KFF Health Tracking Poll – January 2019: The Public On Next Steps For The ACA And Proposals To Expand Coverage
Key Findings:
- Half of the public disapproves of the recent decision in Texas v. United States, in which a federal judge ruled that the 2010 Affordable Care Act (ACA) is unconstitutional and should not be in effect. While the judge’s ruling is broader than eliminating the ACA’s protections for people with pre-existing conditions, this particular issue continues to resonate with the public. Continuing the ACA’s protections for people with pre-existing conditions ranks among the public’s top health care priorities for the new Congress, along with lowering prescription drug costs.
- This month’s KFF Health Tracking Poll continues to find majority support (driven by Democrats and independents) for the federal government doing more to help provide health insurance for more Americans. One way for lawmakers to expand coverage is by broadening the role of public programs. Nearly six in ten (56 percent) favor a national Medicare-for-all plan, but overall net favorability towards such a plan ranges as high as +45 and as low as -44 after people hear common arguments about this proposal.
- Larger majorities of the public favor more incremental changes to the health care system such as a Medicare buy-in plan for adults between the ages of 50 and 64 (77 percent), a Medicaid buy-in plan for individuals who don’t receive health coverage through their employer (75 percent), and an optional program similar to Medicare for those who want it (74 percent). Both the Medicare buy-in plan and Medicaid buy-in plan also garner majority support from Republicans (69 percent and 64 percent).
- Moving forward, half of Democrats would rather see the new Democratic majority in the U.S. House of Representatives focus their efforts on improving and protecting the ACA (51 percent), while about four in ten want them to focus on passing a national Medicare-for-all plan (38 percent).
Texas v. United States: The Future of the Affordable Care Act
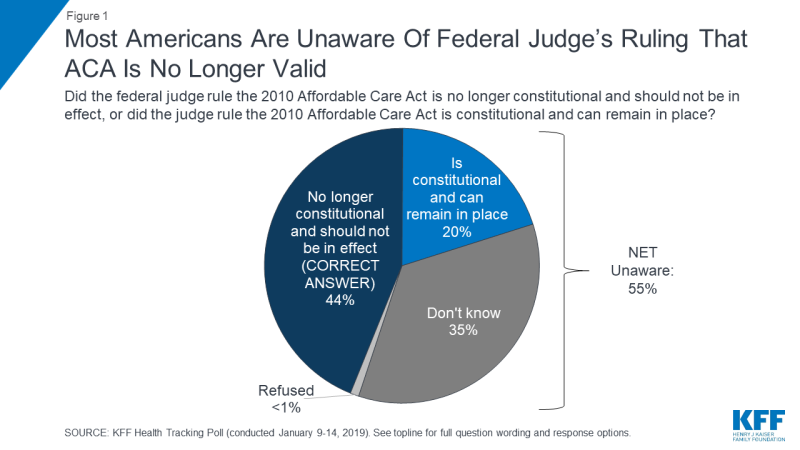
On December 14, 2018, a federal district court judge in Texas issued a ruling challenging the future of the 2010 Affordable Care Act (ACA).The judge sided with Republican state attorneys general and ruled that, since the 2017 tax bill passed by Congress zeroed out the penalty for not having health insurance, the ACA is invalid. Democrat attorneys general have already taken actions to appeal the judge’s ruling in the case and, due to the government shutdown, the 5th Circuit Court of Appeals has paused the case. Currently, the ACA remains the law of the land. If this ruling is upheld, the consequences will be far-reaching.1 Less than half of the public (44 percent) are aware of the judge’s ruling that the ACA is unconstitutional and most (55 percent) either incorrectly say that the judge ruled in favor of the ACA (20 percent) or are unsure (35 percent).
Overall, a larger share of the public disapprove (51 percent) than approve (41 percent) of the judge’s ruling that the ACA is not constitutional. This is largely divided by party identification with a majority of Republicans (81 percent) approving of the decision while a majority of Democrats disapproving (84 percent). Independents are closely divided (49 percent disapprove v. 44 percent approve).
