Kaiser Health Tracking Poll: Health Care Priorities for 2017
KEY FINDINGS:
- The latest Kaiser Health Tracking Poll finds that health care is among the top issues, with the economy and jobs and immigration, Americans want President-elect Donald Trump and the next Congress to address in 2017. When asked about a series of health care priorities for President-elect Trump and the next Congress to act on, repealing the ACA falls behind other health care priorities including lowering the amount individuals pay for health care, lowering the cost of prescription drugs, and dealing with the prescription painkiller addiction epidemic.
- When presented with two general approaches to the future of health care in the U.S., six in ten (62 percent) Americans prefer “guaranteeing a certain level of health coverage and financial help for seniors and lower-income Americans, even if it means more federal health spending and a larger role for the federal government” while three in ten (31 percent) prefer the approach of “limiting federal health spending, decreasing the federal government’s role, and giving state governments and individuals more control over health insurance, even if this means some seniors and lower-income Americans would get less financial help than they do today.”
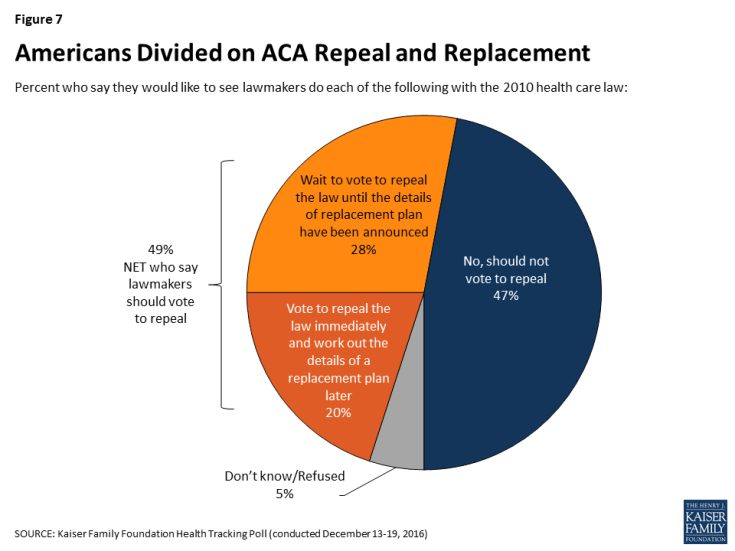
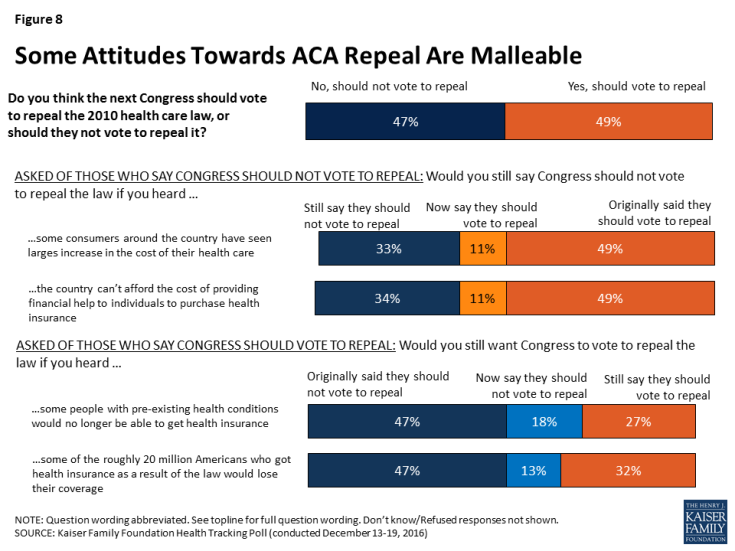
- As Congressional lawmakers make plans for the future of the ACA, the latest survey finds the public is divided on what they would like lawmakers to do when it comes to the 2010 health care law. Forty-nine percent of the public think the next Congress should vote to repeal the law compared to 47 percent who say they should not vote to repeal it. Of those who want to see Congress vote to repeal the law, a larger share say they want lawmakers to wait to vote to repeal the law until the details of a replacement plan have been announced (28 percent) than say Congress should vote to repeal the law immediately and work out the details of a replacement plan later (20 percent). However, the survey also finds malleability of attitudes towards Congress repealing the health care law with both supporters and opponents being persuaded after hearing counter-messages.
