2021 Employer Health Benefits Survey
Published:
Section 1: Cost of Health Insurance
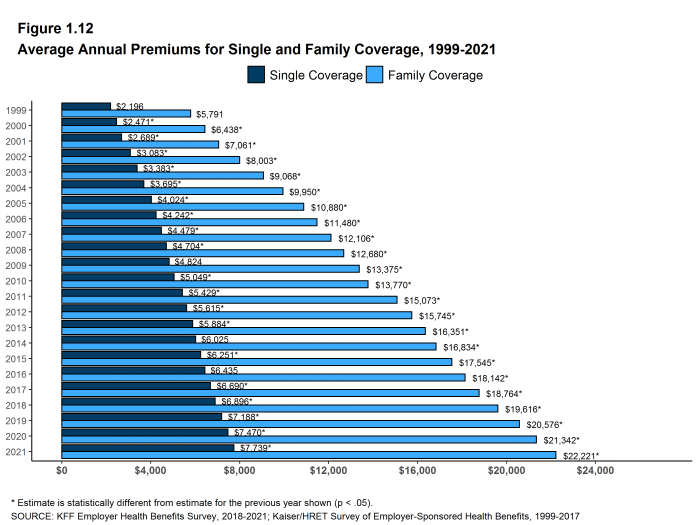
The average annual premiums in 2021, are $7,739 for single coverage and $22,221 for family coverage. Over the last year, the average premium for single coverage increased by 4% and the average premium for family coverage increased by 4%. The average family premium has increased 47% since 2011 and 22% since 2016.
This graphing tool allows users to look at changes in premiums and worker contributions for covered workers at different types of firms over time: https://www.kff.org/interactive/premiums-and-worker-contributions/
PREMIUMS FOR SINGLE AND FAMILY COVERAGE
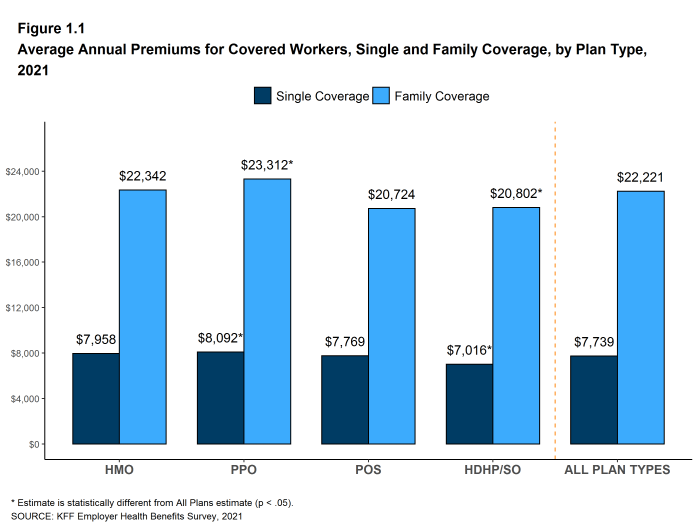
- The average premium for single coverage in 2021 is $7,739 per year. The average premium for family coverage is $22,221 per year [Figure 1.1].