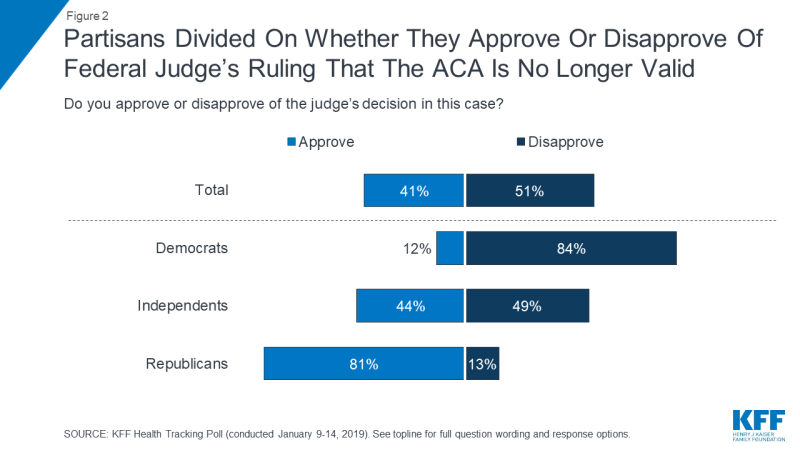
Figure 2: Partisans Divided On Whether They Approve Or Disapprove Of Federal Judge’s Ruling That The ACA Is No Longer Valid
The Trump administration had originally announced that as part of Texas v. United States, it would no longer defend the ACA’s protections for people with pre-existing medical conditions. While the judge’s ruling was broader than just the ACA’s pre-existing condition protections, KFF polling finds attitudes can shift when the public hears that these protections may no longer exist. Among those who originally approve of the federal judge’s ruling, about three in ten (13 percent of the public overall) change their mind after hearing that this means that people with pre-existing conditions may have to pay more for coverage or could be denied coverage, bringing the share who disapprove of the judge’s ruling to nearly two-thirds (64 percent) of the public.2
Fewer – but still about one-fifth (8 percent of total) – change their minds after hearing that as a result of this decision, young adults would no longer be able to stay on their parents’ insurance until the age of 26, bringing the total share who disapprove of the judge’s ruling to 60 percent.
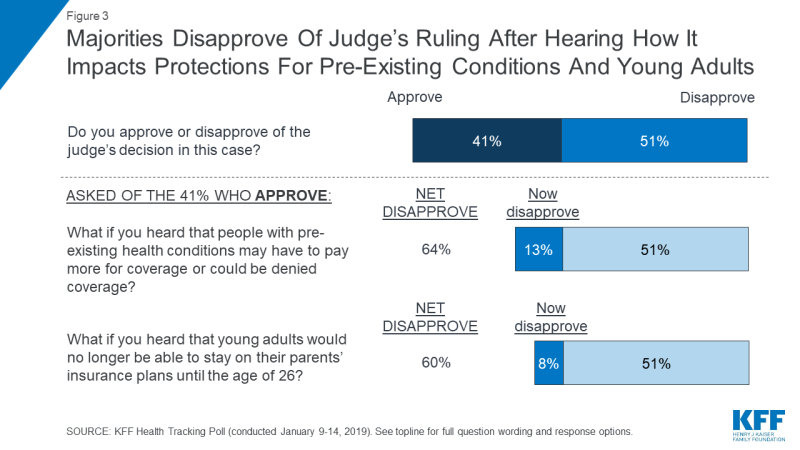
Figure 3: Majorities Disapprove Of Judge’s Ruling After Hearing How It Impacts Protections For Pre-Existing Conditions And Young Adults
Overall, a slight majority of the public hold a favorable view of the ACA (51 percent) while four in ten continue to hold unfavorable views. (INTERACTIVE)
Public’s Views of Democratic Health Care Agenda
With the new Democratic majority in the U.S. House of Representatives, this month’s KFF Health Tracking Poll examines the public’s view of Congressional health care priorities including a national health plan.
