The independent source for health policy research, polling, and news.
State Medicaid Officials Anticipate the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency Will End During State FY 2023, Leading to Medicaid Enrollment Declines, Slower Total Medicaid Spending Growth and a Sharp Rise in States’ Share of Costs
The Pandemic Has Shaped States’ Medicaid Policy Priorities to Include Focuses on Reducing Disparities, Preserving Telehealth, and Boosting Access to Behavioral Health Services, Annual Survey Finds
After steep gains since 2020, state Medicaid agencies expect Medicaid enrollment to begin to decline in FY 2023, following the expiration of the COVID-19 public health emergency (PHE), which most states assumed would occur during FY 2023, according to KFF’s new state Medicaid budget survey.
Projections of declining enrollment tied to the end of the federal continuous enrollment requirement are also expected to translate into slower total Medicaid spending growth in FY 2023. At the same time, the loss of temporary pandemic-era enhanced federal matching funding is expected to result in a rebalancing of the mix of federal and state spending, increasing state spending even though total Medicaid spending growth is expected to slow. Medicaid officials reported that uncertainty related to the end of the PHE makes it difficult for states to plan for unwinding of the PHE and to develop state budgets.
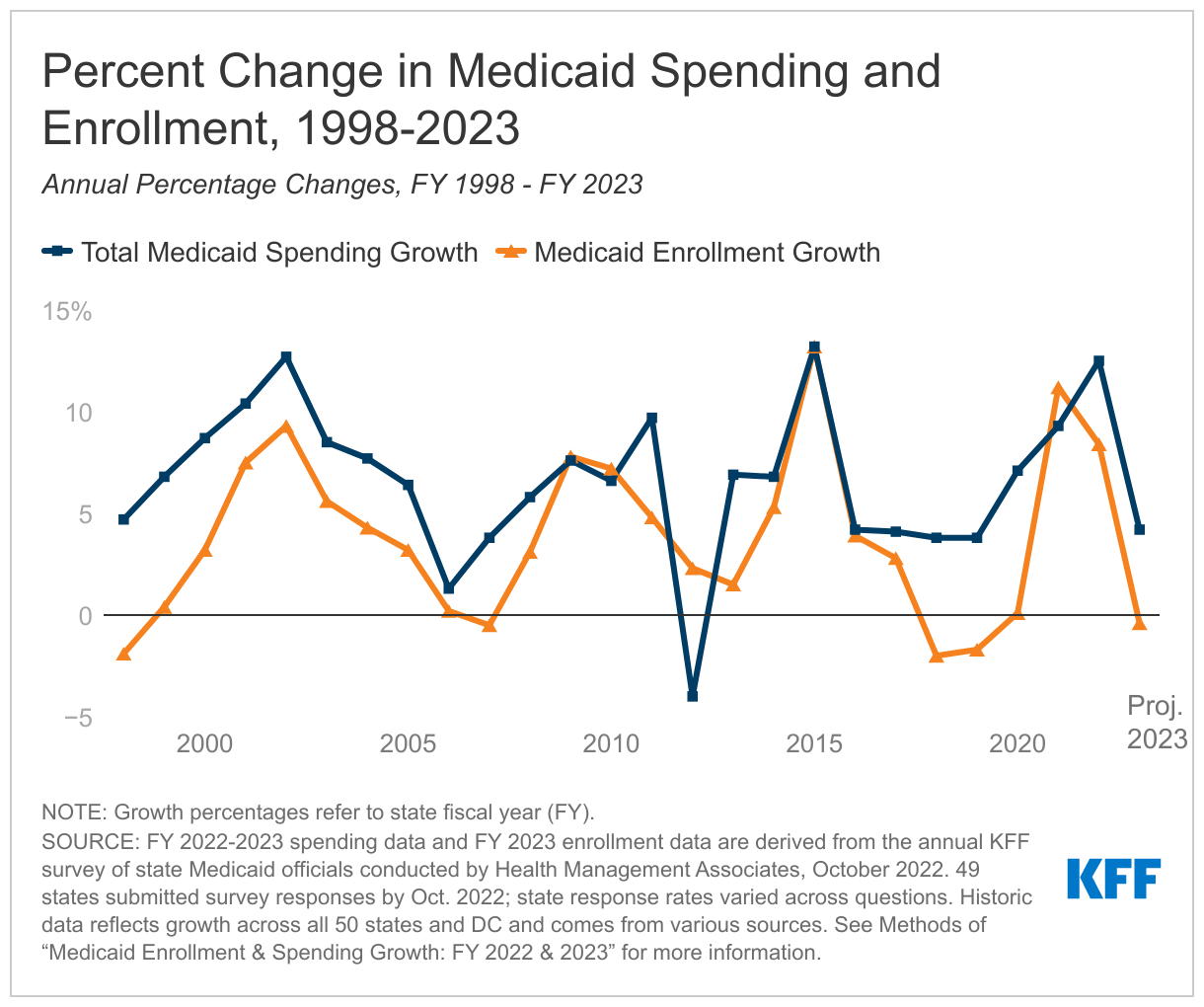
The 22nd annual survey of state Medicaid directors finds that states expect growth in Medicaid enrollment to slow to 8.4 percent in FY 2022 (down from 11.2 percent the previous year) before declining by 0.4 percent in FY 2023.