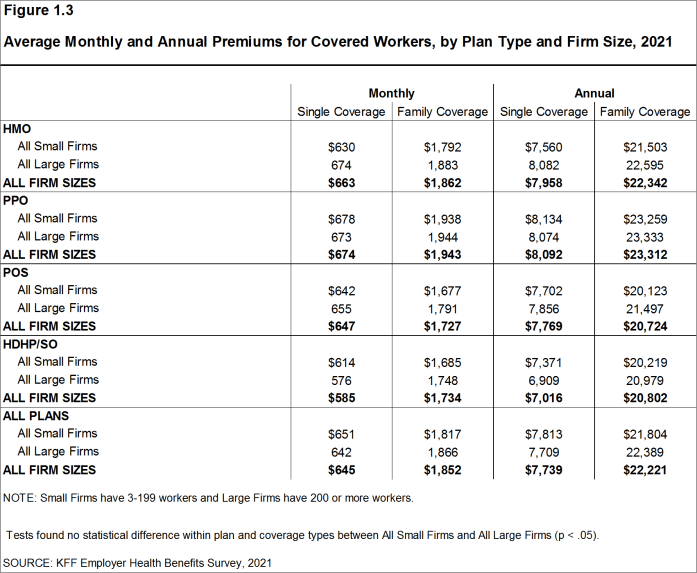
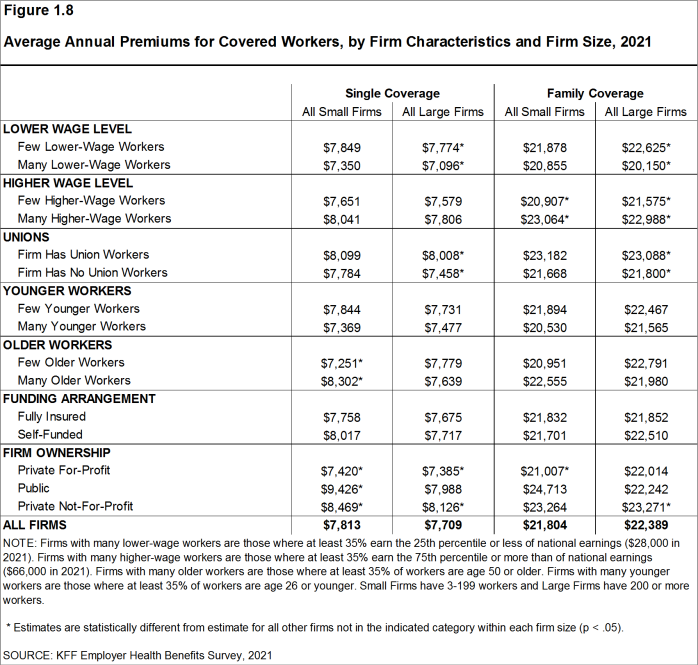
- The average annual premium for single coverage for covered workers in small firms ($7,813) is similar to the average premium for covered workers in large firms ($7,709). The average annual premium for family coverage for covered workers in small firms ($21,804) is similar to the average premium for covered workers in large firms ($22,389). [Figure 1.3].
- The average annual premiums for covered workers in HDHP/SOs are lower than the average premiums for coverage overall for both single coverage ($7,016 v. $7,739) and family coverage ($20,802 vs. $22,221). The average premiums for covered workers enrolled in PPOs are higher than the overall average premiums for both single coverage ($8,092 v. $7,739) and family coverage ($23,312 vs. $22,221) [Figure 1.1].
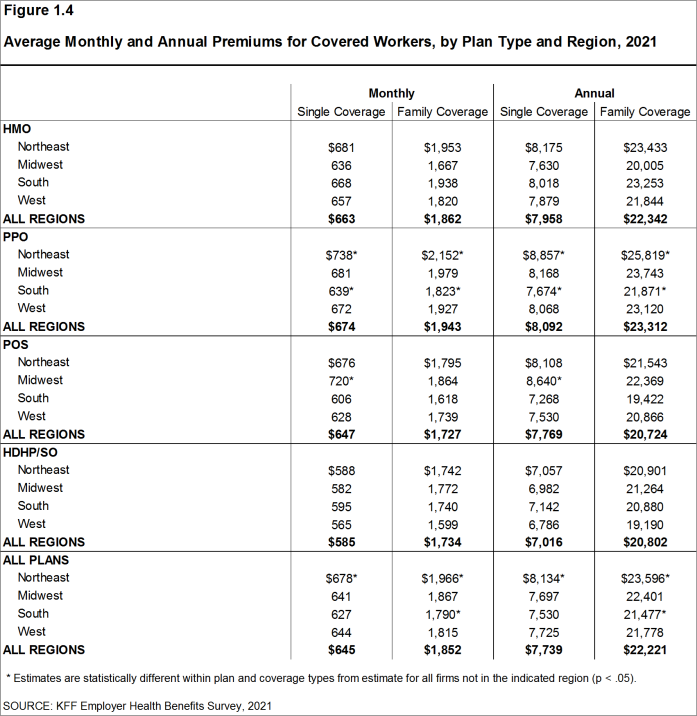
- The average premiums for covered workers with single coverage are relatively high in the Northeast. The average premiums for covered workers with family coverage are relatively high in the Northeast and relatively low in the South [Figure 1.4].