Proposals to Expand Health Care Coverage
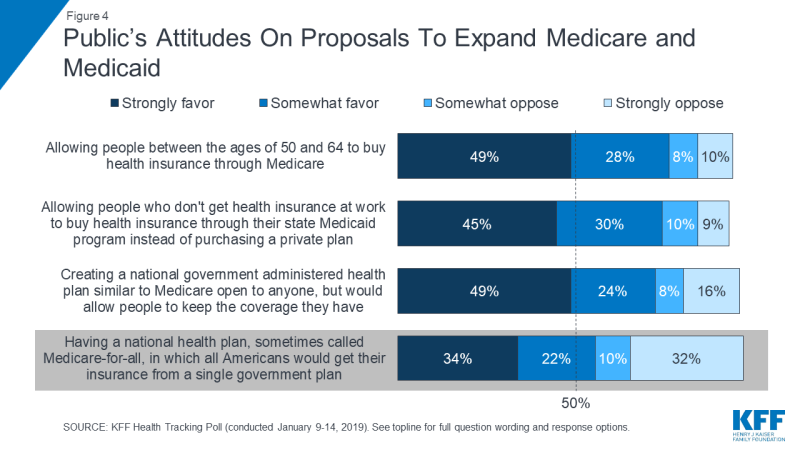
Most of the public favor the federal government doing more to help provide health insurance for more Americans and one way for lawmakers to expand coverage is by broadening the role of public programs, such as Medicare or Medicaid. The Kaiser Family Foundation has been tracking public opinion on the idea of a national health plan since 1998 (see slideshow). More than twenty years ago, about four in ten Americans (42 percent) favored a national health plan in which all Americans would get their insurance from a single government plan. In the decades that followed, there has been a modest increase in support – especially since the 2016 presidential election and Bernie Sanders’ rallying cry for “Medicare-for-all.” The most recent KFF Health Tracking Poll finds 56 percent of the public favor “a national health plan, sometimes called Medicare-for-all, where all Americans would get their insurance from a single government plan” with four in ten (42 percent) opposing such a plan.
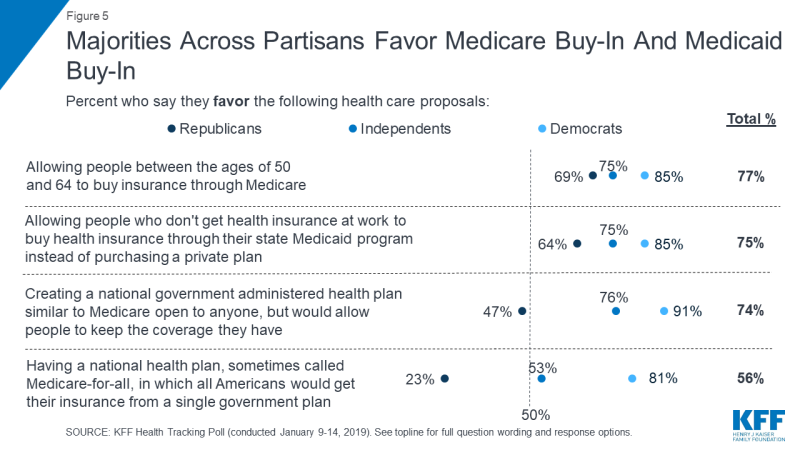
Larger majorities favor more incremental changes to the health care system including a Medicare buy-in plan for adults between the ages of 50 and 64 (77 percent), a Medicaid buy-in plan for individuals who don’t receive health coverage through their employer (75 percent), and an optional program similar to Medicare for those who want it (74 percent).