Top Issues for President-elect Trump and Congress
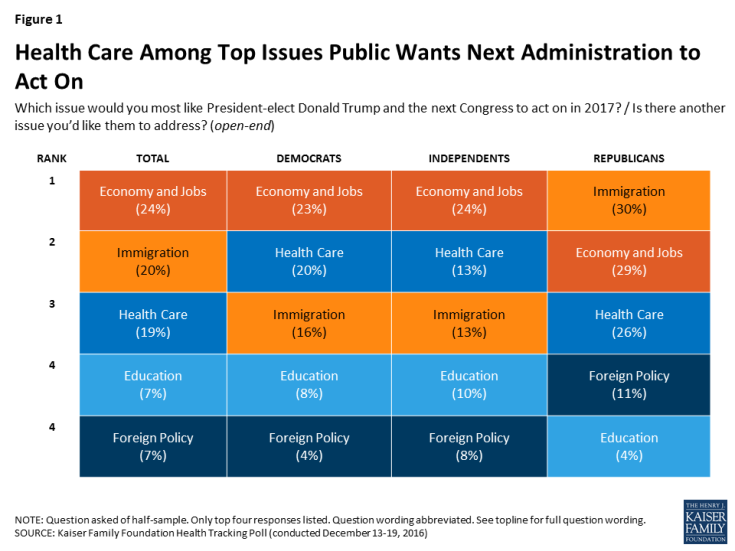
The latest Kaiser Health Tracking Poll finds health care among the top issues Americans want President-elect Donald Trump and the next Congress to address in 2017. When asked which issue they would most like the next administration to act on in 2017, one-fourth of the public mention the economy and jobs (24 percent), followed by immigration (20 percent), and health care (19 percent). Among Democrats and independents, the economy and jobs is the top issue (23 percent and 24 percent, respectively) while the top issues for Republicans are immigration (30 percent) and economy and jobs (29 percent). Among all partisans, health care ranks among the top three issues that the public wants the next administration to act on in 2017.
The top issue for voters who supported President-elect Donald Trump are similar to those among Republicans: economy and jobs (31 percent) and immigration (31 percent), followed closely by health care (27 percent).
When asked to mention which health care issue they would most like President-elect Trump and the next Congress to act on in 2017, about one-third of the public mention the Affordable Care Act (ACA) but attitudes are mixed between wanting the next administration to act on repealing the 2010 health care law (14 percent), improving/fixing the law (11 percent), or keeping/expanding the law (8 percent).
Lowering Out-Of-Pocket Costs Is a Top Priority for Americans
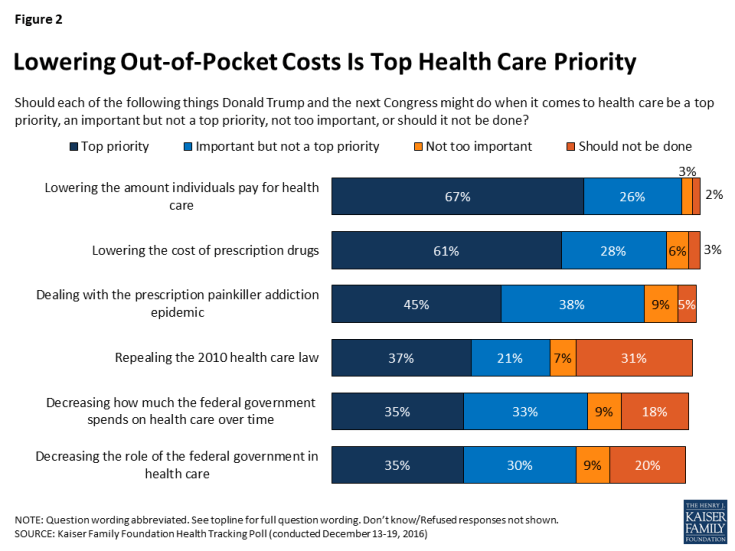
When asked about a series of health care priorities for President-elect Trump and the next Congress to act on, repealing the ACA falls behind other health care priorities. Two-thirds of the public (67 percent) say lowering the amount individuals pay for health care should be a “top priority” for President-elect Trump and the next Congress. This is followed by six in ten (61 percent) who say lowering the cost of prescription drugs should be a “top priority,” and nearly half (45 percent) who say dealing with the prescription pain killer addiction epidemic should be a “top priority.”
Smaller shares say repealing the 2010 health care law (37 percent), decreasing how much the federal government spends on health care over time (35 percent), and decreasing the role of the federal government in health care (35 percent) should be top priorities.