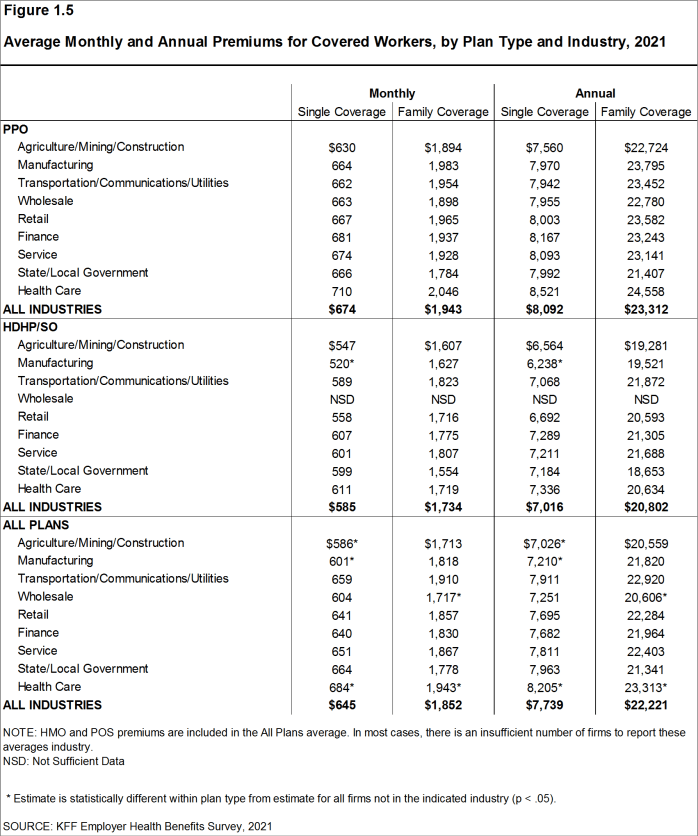
- The average premium for single coverage varies across industries. Compared to the average single premiums for covered workers in other industries, the average premiums for covered workers in the Manufacturing, and in the Agriculture/Mining/Construction categories are relatively low and the average premium for Health Care workers is relatively high [Figure 1.5].
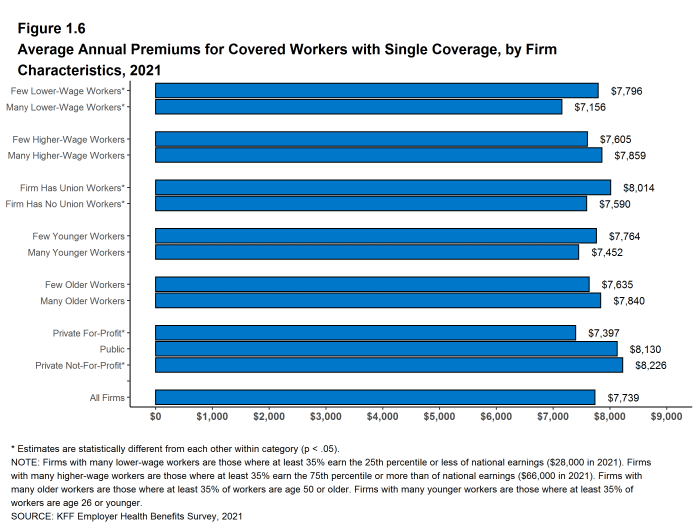
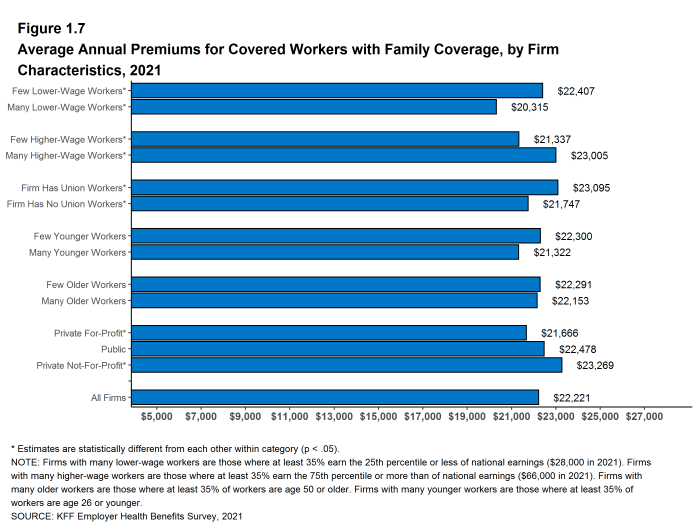
- The average premiums for covered workers in firms with a relatively large share of lower-wage workers (where at least 35% of the workers earn $28,000 annually or less) are lower than the average premium for covered workers in firms with a smaller share of lower-wage workers for both single coverage ($7,156 vs. $7,796) and family coverage ($20,315 vs. $22,407) [Figures 1.6 and 1.7].
