2015 Employer Health Benefits Survey
Section Seven: Employee Cost Sharing
In addition to any required premium contributions, most covered workers face cost sharing for the medical services they use. Cost sharing for medical services can take a variety of forms, including deductibles (an amount that must be paid before most services are covered by the plan), copayments (fixed dollar amounts), and/or coinsurance (a percentage of the charge for services). The type and level of cost sharing often vary by the type of plan in which the worker is enrolled. Cost sharing may also vary by the type of service, such as office visits, hospitalizations, or prescription drugs.
The cost-sharing amounts reported here are for covered workers using services provided in-network by participating providers. Plan enrollees receiving services from providers that do not participate in plan networks often face higher cost sharing and may be responsible for charges that exceed plan allowable amounts. The framework of this survey does not allow us to capture all of the complex cost-sharing requirements in modern plans, particularly for ancillary services (such as durable medical equipment or physical therapy) or cost-sharing arrangements that vary across different settings (such as tiered networks). Therefore, we do not collect information on all plan provisions and limits that affect enrollee out-of-pocket liability.
General Annual Deductibles For Workers in Plans with Deductibles
- A general annual deductible is an amount that must be paid by enrollees before most services are covered by their health plan. Non-grandfathered health plans are required to cover some services such as preventive care without cost sharing. Some plans require enrollees to meet a service-specific deductible such as on prescription drugs or hospital admissions in lieu of or in addition to a general deductible.
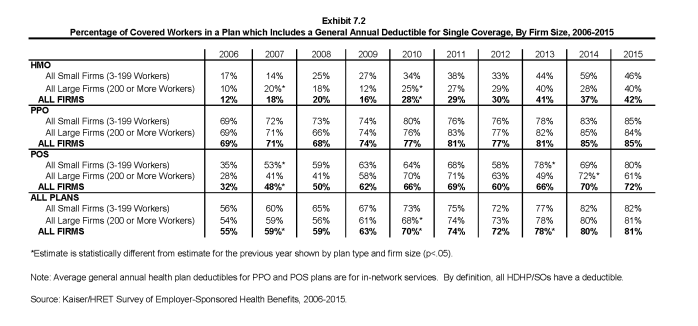
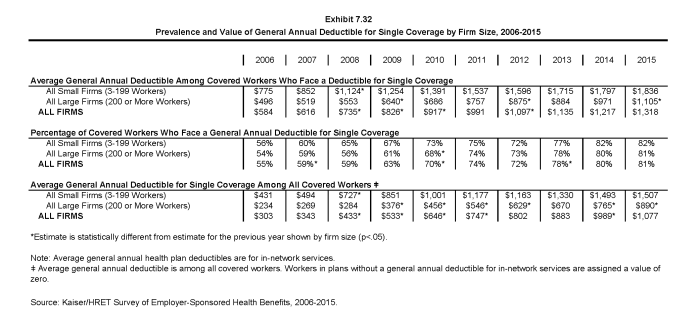
- Eighty-one percent of covered workers are enrolled in a plan with a general annual deductible for single coverage, similar to 80% in 2014. Since 2010, the percentage of covered workers with a general annual deductible for single coverage has increased from 70% to 81% (Exhibit 7.2).
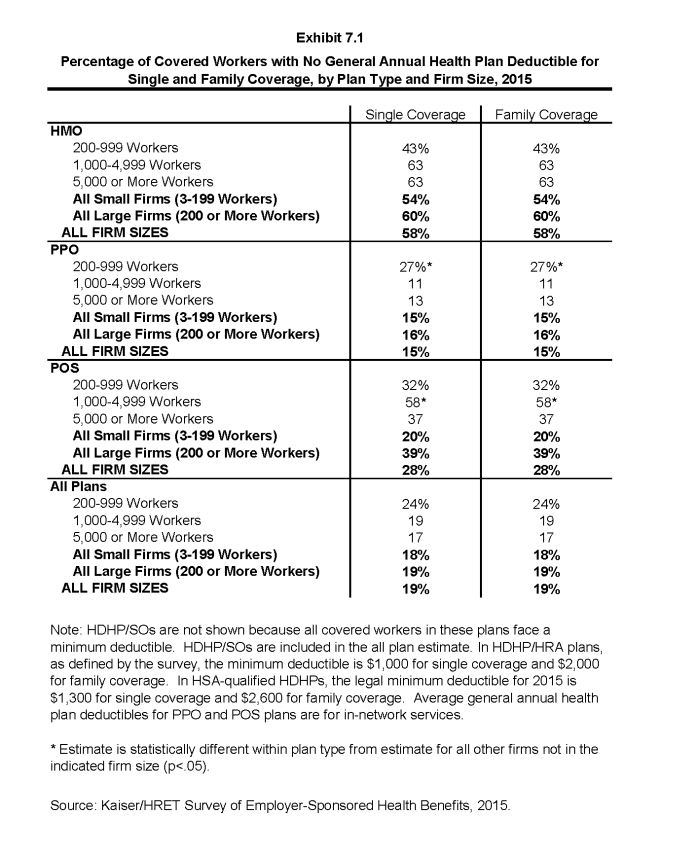
- The percentage of covered workers enrolled in a plan for single coverage without a general annual deductible is similar for small firms (3-199 workers) and large firms (18% and 19%) (Exhibit 7.1).
- The likelihood of having a deductible varies by plan type. Workers in HMOs are less likely to have a general annual deductible for single coverage than workers in other plan types. Fifty-eight percent of workers in HMOs do not have a general annual deductible for single coverage, compared to 28% of workers in POS plans and 15% of workers in PPOs (Exhibit 7.1). The percentage of workers enrolled in HMO plans with a general annual deductible for single coverage has increased from 28% in 2010 to 42% in 2015 (Exhibit 7.2).