A majority of Democrats and independents favor all of these proposals, but only the Medicare buy-in plan for adults 50 and older and the Medicaid buy-in for individuals who don’t receive health coverage through their employer receive a majority of support from Republicans (69 percent and 64 percent, respectively).
MALLEABILITY in Attitudes Towards National Health Plan and Lingering Confusion About Possible Impacts
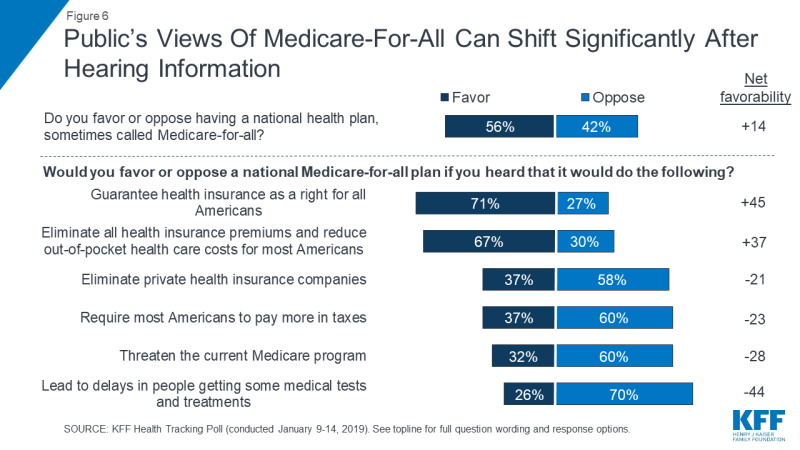
This month’s KFF Health Tracking Poll finds the net favorability of attitudes towards a national Medicare-for-all plan can swing significantly, depending on what arguments the public hears.
Net favorability towards a national Medicare-for-all plan (measured as the share in favor minus the share opposed) starts at +14 percentage points and ranges as high as +45 percentage points when people hear the argument that this type of plan would guarantee health insurance as a right for all Americans. Net favorability is also high (+37 percentage points) when people hear that this type of plan would eliminate all premiums and reduce out-of-pocket costs. Yet, on the other side of the debate, net favorability drops as low as -44 percentage points when people hear the argument that this would lead to delays in some people getting some medical tests and treatments. Net favorability is also negative if people hear it would threaten the current Medicare program (-28 percentage points), require most Americans to pay more in taxes (-23 percentage points), or eliminate private health insurance companies (-21 percentage points).
While most Americans (77 percent) are aware they would have to pay more in taxes to cover the cost of health insurance if a national Medicare-for-all plan was put into place, there is some confusion about whether people would be able to keep their current health insurance. Most people under the age of 65 and who currently have employer-sponsored insurance say that if a national health plan was put into place, they would be able to keep their current coverage (55 percent) while about four in ten (37 percent) are aware they would not be able to keep their current coverage.