- The average annual premiums for covered workers in private for-profit firms are lower than average annual premiums for covered workers in other firms for both single and family coverage. Average annual premiums for covered workers in private not-for-profit firms are higher than average annual premiums for covered workers in other firms for both single and family coverage [Figures 1.6 and 1.7].
- The average annual premiums for covered workers in firms with at least some union workers are higher than the average premiums for workers in firms with no union workers for both single coverage ($8,014 vs. $7,590) and family coverage ($23,095 vs. $21,747) [Figure 1.8].
Figure 1.1: Average Annual Premiums for Covered Workers, Single and Family Coverage, by Plan Type, 2021
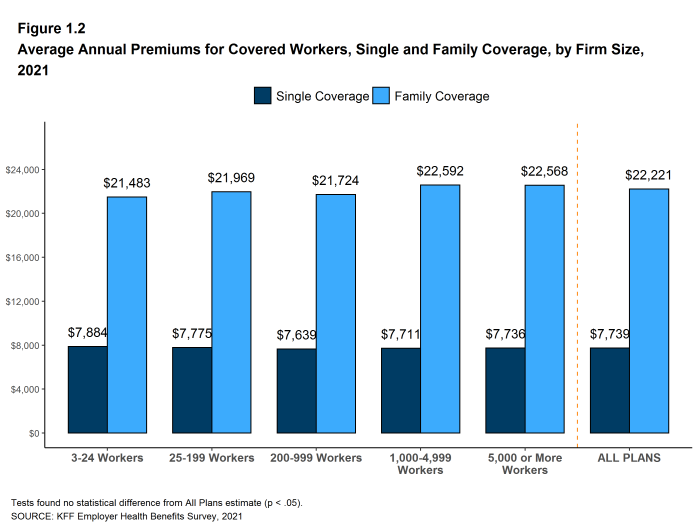
Figure 1.2: Average Annual Premiums for Covered Workers, Single and Family Coverage, by Firm Size, 2021
Figure 1.3: Average Monthly and Annual Premiums for Covered Workers, by Plan Type and Firm Size, 2021
Figure 1.5: Average Monthly and Annual Premiums for Covered Workers, by Plan Type and Industry, 2021
Figure 1.6: Average Annual Premiums for Covered Workers With Single Coverage, by Firm Characteristics, 2021
Figure 1.7: Average Annual Premiums for Covered Workers With Family Coverage, by Firm Characteristics, 2021
PREMIUM DISTRIBUTION
- There remains considerable variation in premiums for both single and family coverage.
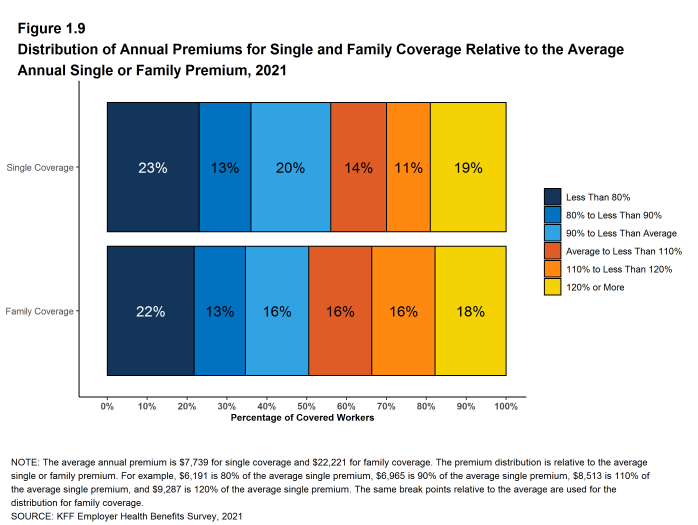
- Nineteen percent of covered workers are employed in a firm with a single premium at least 20% higher than the average single premium, while 23% of covered workers are in firms with a single premium less than 80% of the average single premium [Figure 1.9].