Lowering Out-of-Pocket Costs Tops Priorities Regardless of Partisanship
While about two-thirds of Democrats, Republicans, and independents say lowering the amount individuals pay for health care should be a “top priority,” partisans differ in how they prioritize other health care issues. Most notably, while 63 percent of Republicans say repealing the 2010 health care law should be a top priority – this view is shared by much smaller shares of independents (32 percent) and Democrats (21 percent). Similarly, Republicans (50 percent) are more likely than independents (34 percent) or Democrats (26 percent) to place a top priority on decreasing the role of the federal government in health care. By contrast, Democrats and independents are somewhat more likely than Republicans to place a top priority on lowering the cost of prescription drugs (67 percent, 61 percent, and 55 percent, respectively) and on dealing with the epidemic of prescription painkiller addiction (51 percent, 46 percent, and 39 percent, respectively).
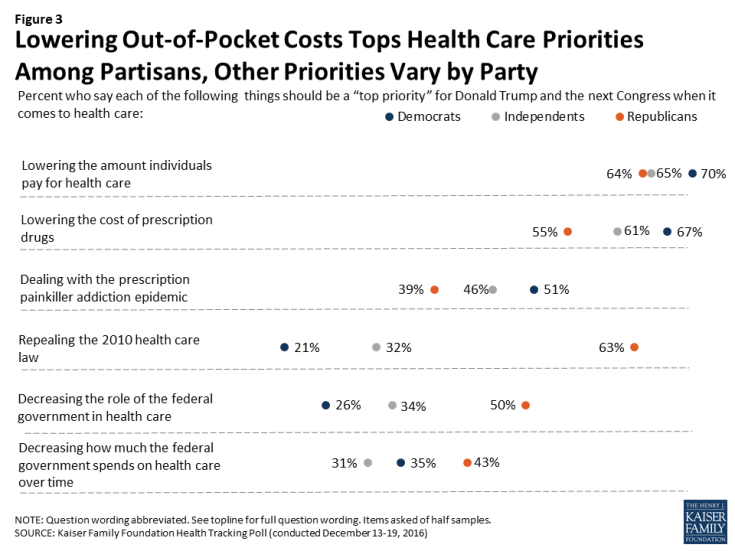
Figure 3: Lowering Out-of-Pocket Costs Tops Health Care Priorities Among Partisans, Other Priorities Vary by Party
Confidence in President-elect Trump’s Ability to Reduce Health Care Costs
Lowering out-of-pocket health care costs is a top priority for Americans, and this was also a campaign promise from Donald Trump during his 2016 presidential campaign. When asked how confident they are in President-elect Trump’s ability to deliver on this campaign promise that Americans will get better health care at a lower cost than they pay now, Americans are split with similar shares saying they are either “not too confident” or “not at all confident” (51 percent) as saying they are “very confident” or “somewhat confident” (47 percent).
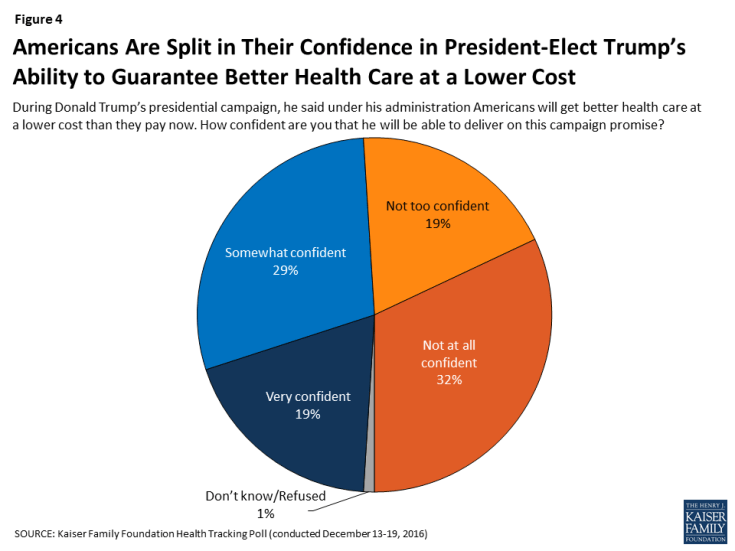
Figure 4: Americans Are Split in Their Confidence in President-Elect Trump’s Ability to Guarantee Better Health Care at a Lower Cost
Confidence in President-elect Trump’s promise that Americans will get better health care at a lower cost is largely divided by party identification and 2016 vote choice with nearly nine in ten Republicans (85 percent) and Trump voters (86 percent) saying they are either “very” or “somewhat” confident in the next administration’s ability to deliver on this campaign promise. This is compared to 81 percent of Democrats and 86 percent of Clinton voters who say they are either “not too confident” or “not at all confident” that the next president will deliver on this promise.