Enrollment declines are likely to accelerate over time, as many states anticipated the public health emergency and continuous coverage requirement to run until the end of this calendar year, midway through fiscal year 2023 for most states. The Biden Administration recently announced that the PHE will go until mid-January, and has promised to give states 60 days notice before ending the emergency declaration.
The survey also finds that total Medicaid spending growth – federal and state spending combined – is expected to peak at 12.5 percent in FY 2022, before slowing to 4.2 percent in FY 2023. State Medicaid officials reported that the state (nonfederal) share of Medicaid spending grew by 9.9 percent in FY 2022. They projected sharper state spending growth of 16.3 percent in FY 2023 with the federal government expected to end its temporary enhanced funding.
In addition to enrollment growth, other drivers of increased Medicaid spending reported by state Medicaid agencies included inflationary pressures, increased service utilization, and increased home and community-based services (HCBS) spending.
The survey, conducted by analysts at KFF and Health Management Associates, provides an annual look at Medicaid enrollment and spending trends, currently for state fiscal years 2022 and 2023. Forty-nine states responded to the survey, although response rates for specific questions varied. A companion survey report offers an in-depth, state-specific examination of policies in place in state Medicaid programs, as well important changes and initiatives taking place around the country.
While states continue to respond to pandemic-related health issues such as increasing vaccination and booster rates and treating long-COVID, states also reported actions to focus on longstanding issues and new priorities including improving equity and reducing health disparities, maintaining access to telehealth, improving behavioral health access and supports, and addressing workforce challenges.
Some notable findings from the report include:
- Health Equity. Advancing health equity is an important longstanding priority that has been elevated during the pandemic. Two-thirds of states reported using at least one strategy to improve race, ethnicity, and language (REL) data completeness. About one quarter of states reported use of financial incentives linked to health equity, mostly in Medicaid managed care arrangements.
- Benefits: States reported far more benefit expansions than benefit cuts in both FY 2022 and FY 2023. States are particularly focused on service expansions across the behavioral health care continuum as well as expansions of pregnancy and postpartum services. Other areas of benefit expansion include preventive services, dental services, and services to address enrollees’ social needs (such as food and housing needs).
- Telehealth. States noted that expanded telehealth policies increased access to care during the COVID-19 pandemic and resulted in high telehealth utilization across populations. Most states have implemented or are planning initiatives to assess telehealth quality and to address other telehealth challenges (including access to technology and broadband, program integrity, outreach and education, and equity). Most states have or plan to adopt permanent Medicaid telehealth policy expansions that will remain in place even after the pandemic, though some are considering adding limitations or guardrails.
- Managed Care. More than three quarters of states that contract with managed care organizations (MCOs) reported that 75 percent or more of their Medicaid beneficiaries were enrolled in MCOs as of July 1, 2022. In FY 2022, North Carolina implemented its first MCO program. Missouri enrolled all ACA expansion adults in Medicaid MCOs when it implemented the ACA Medicaid expansion in October 2021.
- Provider Rates. Provider rate increases outnumbered rate restrictions for fee-for-service in FY 2022 and FY 2023. Increases were more common for nursing facilities and home and community-based services (HCBS) providers than for other provider categories. While most states rely on capitated arrangements with managed care organizations to deliver Medicaid services, fee-for-service rates remain important payment benchmarks for managed care payments. Many states noted that worsening inflation and workforce shortages driving higher labor costs were resulting in pressure for rate increases. Some states noted that adopted FY 2023 budgets do not account for current inflation levels, though inflation remains a concern.
- Looking Ahead. States are preparing for challenges tied to the unwinding of the continuous enrollment requirements and the expiration of other emergency authorities in place during the PHE. In addition, states were facing fiscal uncertainty due to slower revenue growth projections, rising inflation, and workforce shortages as well as potential shifts in political landscapes, as 36 states await the results of gubernatorial elections in November 2022, with outcomes that could have implications for state Medicaid policies and for Medicaid enrollees.
The survey is to be discussed today at Noon ET during a web briefing held by KFF with the National Association of Medicaid Directors. The two new reports released today in advance of the briefing are:
Medicaid Enrollment & Spending Growth: FY 2022 & 2023
For more data and analyses about Medicaid, visit kff.org.