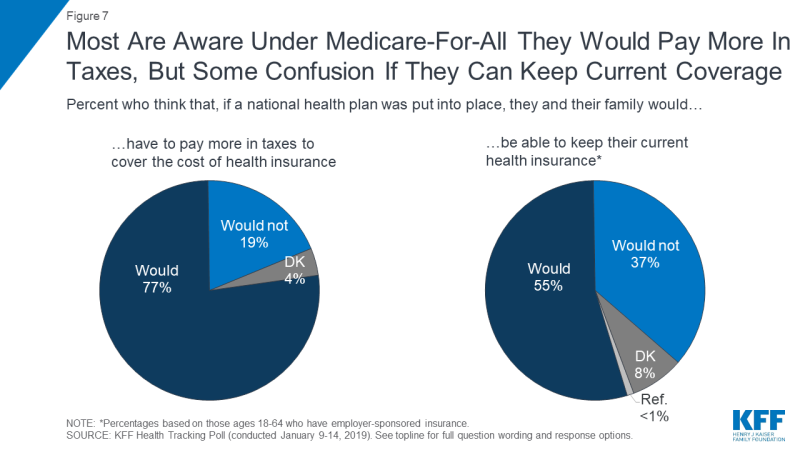
Figure 7: Most Are Aware Under Medicare-For-All They Would Pay More In Taxes, But Some Confusion If They Can Keep Current Coverage
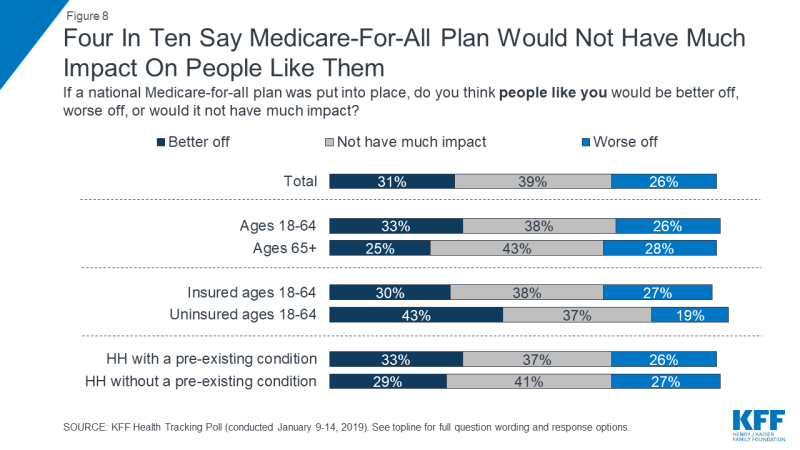
And while majorities say low-income people and people who currently don’t have health insurance would be “better off” if a national Medicare-for-all plan was put into place, there is less certainty among the public about how much it would impact them, personally. Across demographic groups, about four in ten say that if a national Medicare-for-all plan was put into place it “would not have much impact” on them.
Medicare-for-all And Seniors
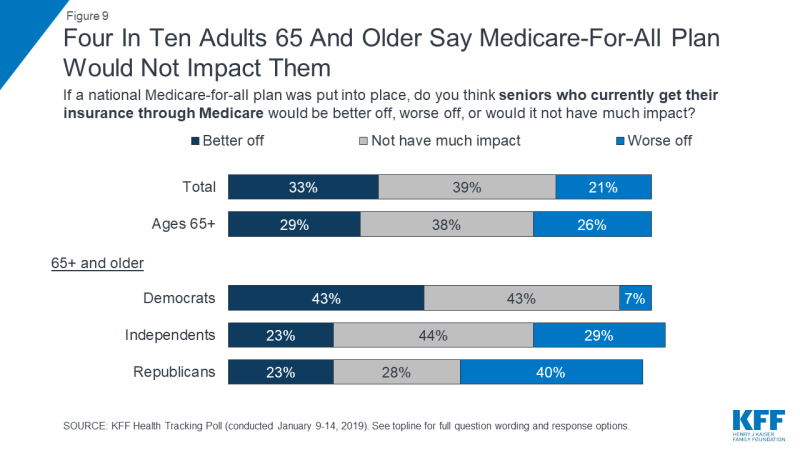
On October 10th, 2018, President Trump wrote an op-ed in USA Today arguing that a Medicare-for-all plan would “end Medicare as we know it and take away benefits they have paid for their entire lives.”3 One-fourth of adults 65 and older (26 percent) say seniors who currently get their insurance through Medicare would be “worse off” if a national Medicare-for-all plan was put into place. Four in ten Republicans, ages 65 and older, say seniors who currently get health coverage through Medicare would be “worse off” under a national Medicare-for-all plan. Overall, a larger share of the public say a Medicare-for-all plan will “not have much impact” on seniors (39 percent) or say that they would be “better off” (33 percent) than say seniors would be “worse off” (21 percent).
