2022 Employer Health Benefits Survey
Section 10: Plan Funding
Many firms, particularly larger firms, choose to pay for some or all of the health services of their workers directly from their own funds rather than by purchasing health insurance for them. This is called self-funding. Both public and private employers can use self-funding to provide health benefits. Federal law (the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, or ERISA) exempts self-funded plans established by private employers (but not public employers) from most state insurance laws, including reserve requirements, mandated benefits, premium taxes, and many consumer protection regulations. Sixty-five percent of covered workers are in a self-funded health plan in 2022. Self-funding is common among larger firms because they can spread the risk of costly claims over a large number of workers and dependents. Some employers which sponsor self-funded plans purchase stoploss coverage to limit their liabilities.
In recent years, a complex funding option, often called level-funding, has become more widely available to small employers. Level-funded arrangements are nominally self-funded options that package together a self-funded plan with extensive stoploss coverage that significantly reduces the risk retained by the employer. Thirty-five percent of covered workers in small firms (3-199 workers) are in a level-funded plan.
SELF-FUNDED PLANS
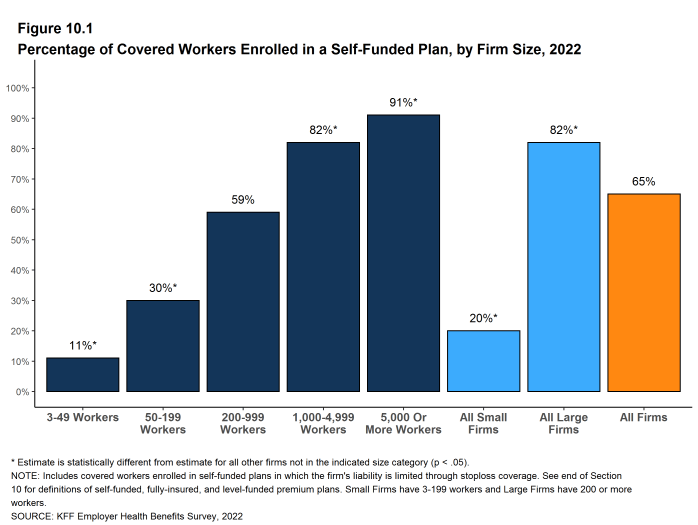
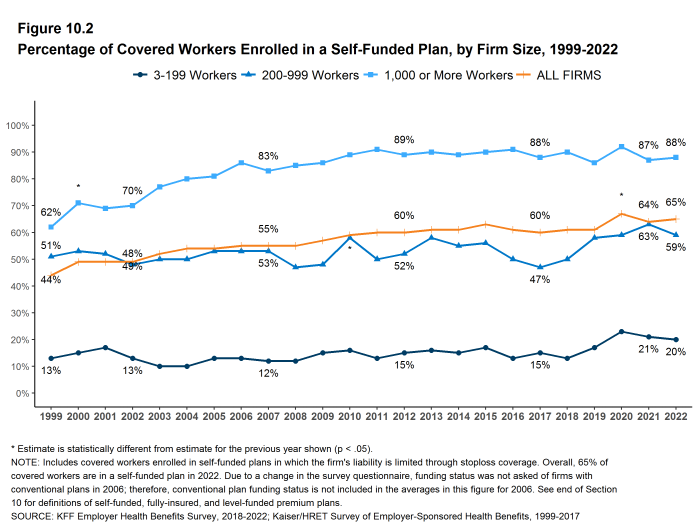
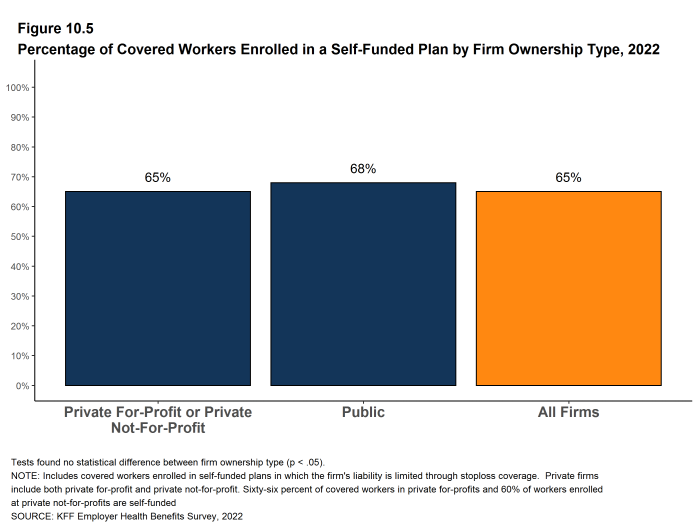
- Sixty-five percent of covered workers are in a plan that is self-funded, similar to the percentage (64%) last year [Figure 10.1] and [Figure 10.2].