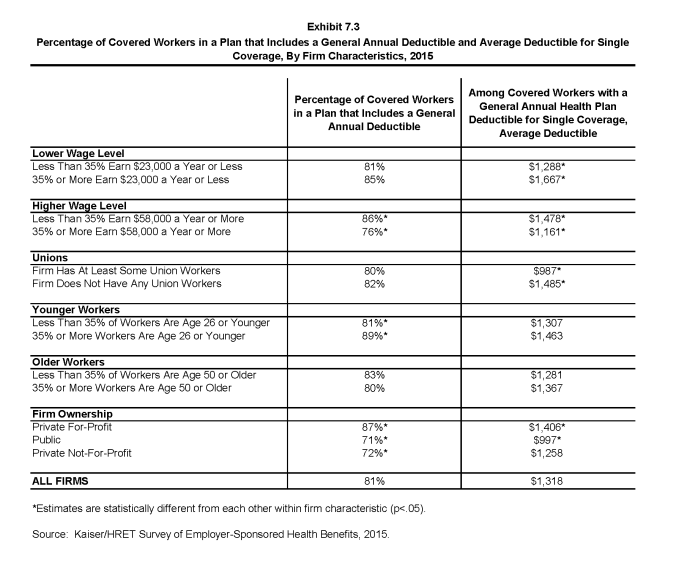
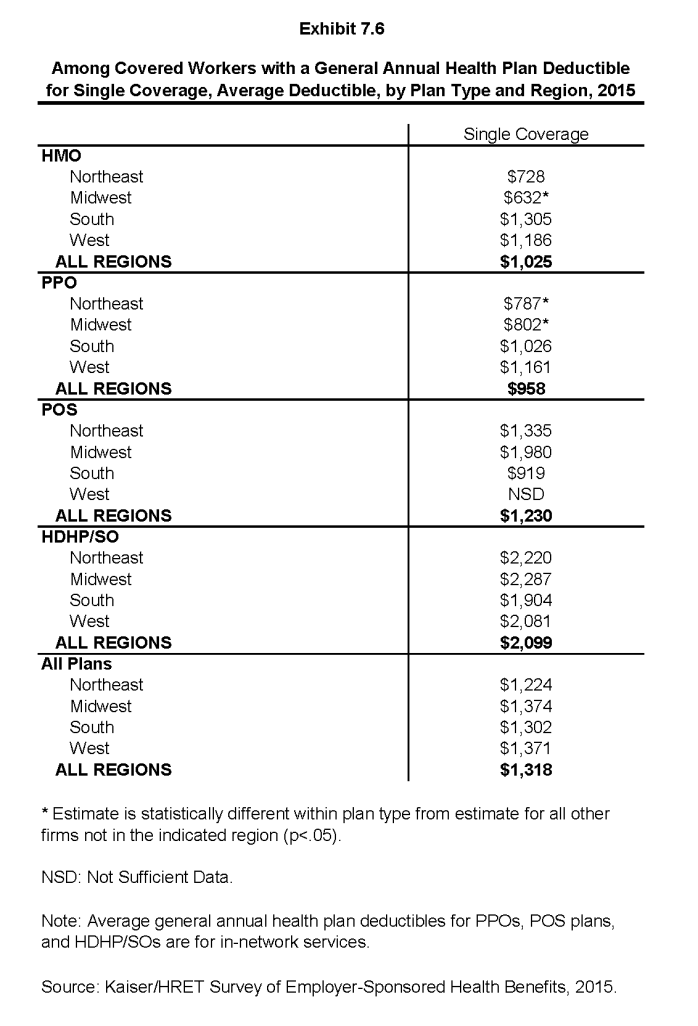
- Workers in firms with many lower-wage workers (35% or more earning $23,000 or less annually) have higher average general annual deductibles for single coverage than workers in firms with fewer such workers ($1,667 vs. $1,288) (Exhibit 7.3).
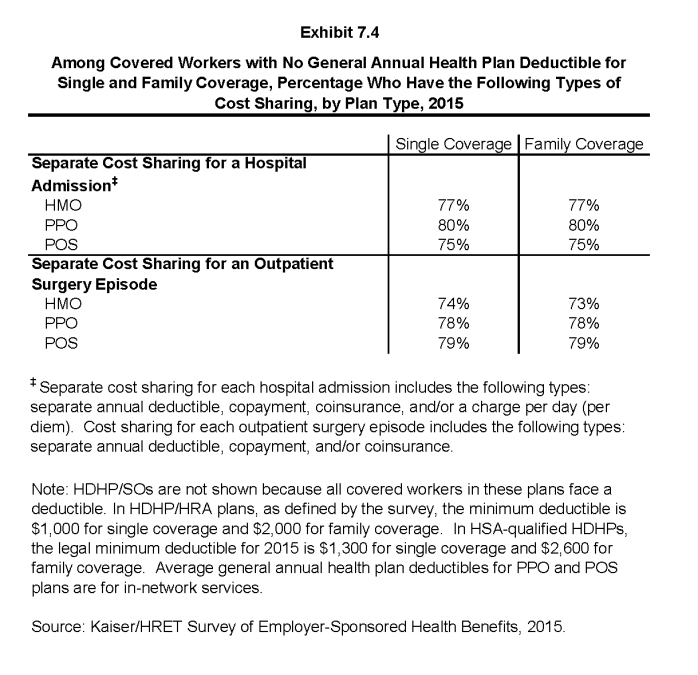
- Workers without a general annual deductible often have other forms of cost sharing for medical services. For workers without a general annual deductible with single coverage, 77% in HMOs, 80% in PPOs, and 75% in POS plans are in plans that require cost sharing for hospital admissions. The percentages are similar for family coverage (Exhibit 7.4).
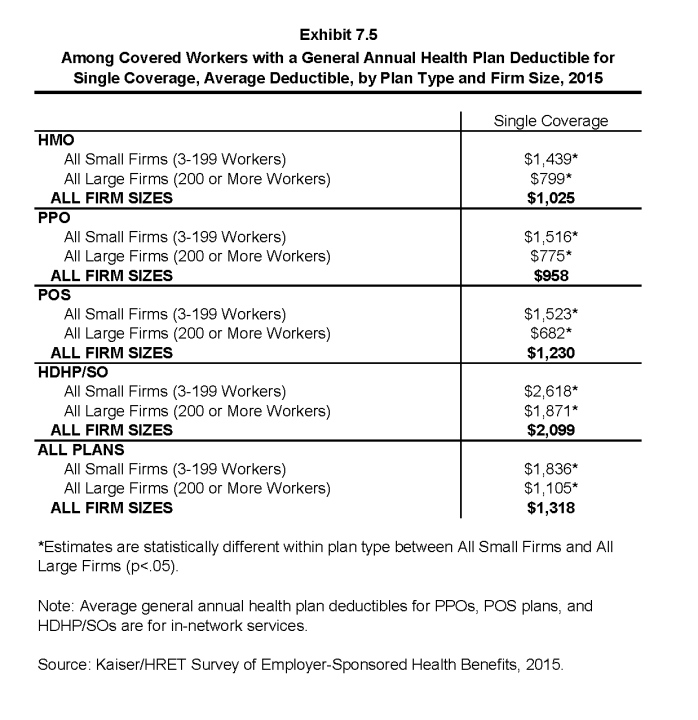
- The dollar amounts of general annual deductibles vary greatly by plan type and firm size.