Americans’ Attitudes on the Future of Health Care in the U.S.
Throughout the 2016 presidential election, it became clear that the two major political parties in the U.S. have competing views on the future of health care. When given two competing approaches to the future of health care, six in ten Americans (62 percent) prefer “guaranteeing a certain level of health coverage and financial help for seniors and lower-income Americans, even if it means more federal health spending and a larger role for the federal government” while about one-third (31 percent) prefer “limiting federal health spending, decreasing the federal government’s role, and giving state governments and individuals more control over health insurance, even if this means some seniors and lower-income Americans would get less financial help than they do today.”
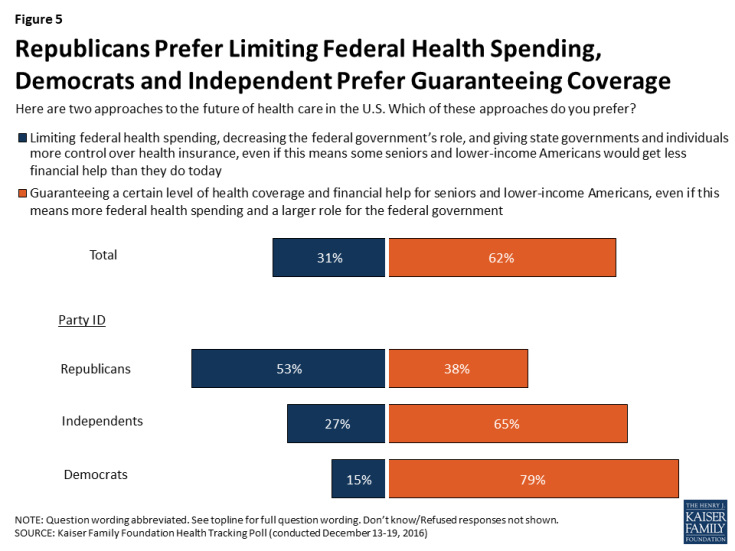
Figure 5: Republicans Prefer Limiting Federal Health Spending, Democrats and Independent Prefer Guaranteeing Coverage
There are also partisan differences, with about half of Republicans (53 percent) preferring the approach that Republican leaders have coalesced around – limiting federal health spending, decreasing the federal government’s role, and giving states and individuals more control; this approach is preferred by much smaller shares of independents (27 percent) and Democrats (15 percent). The majority of Democrats (79 percent) and independents (65 percent) prefer guaranteeing a certain level of coverage for seniors and lower-income Americans – even if it means a larger role for the federal government and increased federal spending.
Attitudes Towards the Future of the Affordable Care Act
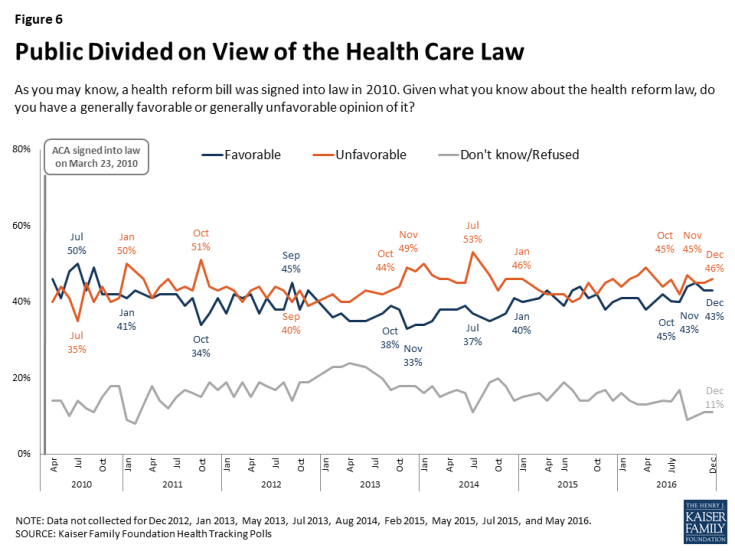
The future of the Affordable Care Act has been at the forefront of the political agenda since the 2016 election with President-elect Trump and Republican lawmakers in Congress saying they will quickly move to repeal the health care law in 2017. The latest survey finds public opinion towards the law is divided with similar shares of the public saying they have an unfavorable opinion (46 percent) as say they have a favorable opinion (43 percent) of the law, which is largely stable from previous months.