- The percentage of covered workers enrolled in self-funded plans is higher than the percentage ten years ago (60%) [Figure 10.2].
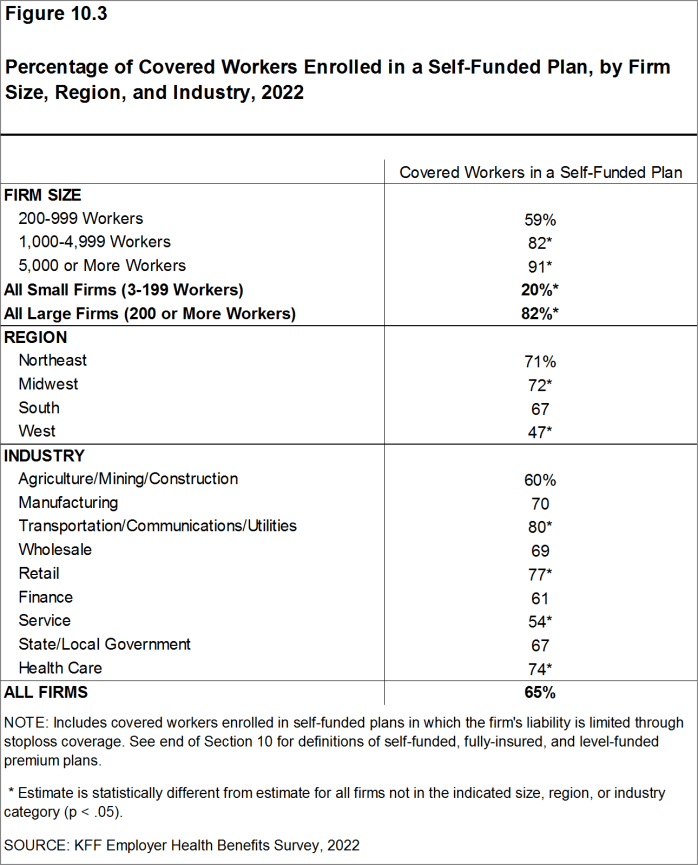
- As expected, covered workers in large firms are significantly more likely to be in a self-funded plan than covered workers in small firms (82% vs. 20%) [Figure 10.1] and [Figure 10.3].
Figure 10.3: Percentage of Covered Workers Enrolled in a Self-Funded Plan, by Firm Size, Region, and Industry, 2022
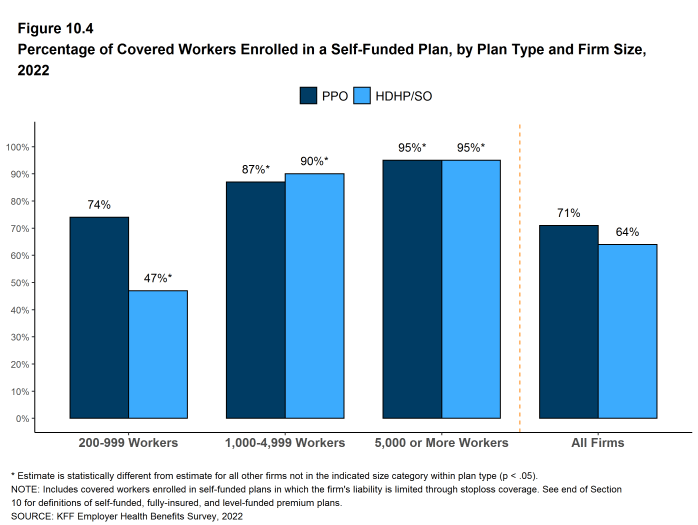
Figure 10.4: Percentage of Covered Workers Enrolled in a Self-Funded Plan, by Plan Type and Firm Size, 2022
LEVEL-FUNDED PLANS
In the past few years, insurers have begun offering health plans that provide a nominally self-funded option for small or mid-sized employers that incorporates stoploss insurance with relatively low attachment points. Often, the insurer calculates an expected monthly expense for the employer, which includes a share of the estimated annual cost for benefits, premium for the stoploss protection, and an administrative fee. The employer pays this “level premium” amount, with the potential for some reconciliation between the employer and the insurer at the end of the year, if claims differ significantly from the estimated amount. These policies are sold as self-funded plans, so they generally are not subject to state requirements for insured plans and, for those sold to employers with fewer than 50 employees, are not subject to the rating and benefit standards in the ACA for small firms.