- For family coverage, 18% of covered workers are employed in a firm with a family premium at least 20% higher than the average family premium, while 22% of covered workers are in firms with a family premium less than 80% of the average family premium [Figure 1.9].
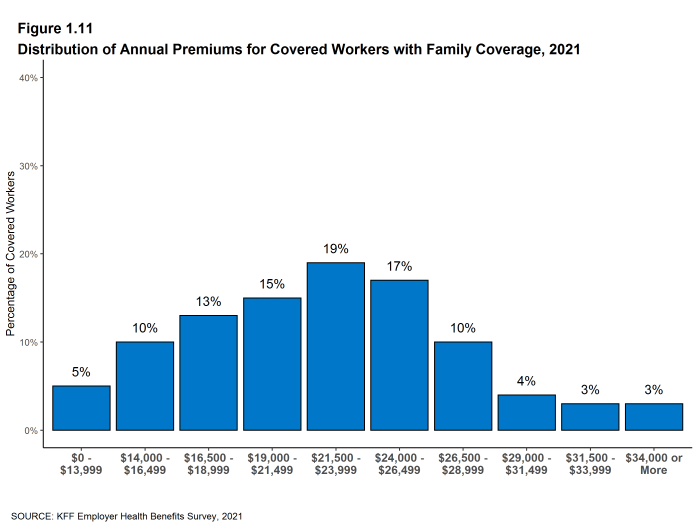
- Ten percent of covered workers are in a firm with an average annual premium of at least $10,000 for single coverage [Figure 1.10]. Ten percent of covered workers are in a firm with an average annual premium of at least $29,000 for family coverage [Figure 1.11].
Figure 1.9: Distribution of Annual Premiums for Single and Family Coverage Relative to the Average Annual Single or Family Premium, 2021
PREMIUM CHANGES OVER TIME
- The average premium for single coverage is 4% higher than the single premium last year, and the average premium for family coverage is 4% higher than the average family premium last year [Figure 1.12].
- The average premium for single coverage has grown 20% since 2016, similar to the growth in the average premium for family coverage (22%) over the same period [Figure 1.12].
- The $22,221 average family premium in 2021 is 22% higher than the average family premium in 2016 and 47% higher than the average family premium in 2011. The 22% family premium growth in the past five years is similar to the 20% growth between 2011 and 2016 [Figure 1.12].
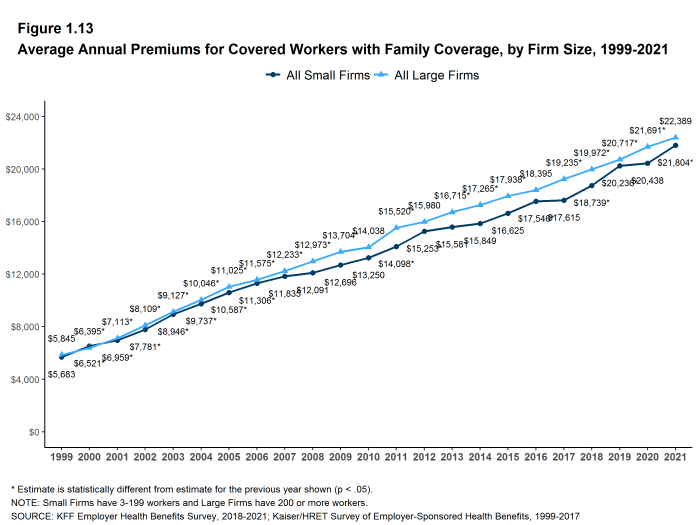
- The average family premiums for both small and large firms have increased at similar rates since 2016 (24% for small firms and 22% for large firms). For small firms, the average family premium rose from $17,546 in 2016 to $21,804 in 2021. For large firms, the average family premium rose from $18,395 in 2016 to $22,389 in 2021 [Figure 1.13].