Repealing and Replacing the Affordable Care Act
As Congressional lawmakers make plans for the future of the ACA, the latest Kaiser Health Tracking survey finds that – similar to overall attitudes towards the law – the public is also divided on what they would like lawmakers to do when it comes to the 2010 health care law.
Overall, 49 percent of the public think the next Congress should vote to repeal the law and 47 percent say they should not vote to repeal it. Of those who want to see Congress vote to repeal the law, a larger share say they want lawmakers to wait to vote on repeal until the details of a replacement plan have been announced (28 percent) than say Congress should vote to repeal the law immediately and work out the details of a replacement plan later (20 percent).
How Flexible Are Americans’ Opinions of Repealing the ACA?
The survey examines the malleability of attitudes towards Congress repealing the health care law and finds that both supporters and opponents of Congress voting to repeal the law can be persuaded after hearing counter-messages. After hearing pro-repeal arguments, the share of the public supporting repeal can grow to as large as 60 percent, while counter-messages against repeal can decrease support to 27 percent.
Among those who originally said Congress should not vote to repeal the 2010 health care law, about one-fifth (22 percent) change their opinion after hearing that some consumers around the country have seen large increases in the cost of their health insurance – which is similar to the share who shifted their opinion after hearing that the country cannot afford the cost of providing financial help to individuals to purchase health insurance.
On the other side of the debate, some of those who originally said they support Congress voting to repeal the health care law are also persuaded by hearing arguments often made by opponents of the repeal efforts. The survey finds that a share shifts their opinion after hearing that some people with pre-existing conditions would no longer be able to get health coverage and after hearing that some of the roughly 20 million Americans who got health insurance as a result of the law would lose their coverage.
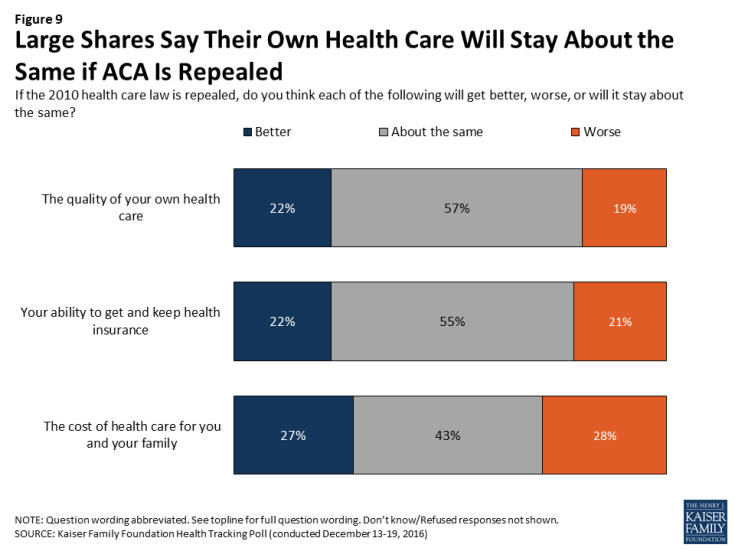
Perceived Effects of Changes to Health Care System
Overall, large shares of Americans say their own health care will “stay about the same” if lawmakers vote to repeal the 2010 health care law. More than half of Americans say the quality of their own health care (57 percent) and their own ability to get and keep health insurance (55 percent) will stay about the same if the law is repealed. Fewer (43 percent) say the cost of health care for them and their family will stay about the same if the law is repealed. In each of these cases, about equal shares believe their own situation will get better as say it will get worse.