Due to the complexity of the funding (and regulatory status) of these plans, and because employers often pay a monthly amount that resembles a premium, respondents may be confused as to whether or not their health plan is self-funded or insured. We asked employers with fewer than 200 workers whether they have a level-funded plan.
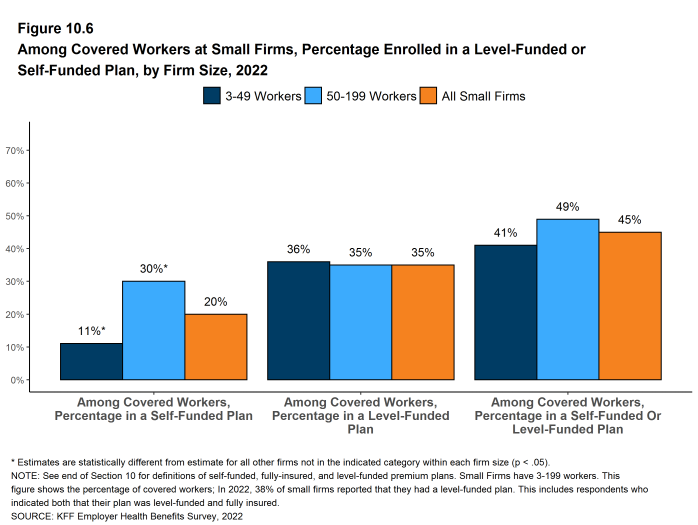
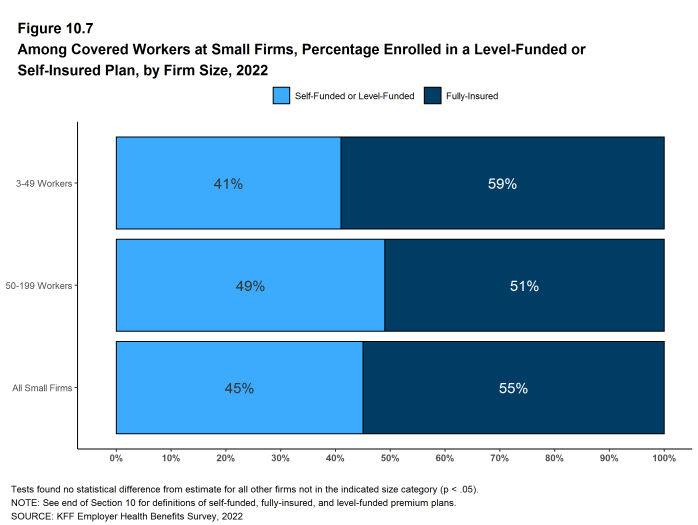
- Thirty-eight percent of small firms report offering health benefits offer a level-funded plan in 2022, similar to the percentage (42%) last year. Last year we reported a substantial increase from 2020, so it is possible that the instability reflects some uncertainty among respondents over the type of plan that they have. These arrangements are complex and are labeled differently by different carriers, so they are difficult to describe them accurately to respondents. We modified our survey question somewhat for 2022 to provide more examples of how these plans are labeled in the market, although we may have expected this to increase rather than decrease the reported prevalence. That said, this is an important development in the small group market so we will continue to monitor the prevalence of these plans [Figure 10.6].
Figure 10.6: Among Covered Workers at Small Firms, Percentage Enrolled in a Level-Funded or Self-Funded Plan, by Firm Size, 2022
STOPLOSS COVERAGE
Employers purchase insurance, often referred to as “stoploss” coverage, to limit the amount that they may have to pay for claims in a self-funded plan. There are different types of stoploss; for example a stoploss policy may cover any amount that the plan sponsor must pay over a specified amount for each worker or enrollee (referred to as specific stoploss coverage) or it may limit the total amount the plan sponsor must pay for all claims in the plan over the plan year (referred to as aggregate stoploss coverage). Stoploss coverage also could be focused on particular types of claims. A firm may have more than one type of stoploss coverage.
