Public Opinion Snapshot on Health Information Sources – July 2005
While Americans of all ages are most likely to get information about health and health care mainly from traditional media sources, there are significant generational differences in their reliance on other sources of health information, according to the latest Kaiser Health Poll Report survey.
For example, younger Americans are more likely than older adults to say they get health information from friends and family (25% of ages 18-29, versus 13% of ages 30-49 and 9% of ages 50 and over). Older adults are more likely to rely on doctors or other health professionals (27% of ages 50 and over, versus 14% of ages 18-29 and 16% of ages 30-49).
The Internet is also a more popular source of health information among younger adults. About one in 10 adults ages 18-29 (12%) and ages 30-49 (10%) say the Internet is their main source for health information, compared with just 4% of adults ages 50 and over.
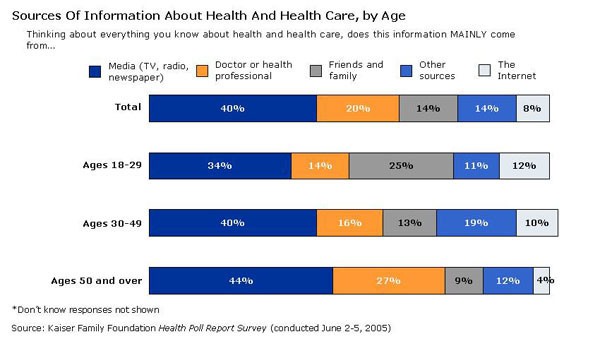
Overall, the Kaiser Health Poll Report survey finds that four in 10 (40%) of all adults say their information about health and health care comes mainly from traditional media sources such as TV, radio and newspapers. Two in 10 (20%) adults say doctors and other health professionals are their main source for health information, while fewer than one in ten (8%) get this information primarily from the Internet. Findings for the current survey are based on a national random sample of 1,202 adults conducted June 2-5, 2005. The margin of sampling error is +/- 3 %. Complete topline results for the survey are available online.