- The average annual deductible for single coverage for covered workers in a plan with a deductible is $1,318. However, average deductibles vary considerably by plan type. The average annual deductibles for single coverage among covered workers with a deductible are $1,025 for HMOs, $958 for PPOs, $1,230 for POS plans, and $2,099 for HDHP/SOs (Exhibit 7.5).
- Deductibles for single coverage generally are higher for covered workers in small firms (3-199 workers) than for covered workers in large firms (200 or more workers) across plan types. For example, for covered workers in PPOs with a general annual deductible, the average deductible amount for single coverage in small firms is more than twice as large as the average deductible amount in large firms ($1,516 vs. $775). Overall, for covered workers in plans with a general annual deductible, the average deductible amount for single coverage in small firms (3-199 workers) is higher than the average deductible amount in large firms ($1,836 vs. $1,105) (Exhibit 7.5).
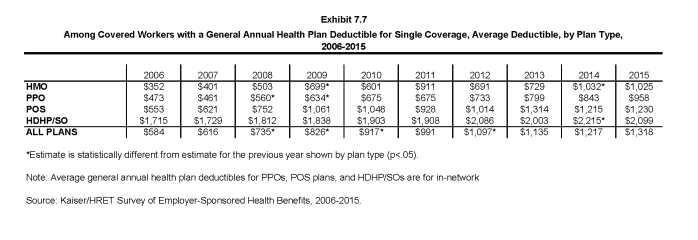
- The average general annual deductible for single coverage for covered workers in plans with a deductible has increased significantly over time. The average deductible for covered workers with a deductible is similar to last year, but significantly higher than $917 in 2010 (Exhibit 7.7).
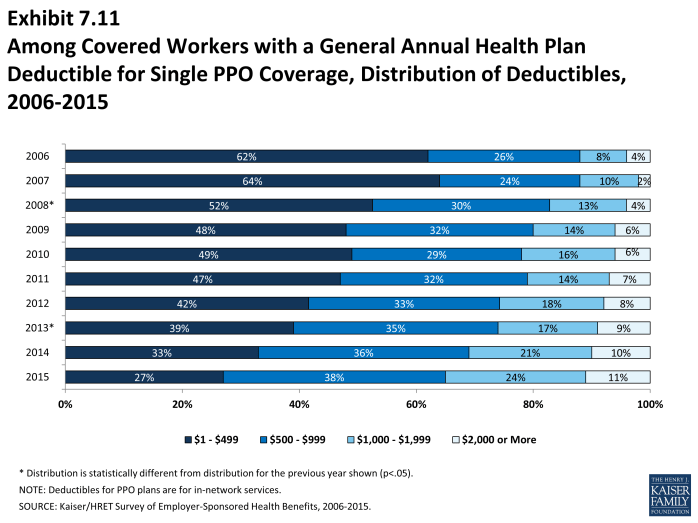
- There is considerable variation in the dollar values of general annual deductibles for workers at different firms. For example, 27% of covered workers enrolled in a PPO plan with a general annual deductible for single coverage have a deductible of less than $500 while 11% have a deductible of $2,000 or more (Exhibit 7.11).
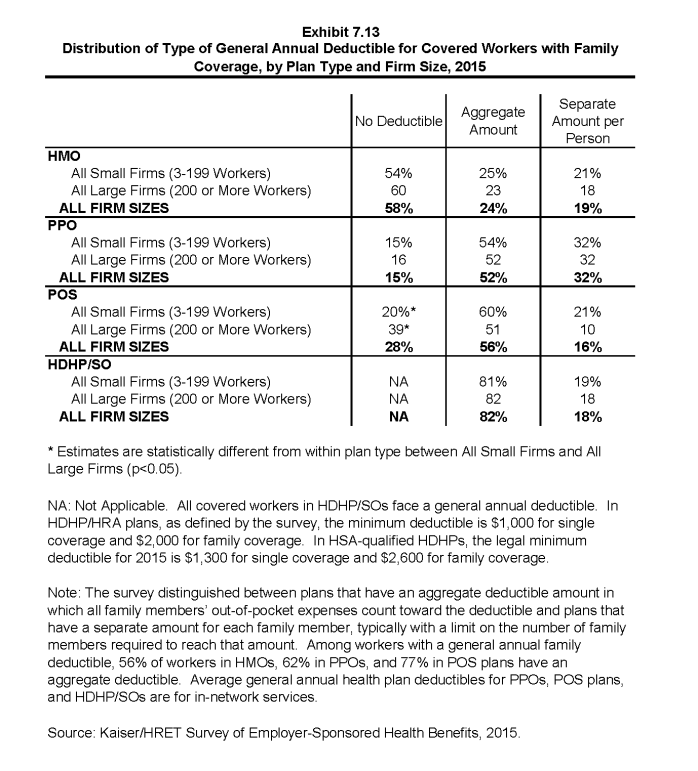