Democrats Want Democratic Lawmakers to Focus on ACA Rather than Medicare-for-all
Despite the recent attention on proposals to expand Medicare or Medicaid, when asked to choose Democrats would rather the new Democratic majority in the U.S. House of Representatives focus their efforts on “improving and protecting the ACA” rather than “passing a national Medicare-for-all plan.” Half (51 percent) of Democrats say House Democrats should focus on the ACA while four in ten (38 percent) say they should focus on passing a national Medicare-for-all plan. The share of Democrats who want Congress to focus on passing a national Medicare-for-all plan is down 10 percentage points from March 2018.
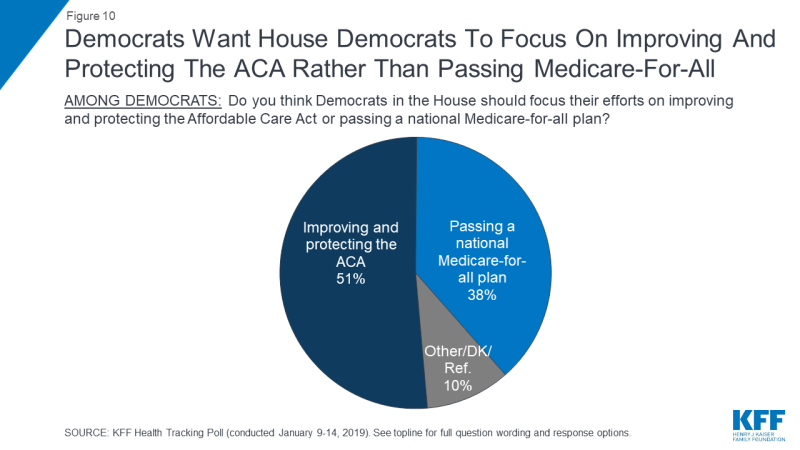
Figure 10: Democrats Want House Democrats To Focus On Improving And Protecting The ACA Rather Than Passing Medicare-For-All
Partisans Have different health priorities for Congress, Except for Prescription Drug Prices
A majority of the public say it is either “extremely important” or “very important” that Congress work on lowering prescription drug costs for as many Americans as possible (82 percent), making sure the ACA’s protections for people with pre-existing health conditions continue (73 percent), and protecting people with health insurance from surprise high out-of-network medical bills (70 percent). Fewer – about four in ten – say repealing and replacing the ACA (43 percent) and implementing a national Medicare-for-all plan (40 percent) are an “extremely important” or “very important” priority. When forced to choose the top Congressional health care priorities, the public chooses continuing the ACA’s pre-existing condition protections (21 percent) and lowering prescription drug cost (20 percent) as the most important priorities for Congress to work on. Smaller shares choose implementing a national Medicare-for-all plan (11 percent), repealing and replacing the ACA (11 percent), or protecting people from surprise medical bills (9 percent) as a top priority. One-fourth said none of these health care issues was their top priority for Congress to work on.
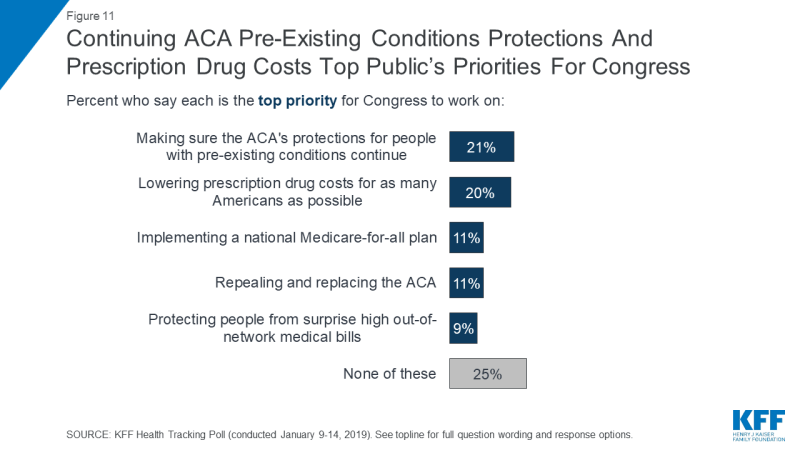
Figure 11: Continuing ACA Pre-Existing Conditions Protections And Prescription Drug Costs Top Public’s Priorities For Congress
Continuing the ACA’s pre-existing condition protections is the top priority for Democrats (31 percent) and ranks among the top priorities for independents (24 percent) along with lowering prescription drug costs, but ranks lower among Republicans (11 percent). Similar to previous KFF Tracking Polls, repealing and replacing the ACA remains one of the top priority for Republicans (27 percent) along with prescription drug costs (20 percent).