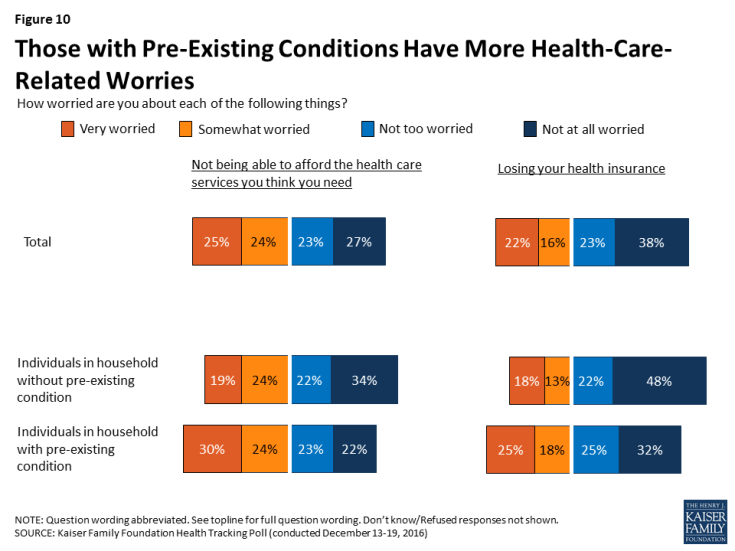
Individuals with a Pre-existing Condition
After being read a definition of “pre-existing condition,” just over half (56 percent) of U.S. adults say that they or someone in their household would be considered to have such a condition. Overall, these individuals are more likely than those without a pre-existing condition to say their access, quality, and cost of health care will get “worse” if the ACA is repealed. However, about one in five of these individuals say their access, quality, and cost of health care will get “better” if the ACA is repealed.
One-third of individuals who have someone in their household with a pre-existing condition say the cost of health care for them and their family will get worse if the ACA is repealed, compared to about one in five of those living in a household without someone with a pre-existing condition. Larger shares of those with a pre-existing condition also say their ability to get and keep health insurance will get worse than those without a pre-existing condition (24 percent vs. 17 percent), and the quality of their own health care will get worse (21 percent vs. 15 percent).
| Table 1: Those with Pre-existing Conditions More Likely to Say Repeal of the ACA Will Make Own Ability to Access Affordable and Quality Health Care Worse | |||
| Percent who say the following will get worse if the 2010 health care law is repealed: | Total | Households with Pre-existing Condition |
Households without Pre-existing Condition |
| The cost of health care for you and your family | 28% | 33% | 22% |
| Your ability to get and keep health insurance | 21 | 24 | 17 |
| The quality of your own health care | 19 | 21 | 15 |
In addition, individuals with a pre-existing condition in their household also report being more worried about health-care related issues than those without a pre-existing condition. Slightly more than half (54 percent) of those with a pre-existing condition say they are either “very worried” or “somewhat worried” about not being able to afford the health care services they need, compared to 43 percent of those without a pre-existing condition. Similarly, 43 percent of those with a pre-existing condition are worried (either “very” or “somewhat”) about losing their health insurance compared to 30 percent of those without a pre-existing condition.
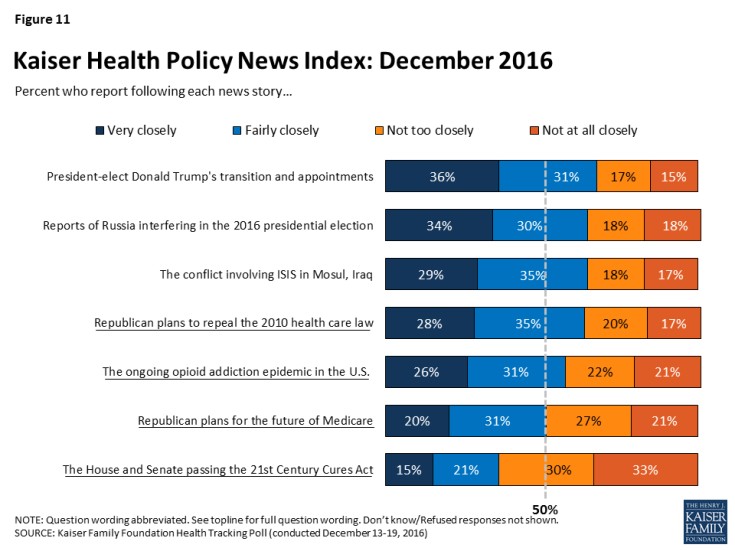
Kaiser Health Policy News Index
The latest Kaiser Health Tracking Poll finds President-elect Donald Trump’s transition and cabinet appointments was the most closely followed news story during the past month with seven in ten (68 percent) Americans closely following news about his transition. Other stories that captured the attention of Americans include the conflict involving ISIS in Mosul, Iraq (64 percent), the CIA’s report of Russia interfering in the 2016 presidential election (64 percent), and the top health policy story this month – Republican plans to repeal the ACA (63 percent). Other health policy stories followed by Americans this month include the ongoing heroin and prescription painkiller addiction epidemic in the U.S. (57 percent), Republican plans for the future of Medicare (51 percent), and the passing of the 21st Century Cures Act (37 percent).