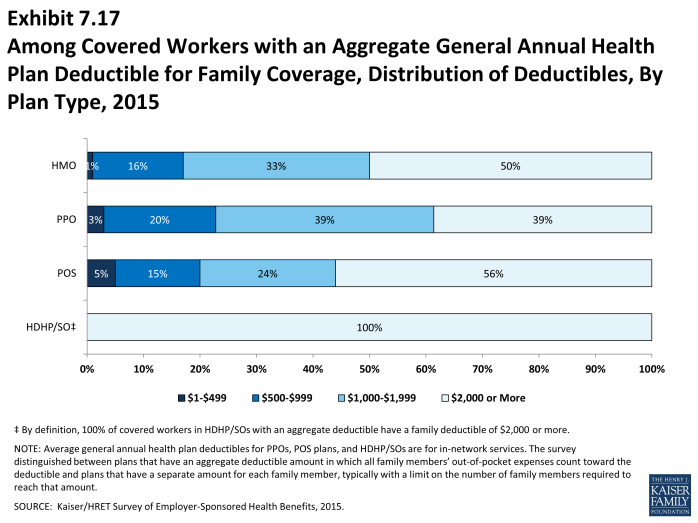
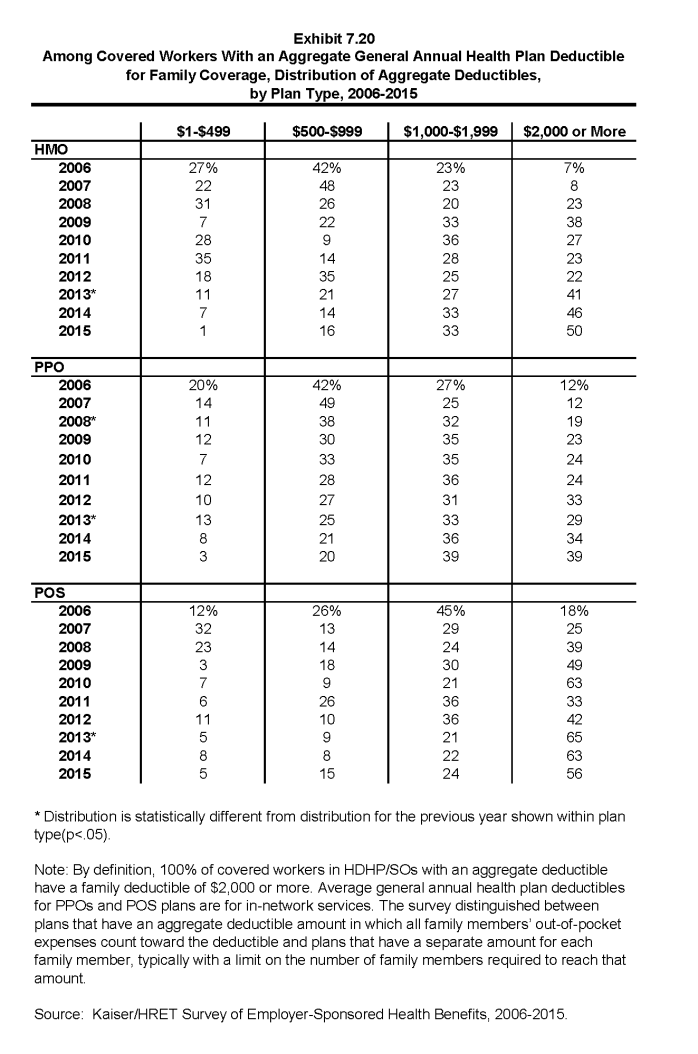
- For family coverage, the majority of workers with general annual deductibles have an aggregate deductible, meaning all family members’ out-of-pocket expenses count toward meeting the deductible amount. Among those with a general annual deductible for family coverage, the percentage of covered workers with an average aggregate general annual deductible is 56% for workers in HMOs, 62% for workers in PPOs, 77% for workers in POS plans and 82% for workers in HDHP/SOs (Exhibit 7.13).
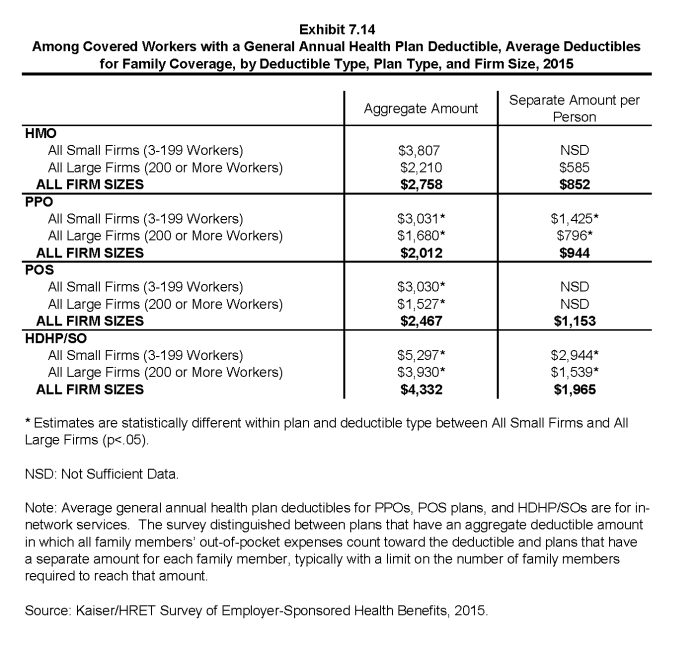
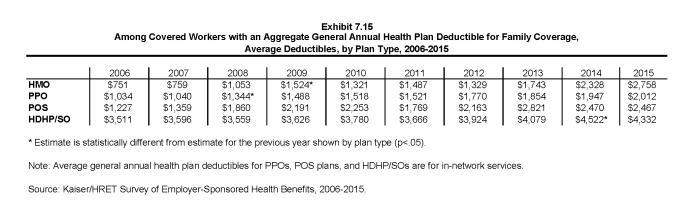
- The average amounts for workers with an aggregate deductible for family coverage are $2,758 for HMOs, $2,012 for PPOs, $2,467 for POS plans, and $4,332 for HDHP/SOs (Exhibit 7.14). Deductible amounts for aggregate family deductibles are similar to last year for all plan types (Exhibit 7.15).
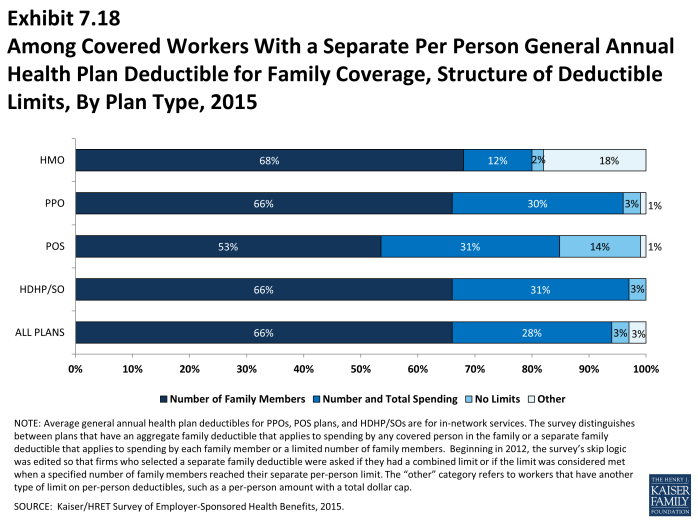
- The other type of family deductible, a separate per-person deductible, requires each family member to meet a separate per-person deductible amount before the plan covers expenses for that member. Many plans with separate per-person family deductibles consider the deductible met for all family members if a prescribed number of family members each reaches his or her separate deductible amounts (Exhibit 7.18). Plans may also require each family member to meet a separate per-person deductible until the family’s combined spending reaches a specified dollar amount.
- For covered workers in health plans that have separate per-person general annual deductible amounts for family coverage, the average plan deductibles are $852 for HMOs, $944 for PPOs, $1,153 for POS plans, and $1,965 for HDHP/SOs (Exhibit 7.14).
