foundation/New York Times survey. As expected, the situation is even worse among people who are uninsured: half (53%) face problems with medical bills, bringing the overall total to 26 percent.
While insurance can protect people from problem medical bills, the survey suggests that those with employer coverage or other insurance suffer similar consequences as the uninsured once such problems occur. Among those facing problems with medical bills, almost identical shares of the insured (44%) and uninsured (45%) say the bills had a major impact on their families.
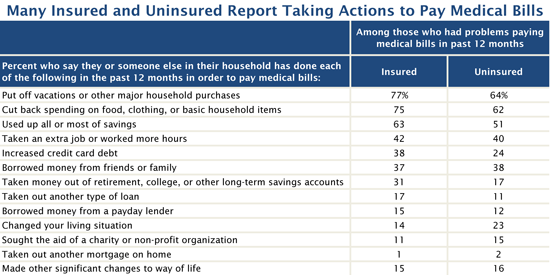
People with insurance who face problem medical bills also report a wide range of consequences and sacrifices during the past year as a result, including delaying vacations or major household purchases (77%), spending less on food, clothing and basic household items (75%), using up most or all their savings (63%), taking an extra job or working more hours (42%), increasing their credit card debt (38%), borrowing money from family or friends (37%), changing their living situation (14%), and seeking the aid of a charity (11%). These shares generally are as large as or larger than the shares among uninsured people with problem medical bills.
Overall, 62 percent of those who had medical bill problems say the bills were incurred by someone who had health coverage at the time (most often through an employer). Of those who were insured when the bills were incurred, three-quarters (75%) say that the amount they had to pay for their insurance copays, deductibles, or coinsurance was more than they could afford.
People with health insurance who have problems with medical bills also report skipping or putting off other health care in the past year because of the cost, such as postponing dental care (62%), skipping doctor-recommended tests or treatments (43%), or not filling a prescription (41%). In general, people with medical bill problems are two to three times as likely to report each of these problems as those without problems paying medical bills.
The Kaiser/Times survey provides an in-depth, quantitative look at the extent and causes of Americans’ medical-debt issues and their impact on people’s lives, families, finances and access to health care. The New York Times is reporting on the findings this week, and the Foundation is issuing a report detailing the survey’s results and implications.
Other findings include:
- Among the insured with problem medical bills, a quarter (26%) say they received unexpected claim denials; and about a third (32%) say they received care from an out-of-network provider that their insurance wouldn’t cover. The out-of-network charges were a surprise for a large majority: 69 percent were unaware that the provider was not in their plan’s network when they received the care.
- Among those with private insurance, those in higher deductible plans are more likely to report medical bill problems than those in plans with lower deductibles (26% versus 15%).
- Most (61%) of those with medical bill problems say they’ve had difficulty paying other bills as a result of their medical debt, and more than a third (35%) say they were unable to pay for basic necessities like food, heat, or housing. Almost six in ten of those with problems paying medical bills (58%) say they’ve been contacted by a collection agency in the past year. Those who faced medical bill problems with and without insurance are about equally likely to report each of these situations.
- Among those with medical bill problems, 31 percent say the total reached at least $5,000, including 13 percent who say the total reached at least $10,000. Significant shares also report having problems with smaller totals, including one in four (24%) who say their bills totaled less than $1,000.
- Relatively small amounts pose major problems for some families because they are living paycheck to paycheck. Of all those with medical bill problems, most (61%) say they are either just meeting their basic expenses (43%) or aren’t able to do so (18%). While people without health insurance are more likely to find themselves in such circumstances, more than half (55%) of those with insurance who have medical bill problems say they are either just getting by or don’t have enough to make ends meet.
- People who have had difficulty paying medical bills are more likely to report taking a variety of extra steps to negotiate prices or shop around for health care than their peers. However, for those with medical bill problems, seven in ten (69%) of those who shopped around for a lower price say it was difficult to find out how much they would have to pay, and a similar share (67%) of those who attempted to negotiate price with a provider say their efforts were unsuccessful.
Teams from the Foundation and The Times worked together to develop the questionnaire and analyze the data. Each organization is solely responsible for the content it publishes based on the survey. The survey was conducted from Aug. 28 through Sept. 28 among a national probability-based sample of 2,575 adults ages 18-64, including 1,204 who reported problems paying medical bills and 1,371 who did not. Interviews were conducted online and by telephone in English and Spanish. The margin of sampling error is plus or minus 3 percentage points for the full sample, and plus or minus 4 percentage points both for those with and without problems paying medical bills. Among those with medical bill problems, the margin of sampling error is plus or minus 5 percentage points for those with insurance and plus or minus 8 percentage points for those without insurance.