| Table 1: Pre-Existing Condition Protections and Prescription Drug Costs Top Public’s Health Care Priorities for Congress; Republicans Still Focused on ACA Repeal | ||||
| Percent who say the following is the top priority for Congress to work on: | Total | Democrats | Independents | Republicans |
| Making sure the ACA’s pre-existing condition protections continue | 21% | 31% | 24% | 11% |
| Lowering prescription drug costs for as many Americans as possible | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Implementing a national Medicare-for-all plan | 11 | 20 | 8 | 3 |
| Repealing and replacing the ACA | 11 | 3 | 7 | 27 |
| Protecting people from surprise high out-of-network medical bills | 9 | 4 | 10 | 8 |
| Note: If more than one priority was chosen as “extremely important,” respondent was forced to choose which priority was the “most important.” | ||||
The Role of Independents in the Democratic Health Care Debate
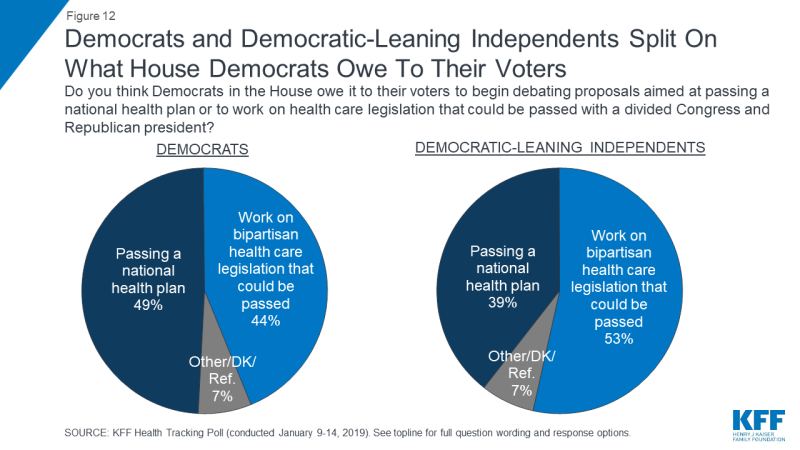
One of the major narratives coming out of the 2018 midterm elections was the role that health care was playing in giving Democratic candidates the advantage in close Congressional races. Consistently throughout the election cycle, KFF polling found health care as the top campaign issue for both Democratic and independent voters. While a majority of Democrats want the new Democratic majority in the U.S. House of Representatives to focus on improving and protecting the ACA, Democratic-leaning independents have more divided opinions of the future of 2010 health care law. These individuals – who tend to be younger and male – would rather Democrats in Congress focus efforts on passing a national Medicare-for-all plan (54 percent) than improving the ACA (39 percent) – which is counter to what Democrats overall report. In addition, when asked whether House Democrats owe it to their voters to begin debating proposals aimed at passing a national health plan or work on health care legislation that can be passed with a divided Congress and a Republican President, Democrats are divided (49 percent v. 44 percent) while Democratic-leaning independents prioritize House Democrats working on bipartisan health care legislation (53 percent) over debating national health plan proposals (39 percent).