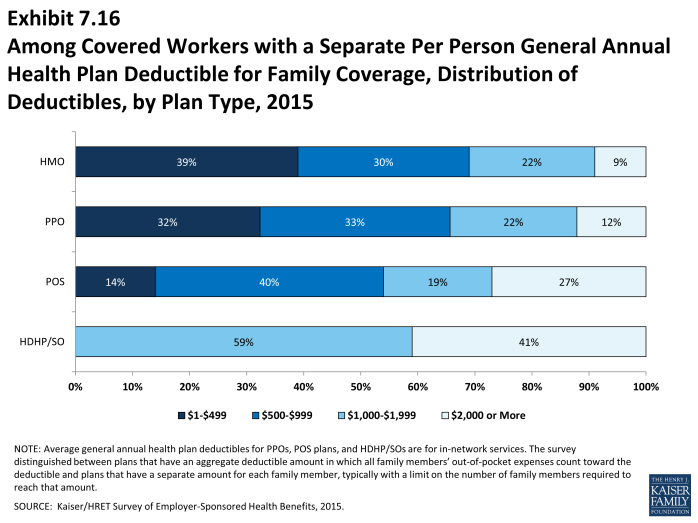
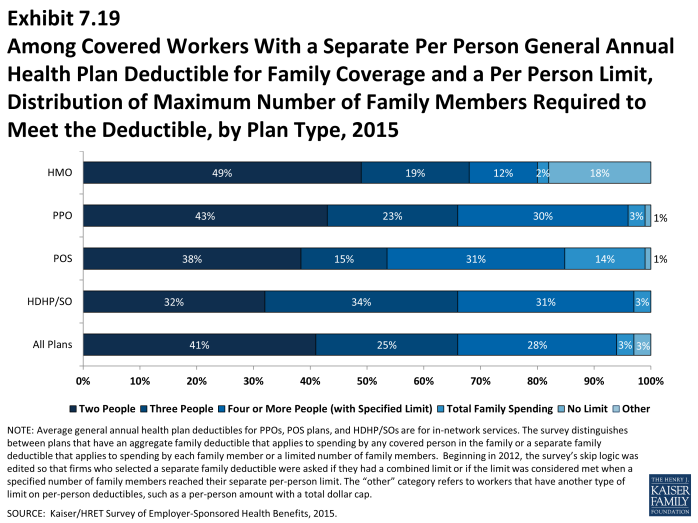
- Most covered workers in plans with a separate per-person general annual deductible for family coverage have a limit to the number of family members required to meet the separate deductible amounts (Exhibit 7.18).1 Among those workers in plans with a limit on the number of family members, the most frequent number of family members required to meet the separate deductible amounts is two for HMO, PPO, and POS plans, and three for HDHP/SO plans (Exhibit 7.19).
- The majority of covered workers with a general annual deductible are in plans where the deductible does not have to be met before certain services, such as physician office visits or prescription drugs, are covered.
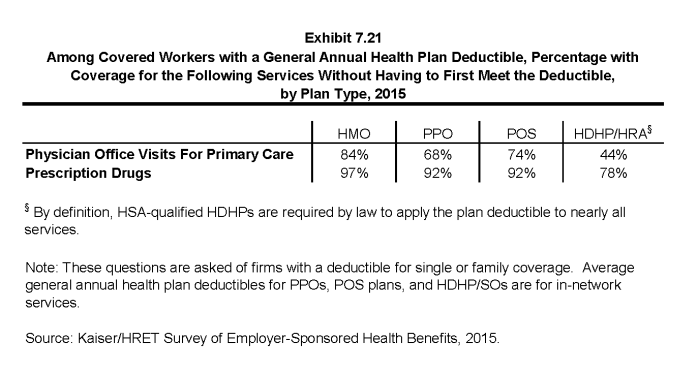
- Large majorities of covered workers (84% in HMOs, 68% in PPOs, and 74% in POS plans) with general annual deductibles are enrolled in plans where the deductible does not have to be met before physician office visits for primary care are covered (Exhibit 7.21).
- Similarly, among workers with a general annual deductible, large shares of covered workers in HMOs (97%), PPOs (92%), and POS plans (92%) are enrolled in plans where the general annual deductible does not have to be met before prescription drugs are covered (Exhibit 7.21).
General Annual Deductibles Among All Covered Workers
- As discussed above, the share of covered workers in plans with a general annual deductible has increased significantly over time: from 55% in 2006, to 70% in 2010, to 81% in 2015, as have the average deductible amounts for covered workers in plans with deductibles: from $584 in 2006, to $917 in 2010, to $1,318 in 2015. Neither trend by itself captures the full impact of changes in deductibles on covered workers. We can look at the average impact of both trends together on covered workers by assigning a zero deductible value to covered workers in plans with no deductible and looking at how the resulting averages change over time. These average deductible amounts are lower in any given year but the changes over time reflect both the higher deductibles in plans with deductibles and the fact that more workers face them.
- Using this approach, the average general annual deductible for single coverage for all covered workers in 2015 is $1,077 (Exhibit 7.32).
- The 2015 value is 67% higher than the average general annual deductible of $646 in 2010 and 255% higher than the average general annual deductible of $303 in 2006 (Exhibit 7.32).
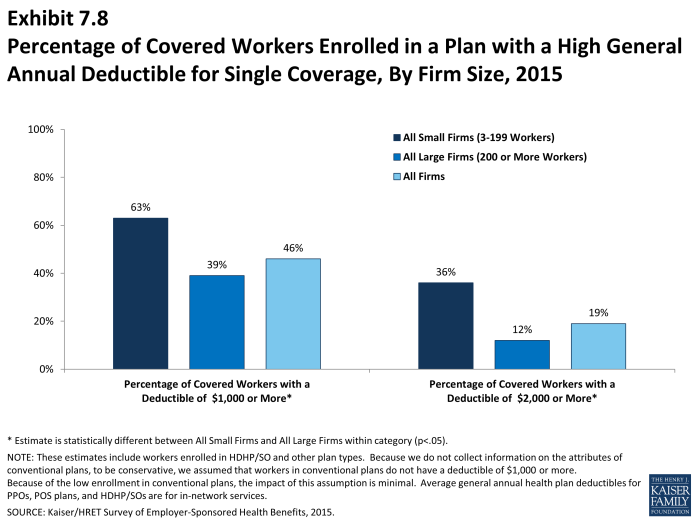
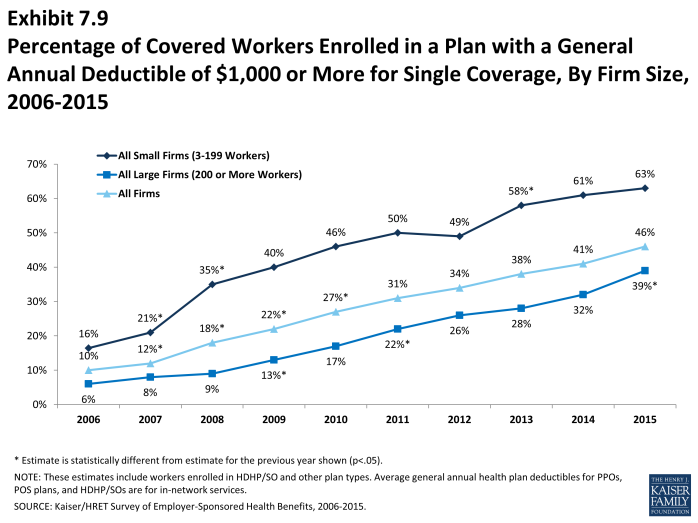
- Another way to look at deductibles is to look at the percentage of all covered workers who are in a plan with a deductible that exceeds certain thresholds. Forty-six percent of covered workers are in plans with a general annual deductible of $1,000 or more for single coverage, similar to the percentage (41%) in 2014 (Exhibit 7.9).