- The average family premium has grown faster since 2011 for covered workers in small as compared to covered workers in large firms (55% in small firms and 44% in large firms). In small firms, the average family premium rose from $14,098 in 2011 to $21,804 in 2021. In large firms, the average family premium rose from $15,520 in 2011 to $22,389 in 2021 [Figures 1.13].
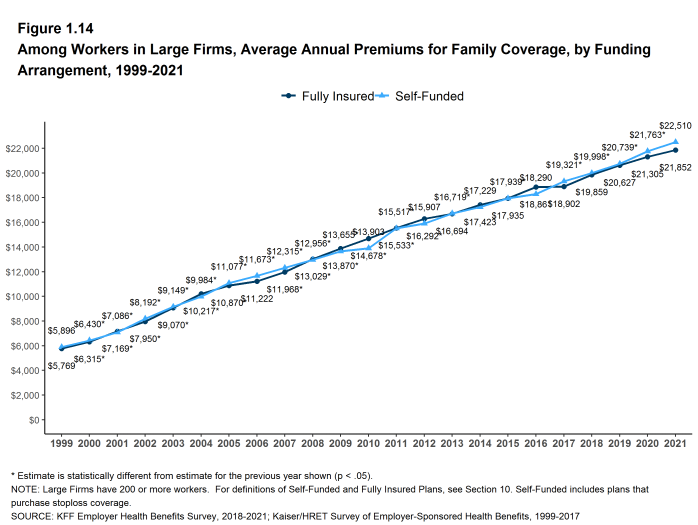
- For covered workers in large firms, over the past five years, the average family premium in firms that are fully insured has grown at a similar rate to the average family premium for covered workers in fully or partially self-funded firms (16% for fully insured plans and 23% for self-funded firms) [Figure 1.14].
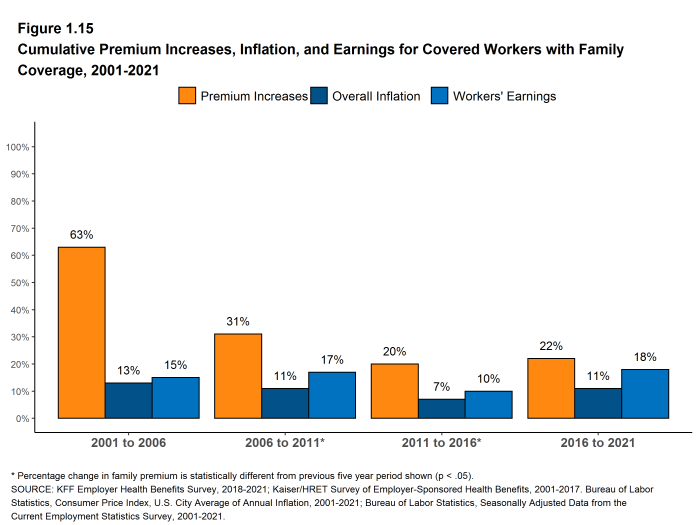
- The average premiums for family coverage have risen faster than inflation over the last 5 years (22% vs. 11%) and the last 10 years (47% vs. 19%) [Figure 1.15].
Figure 1.13: Average Annual Premiums for Covered Workers With Family Coverage, by Firm Size, 1999-2021
Figure 1.14: Among Workers in Large Firms, Average Annual Premiums for Family Coverage, by Funding Arrangement, 1999-2021
Sections
- Section 1: Cost of Health Insurance
- Section 2: Health Benefits Offer Rates
- Section 3: Employee Coverage, Eligibility, and Participation
- Section 4: Types of Plans Offered
- Section 5: Market Shares of Health Plans
- Section 6: Worker and Employer Contributions for Premiums
- Section 7: Employee Cost Sharing
- Section 8: High-Deductible Health Plans with Savings Option
- Section 9: Prescription Drug Benefits
- Section 10: Plan Funding
- Section 11: Retiree Health Benefits
- Section 12: Health Screening and Health Promotion and Wellness Programs
- Section 13: Employer Practices, Telehealth and Employer Responses to the Pandemic