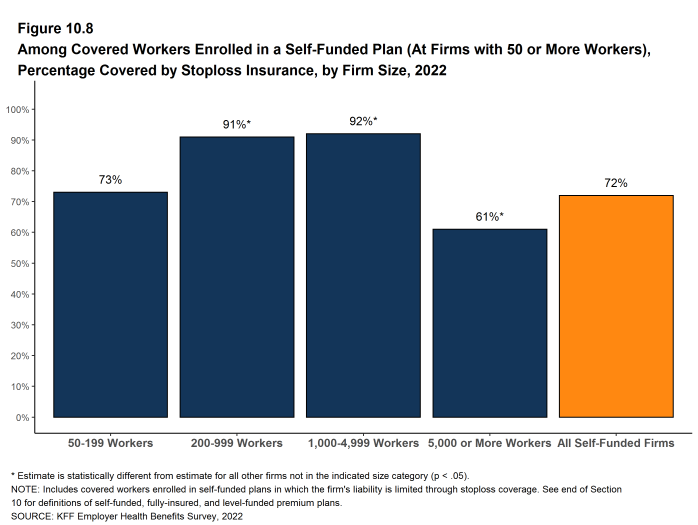
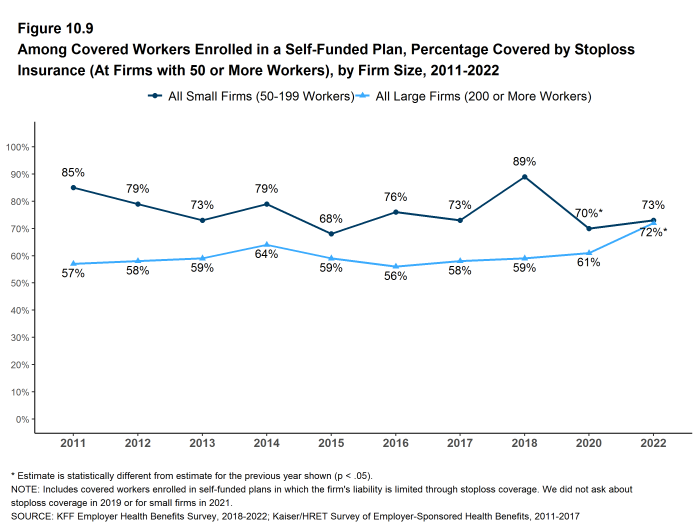
- At large firms (200 or more workers), 72% of covered workers in self-funded health plans are in plans that have stoploss insurance [Figure 10.8]. The percentage this year is not significantly higher than the percentage last year (62%) but is higher than the percentages in other recent years (61% in 2020) and (59% in 2018) [Figure 10.9].
Figure 10.8: Among Covered Workers Enrolled in a Self-Funded Plan (At Firms With 50 or More Workers), Percentage Covered by Stoploss Insurance, by Firm Size, 2022
Figure 10.9: Among Covered Workers Enrolled in a Self-Funded Plan, Percentage Covered by Stoploss Insurance (At Firms With 50 or More Workers), by Firm Size, 2011-2022
Self-Funded Plan An insurance arrangement in which the employer assumes direct financial responsibility for the costs of enrollees’ medical claims. Employers sponsoring self-funded plans typically contract with a third-party administrator or insurer to provide administrative services for the self-funded plan. In some cases, the employer may buy stoploss coverage from an insurer to protect the employer against very large claims.
Fully-Insured Plan An insurance arrangement in which the employer contracts with a health plan that assumes financial responsibility for the costs of enrollees’ medical claims.
Level-Funded Plan An insurance arrangement in which the employer makes a set payment each month to an insurer or third party administrator which funds a reserve account for claims, administrative costs, and premiums for stop-loss coverage. When claims are lower than expected, surplus claims payments may be refunded at the end of the contract.
Stoploss Coverage Stoploss coverage limits the amount that a plan sponsor has to pay in claims. Stoploss coverage may limit the amount of claims that must be paid for each employee or may limit the total amount the plan sponsor must pay for all claims over the plan year.
Attachment Point Attachment points refer to the amount at which the insurer begins to pay its obligations for stoploss coverage, either because plan, individual or claim spending exceed a designated value.