- Over the last five years, the percentage of covered workers with a general annual deductible of $1,000 or more for single coverage has grown substantially, increasing from 27% to 46% (Exhibit 7.9). The share of workers in large firms with a deductible of $1,000 or more increased significantly since 2014; from 32% to 39%.
- Workers in small firms (3-199 workers) are more likely to have a general annual deductible of $1,000 or more for single coverage than workers in large firms (200 or more workers) (63% vs. 39%) (Exhibit 7.8).
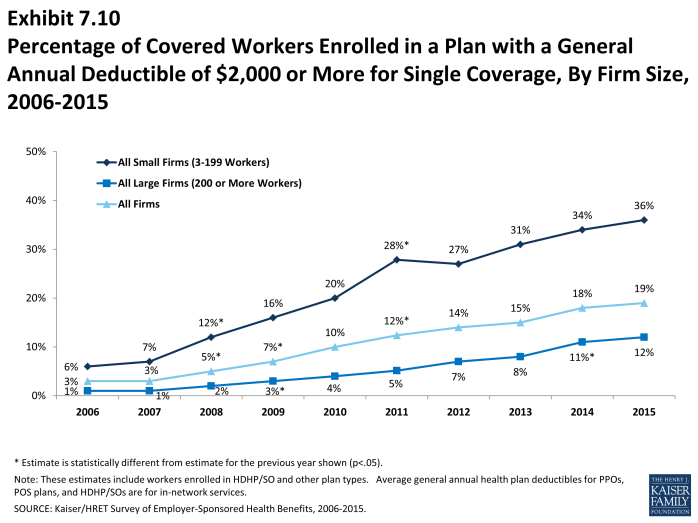
- Nineteen percent of covered workers are enrolled in a plan with a deductible of $2,000 or more. Thirty-six percent of covered workers at small firms (3-199 workers) have a general annual deductible of $2,000 or more, in contrast to just 12% in large firms (Exhibit 7.8).
Hospital and Outpatient Surgery Cost Sharing
- Whether or not a worker has a general annual deductible, most workers face additional types of cost sharing (such as a copayment, coinsurance, or a per diem charge) when admitted to a hospital or having outpatient surgery. The distribution of workers with cost sharing for hospital and outpatient surgery does not equal 100% as workers may face a combination of types of cost sharing. In addition, the average copayment and coinsurance rates for hospital admissions include workers who may have a combination of these types of cost sharing.
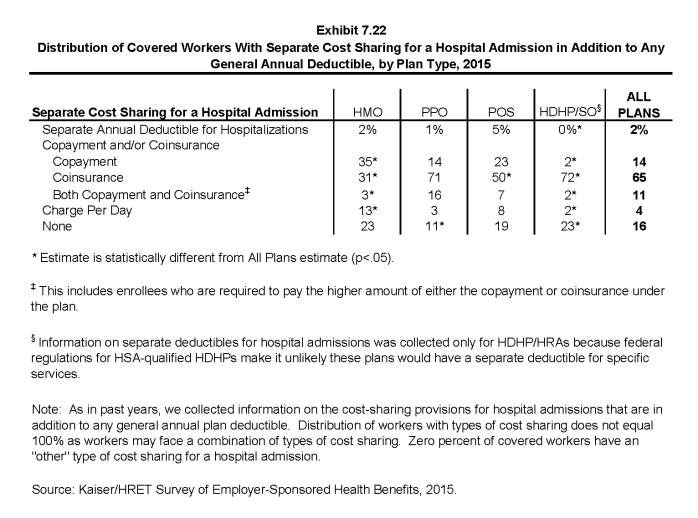
- For hospital admissions, 65% of covered workers have coinsurance and 14% have copayments. Lower percentages of workers have per day (per diem) payments (4%), a separate hospital deductible (2%), or both copayments and coinsurance (11%), while 16% have no additional cost sharing for hospital admissions after any general annual deductible has been met. For covered workers in HMO plans, copayments are more common (35%) and coinsurance (31%) is less common than in other plan types (Exhibit 7.22).
- The percentage of covered workers in a plan that requires coinsurance for hospital admissions has increased from 55% in 2011 to 65% in 2015 (Exhibit 7.22).
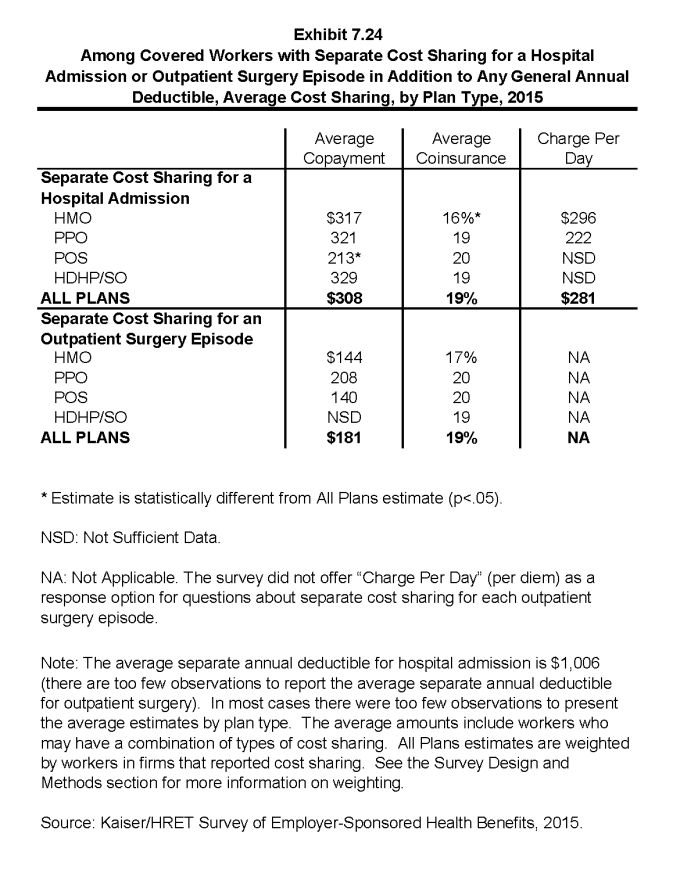
- The average coinsurance rate is 19%; the average copayment is $308 per hospital admission; the average per diem charge is $281; and the average separate annual hospital deductible is $1,006 (Exhibit 7.24).
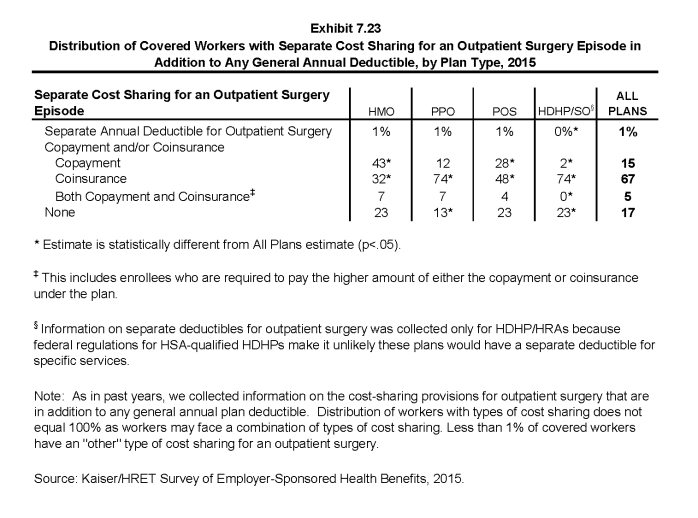
- The cost-sharing provisions for outpatient surgery are similar to those for hospital admissions, as most workers have coinsurance or copayments. Sixty-seven percent of covered workers have coinsurance and 15% have copayments for an outpatient surgery episode. In addition, 1% has a separate annual deductible for outpatient surgery, and 5% have both copayments and coinsurance, while 17% have no additional cost sharing after any general annual deductible has been met (Exhibit 7.23).
- For covered workers with cost sharing for outpatient surgery, the average coinsurance is 19% and the average copayment is $181 (Exhibit 7.24).
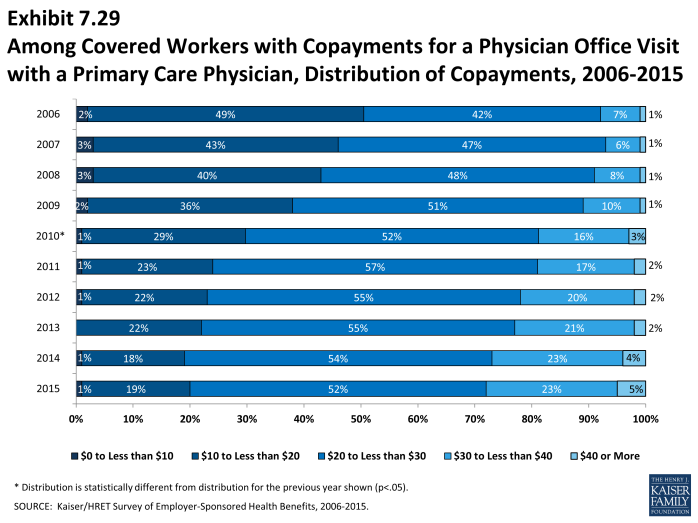
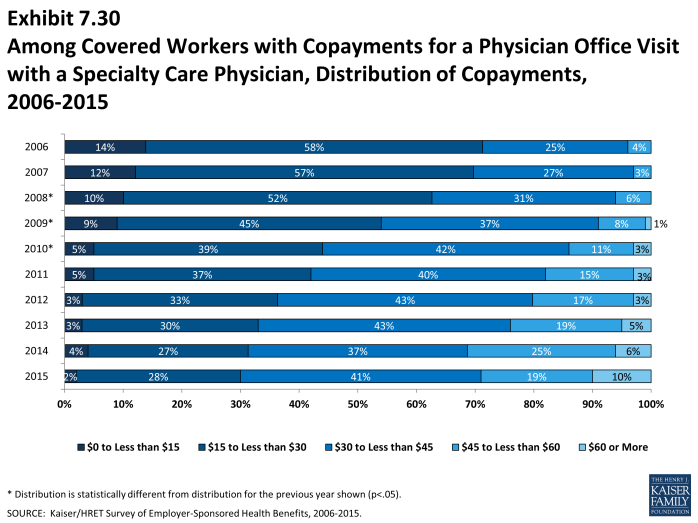
Cost Sharing for Physician Office Visits
- The majority of covered workers are enrolled in health plans that require cost sharing for an in-network physician office visit, in addition to any general annual deductible2.
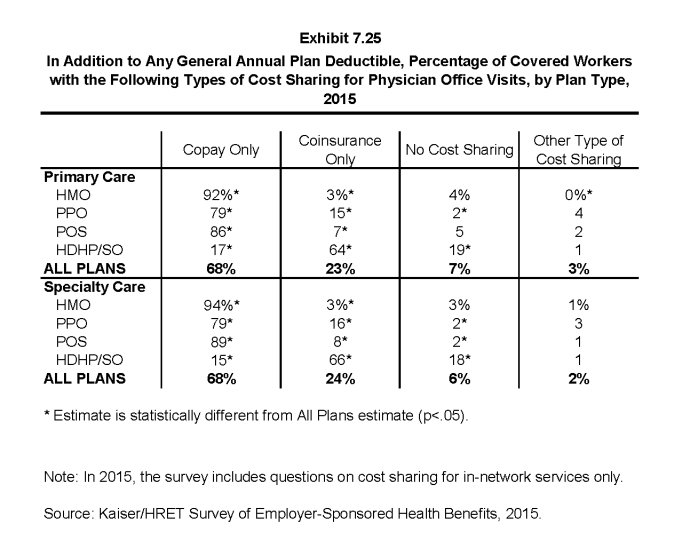
- The most common form of physician office visit cost sharing for in-network services is copayments. Sixty-eight percent of covered workers have a copayment for a primary care physician office visit and 23% have coinsurance. For office visits with a specialty physician, 68% of covered workers have copayments and 24% have coinsurance. Workers in HMOs, PPOs, and POS plans are much more likely to have copayments than workers in HDHP/SOs for both primary care and specialty care physician office visits. The majority of workers in HDHP/SOs have coinsurance (64%) or no cost sharing after the general annual plan deductible is met (19%) for primary care physician office visits (Exhibit 7.25).
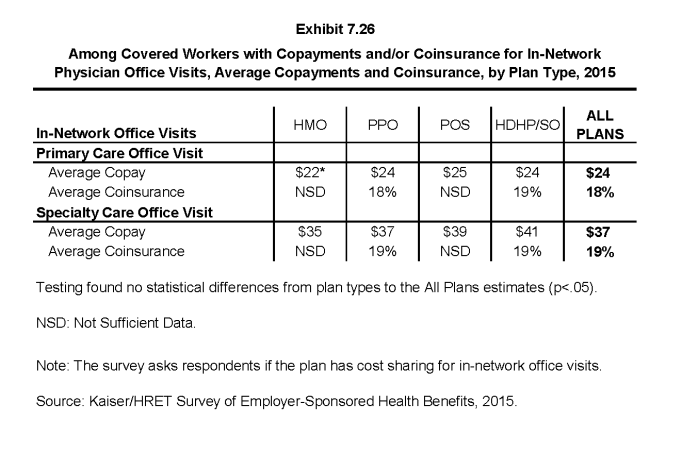
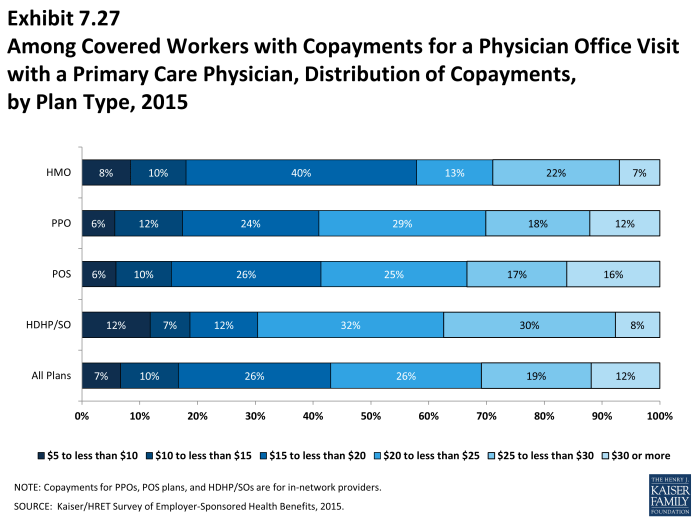
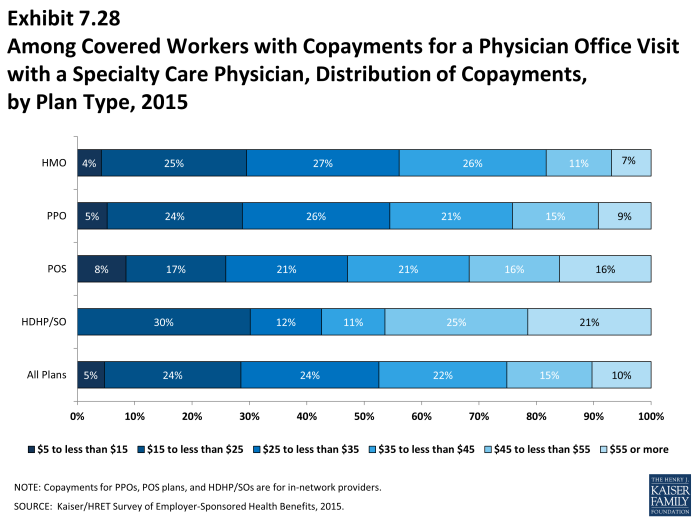
- Among covered workers with a copayment for in-network physician office visits, the average copayment is $24 for primary care and $37 for specialty physician office visits (Exhibit 7.26), similar to $24 and $36 reported in 2014.
- Among workers with coinsurance for in-network physician office visits, the average coinsurance rates are 18% for a visit with a primary care physician and 19% for a visit with a specialist (Exhibit 7.26).
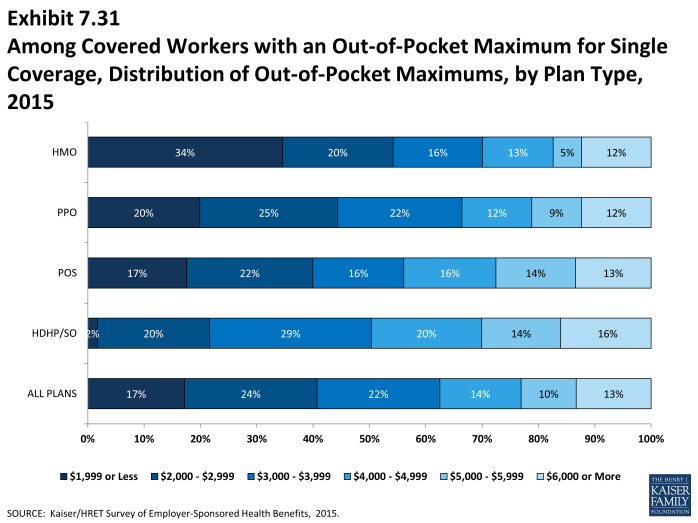
Out-Of-Pocket Maximum Amounts
- Most covered workers are in a plan that partially or totally limits the cost sharing that a plan enrollee must pay in a year. These limits are generally referred to as out-of-pocket maximum amounts. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) requires that non-grandfathered health plans have an out-of-pocket maximum of $6,600 or less for single coverage and $13,200 for family coverage for 2015. Many plans have complex out-of-pocket structures, increasing the difficulty of accurately collecting information on this element of plan design.
- In 2015, 98% percent of covered workers have an out-of-pocket maximum for single coverage; significantly more than 82% in 2010.
- For covered workers with out-of-pocket maximums, there is wide variation in spending limits.
- Seventeen percent of covered workers with an out-of-pocket maximum for single coverage have an out-of-pocket maximum of less than $2,000, while 13% have an out-of-pocket maximum of $6,000 or more (Exhibit 7.31).